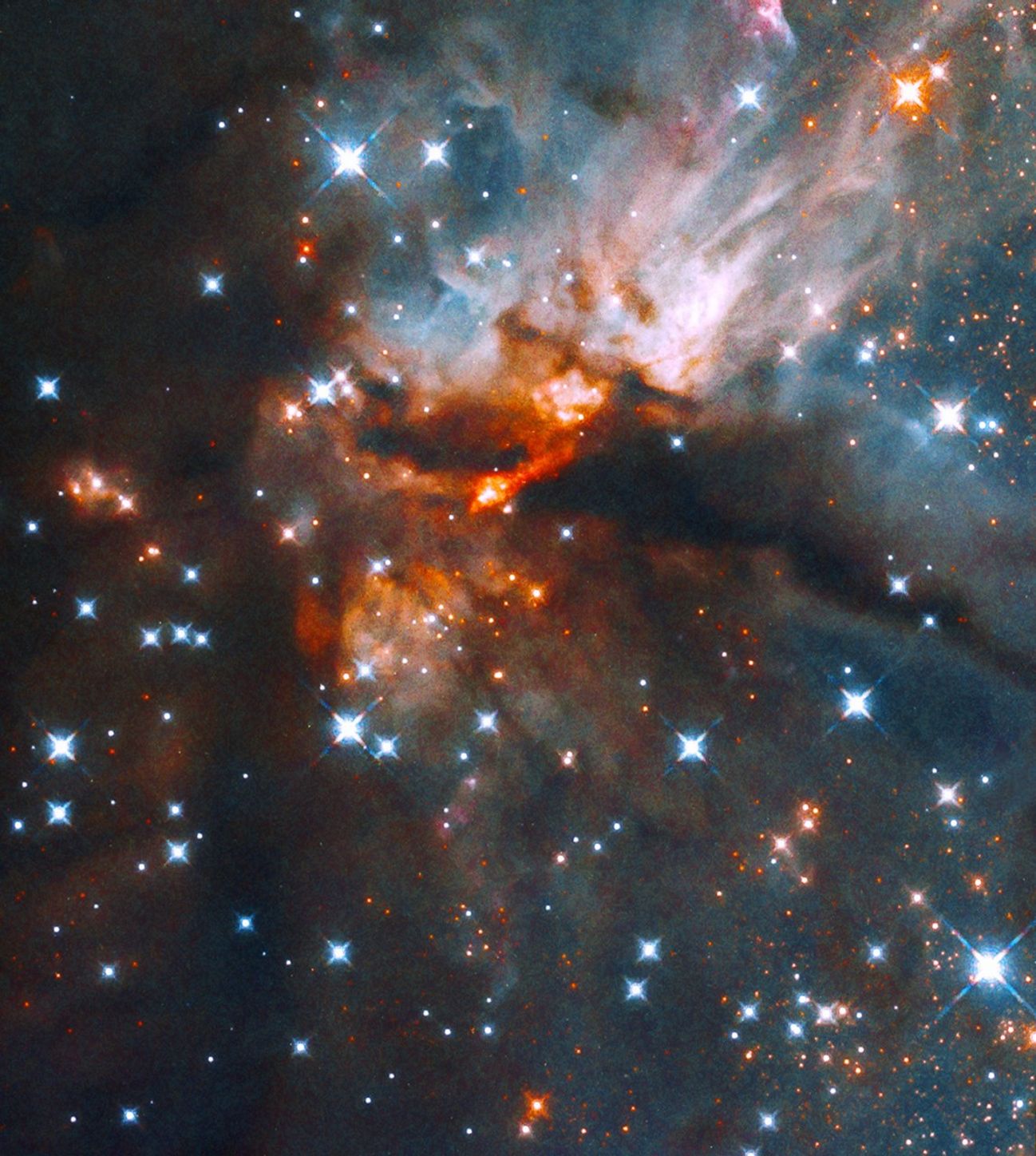
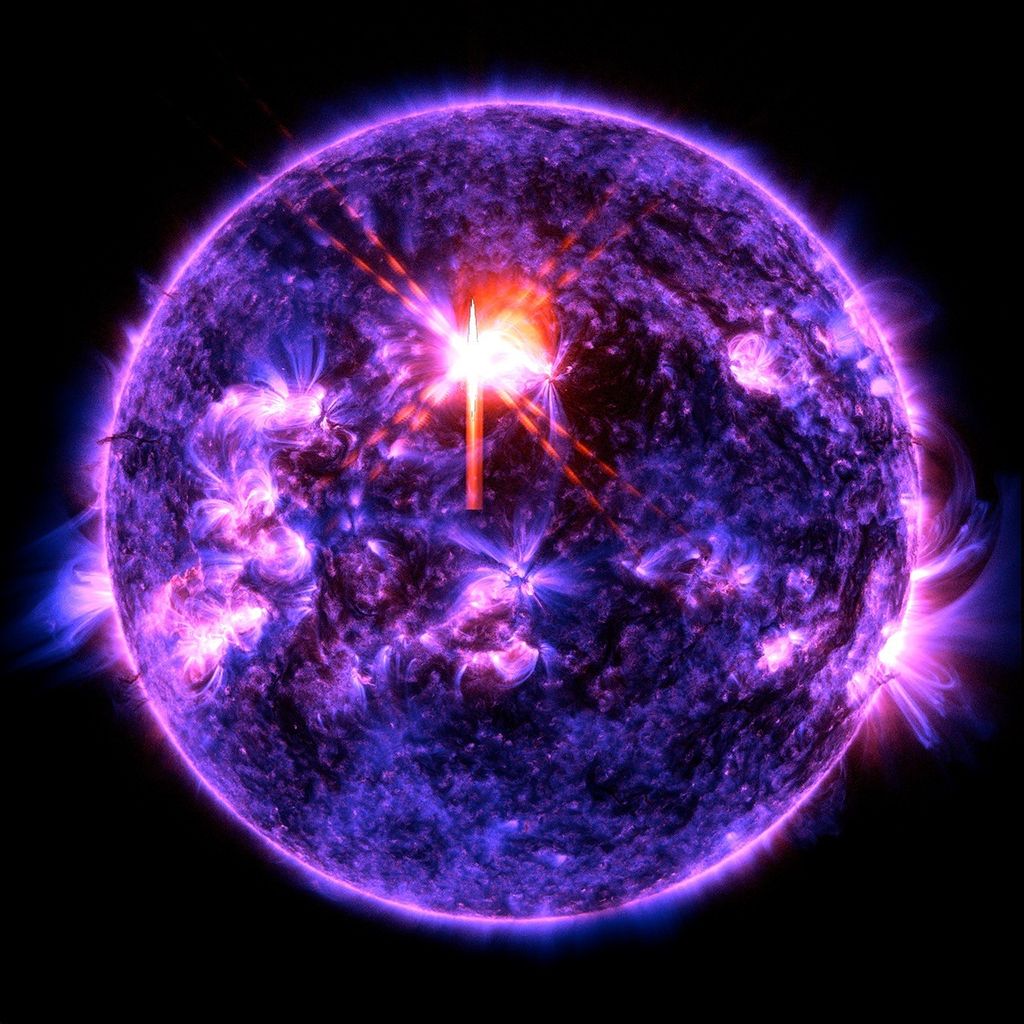
Star-forming Region G035.20-0.74
Stars are born from turbulent clouds of gas and dust that collapse under their own gravitational attraction. As the cloud collapses, a dense, hot core forms and begins gathering dust and gas, creating a protostar. This star-forming nebula in the constellation Aquila, G035.20-0.74, is known for producing a particular kind of massive star known as a B-type star. These stars are hot, young, blue stars up to five times hotter than our Sun. The Hubble Space Telescope observed this region because it is home to a massive protostar, specifically as part of a program examining jets of glowing gas blasted into space by massive protostars. These fast-moving jets, which form as gas collects around newly forming stars and last for only about 100,000 years, are known to play a role in star formation.
- X