SMAP News and Articles
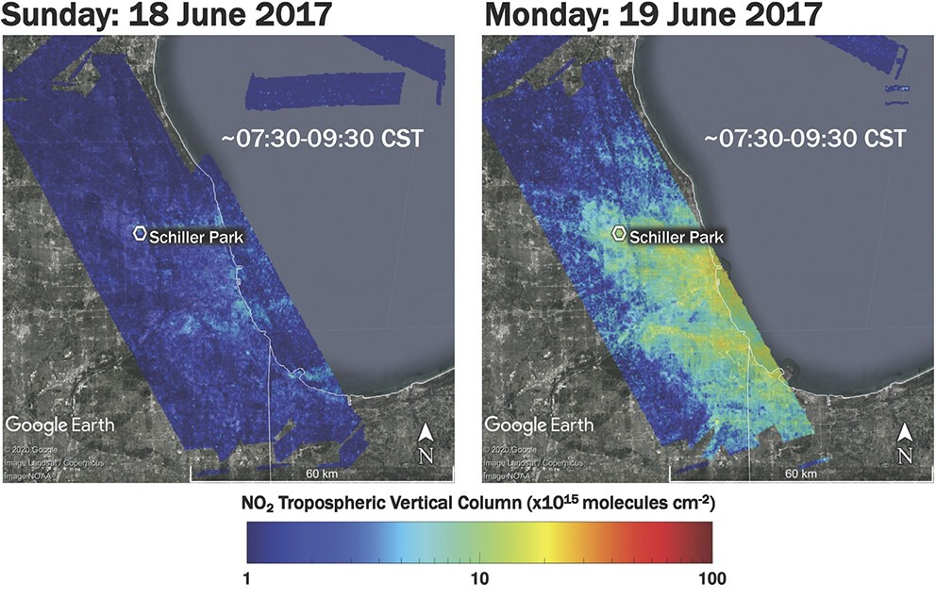
Air quality planning agencies in the U.S. Great Lakes region now include high-resolution NASA satellite data and near real-time Earth observations in their ozone pollution assessments. Creating models that accurately predict the complex lake and land breezes along Lake Michigan’s…
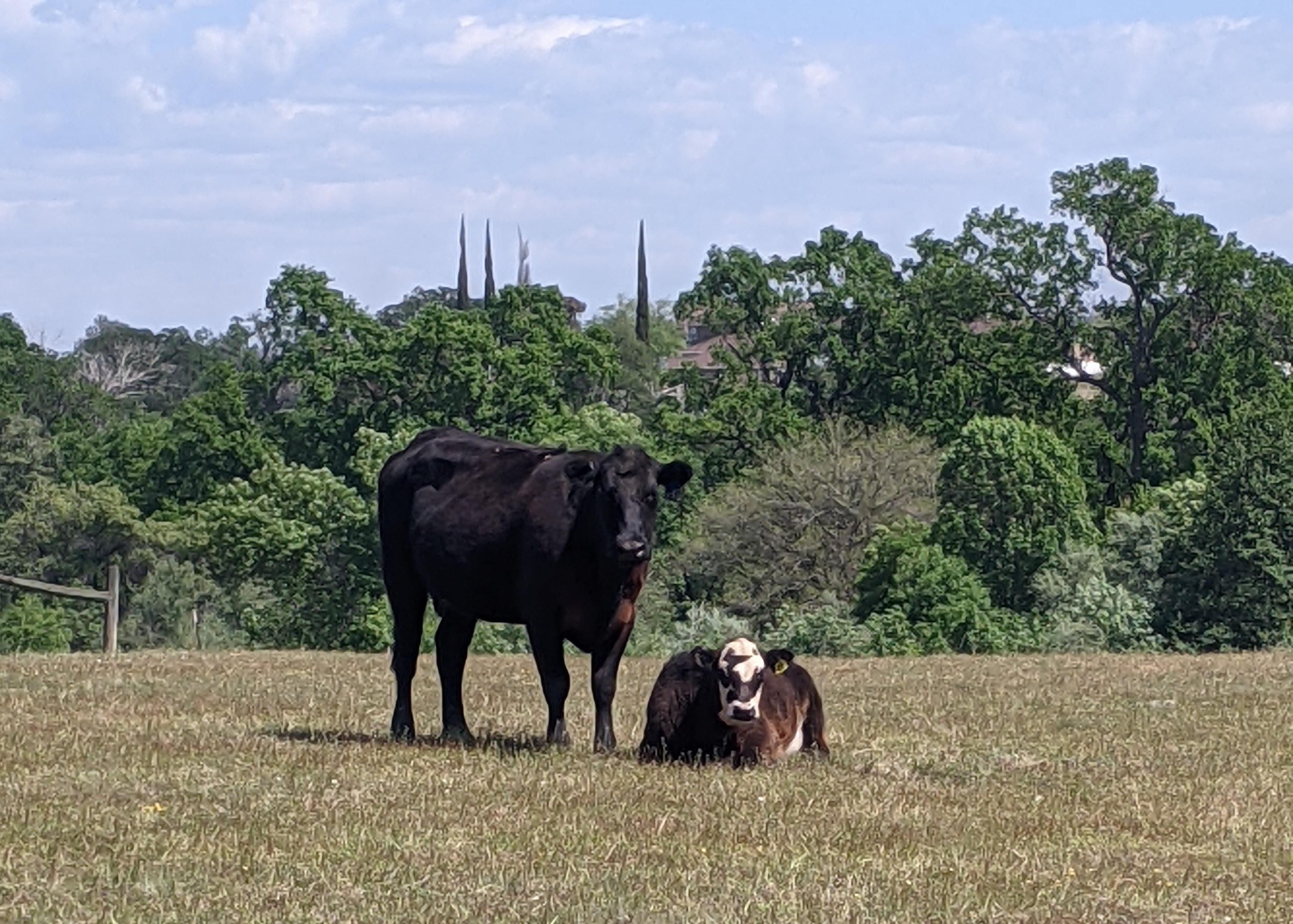

As Tracy Schohr goes about her day, water is always on her mind. She’s thinking of it as she rides an all-terrain vehicle around the pasture, looks up hay prices and weather forecasts, and collects data on grazing and invasive…
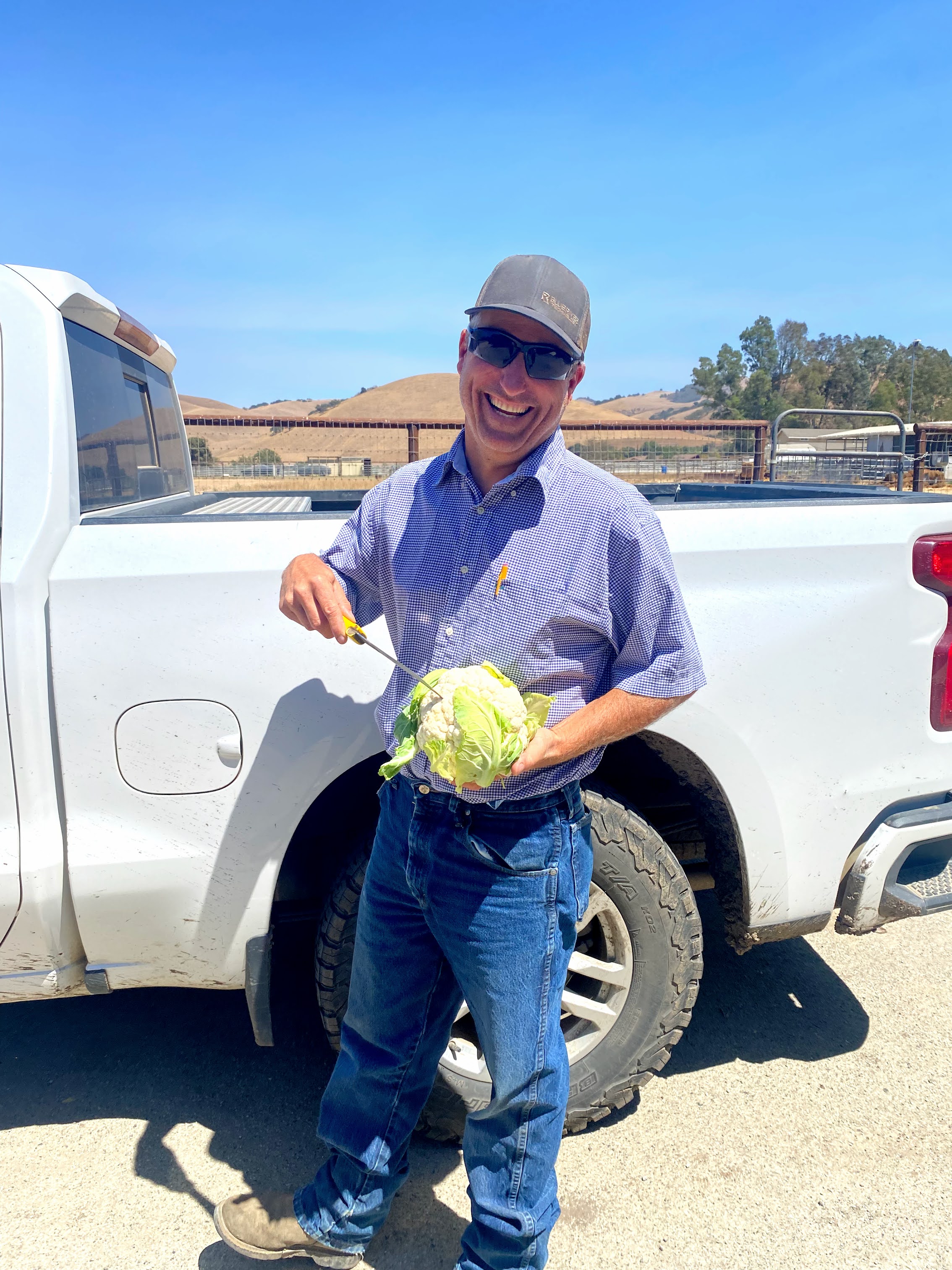

Every day – up to thirty times a day, in fact – one of Mark Mason’s employees at Nature’s Reward Farms in Monterey County, California brings him the results of a soil test for discussion. Mason supervises fertilizer and irrigation…
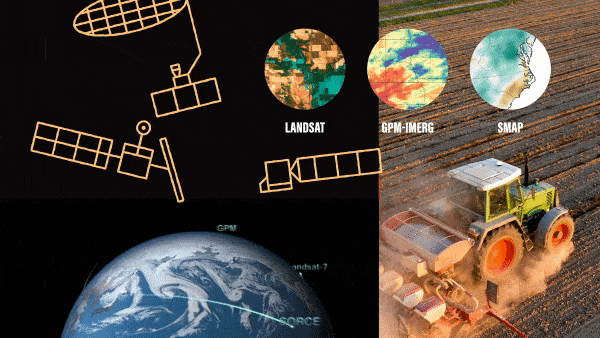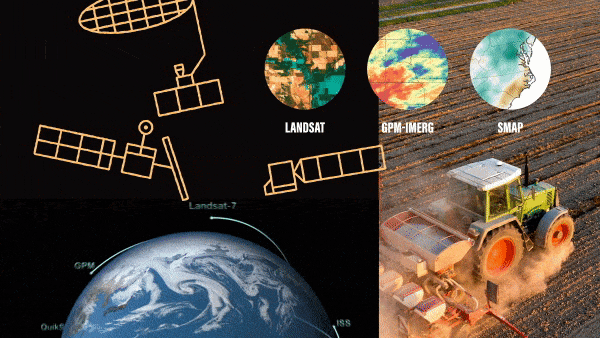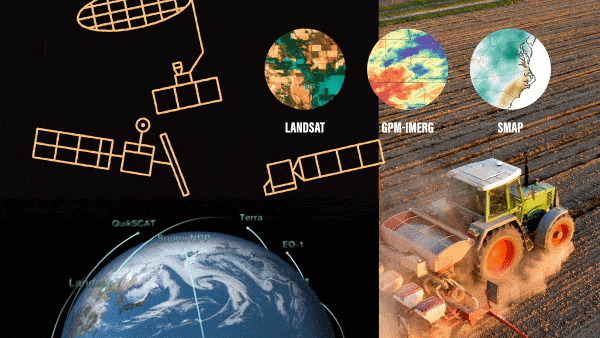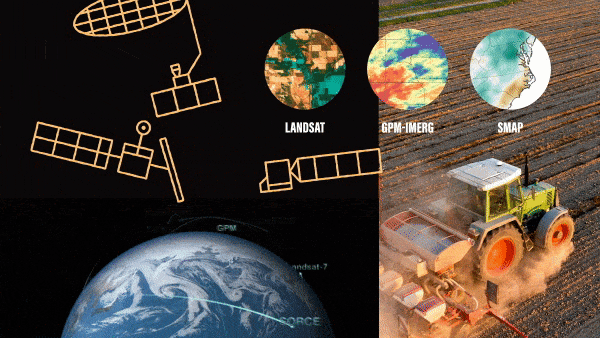
As the seasons turn from spring, to summer, to fall – farmers plant crops, monitor their growth and harvest them. And now increasingly they are using NASA Earth science data to help make their decisions. While NASA satellites primarily support…
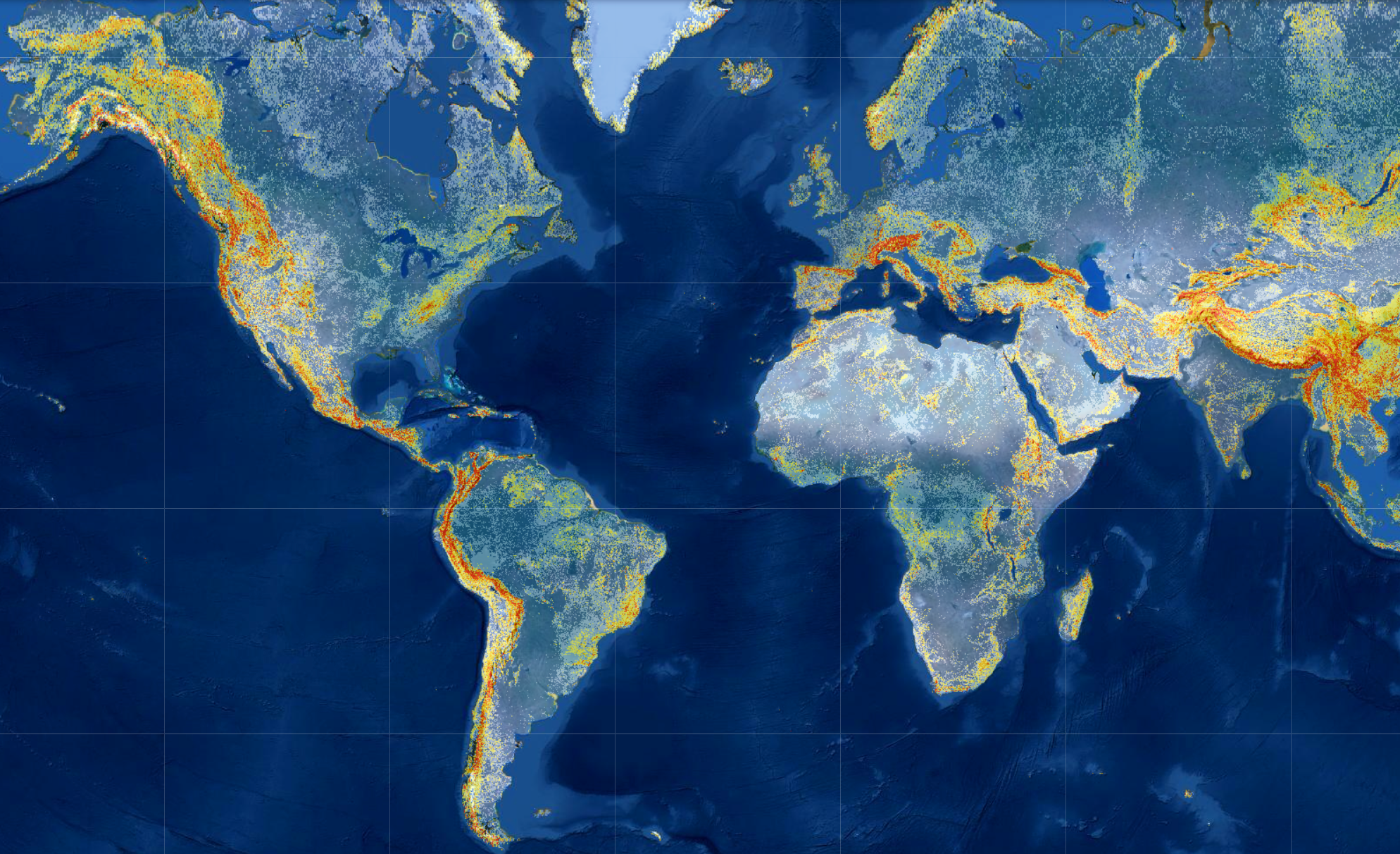
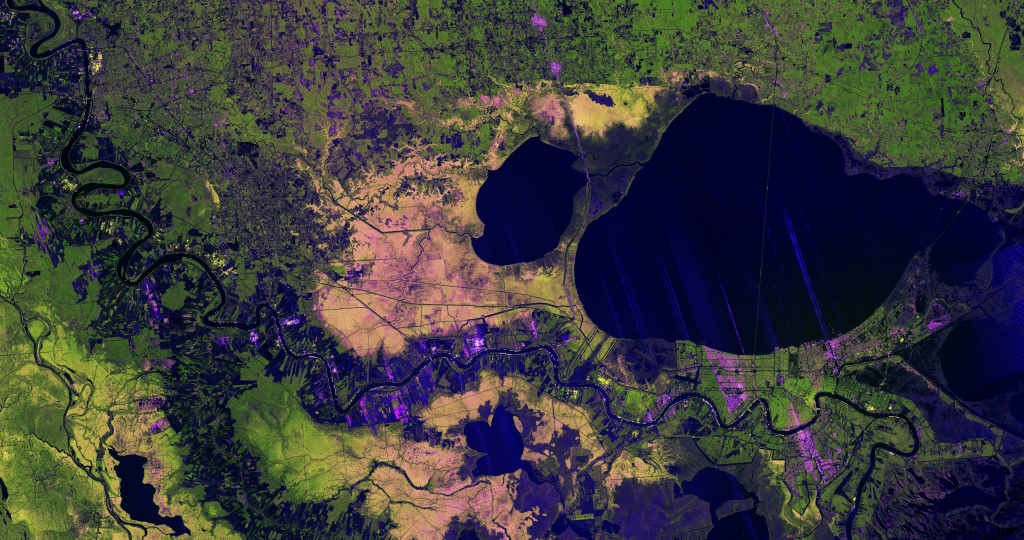
Every year, landslides – the movement of rock, soil, and debris down a slope – cause thousands of deaths, billions of dollars in damages, and disruptions to roads and power lines. Because terrain, characteristics of the rocks and soil, weather,…
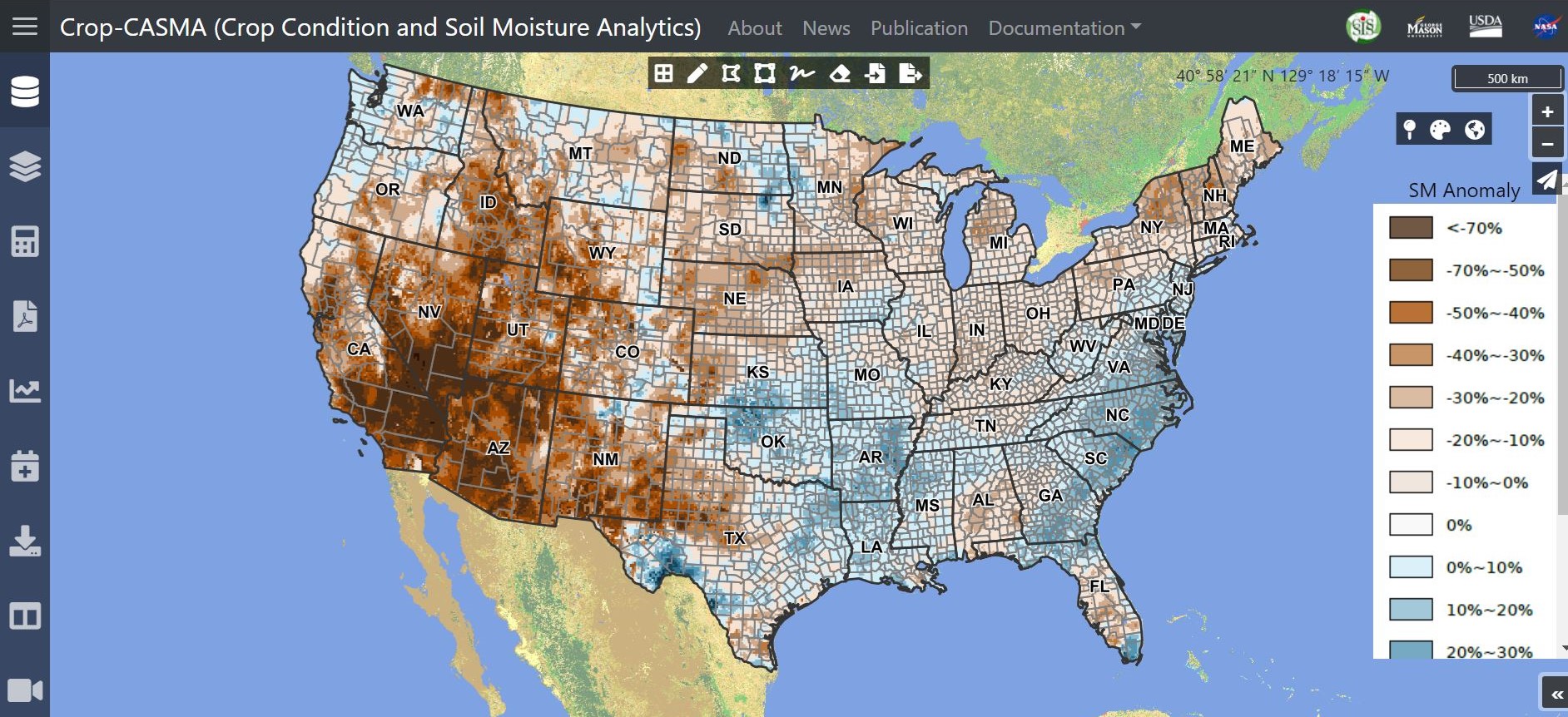
Farmers, researchers, meteorologists and others now have access to high-resolution NASA data on soil moisture, thanks to a new tool developed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)’s National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) in collaboration with NASA and George Mason…
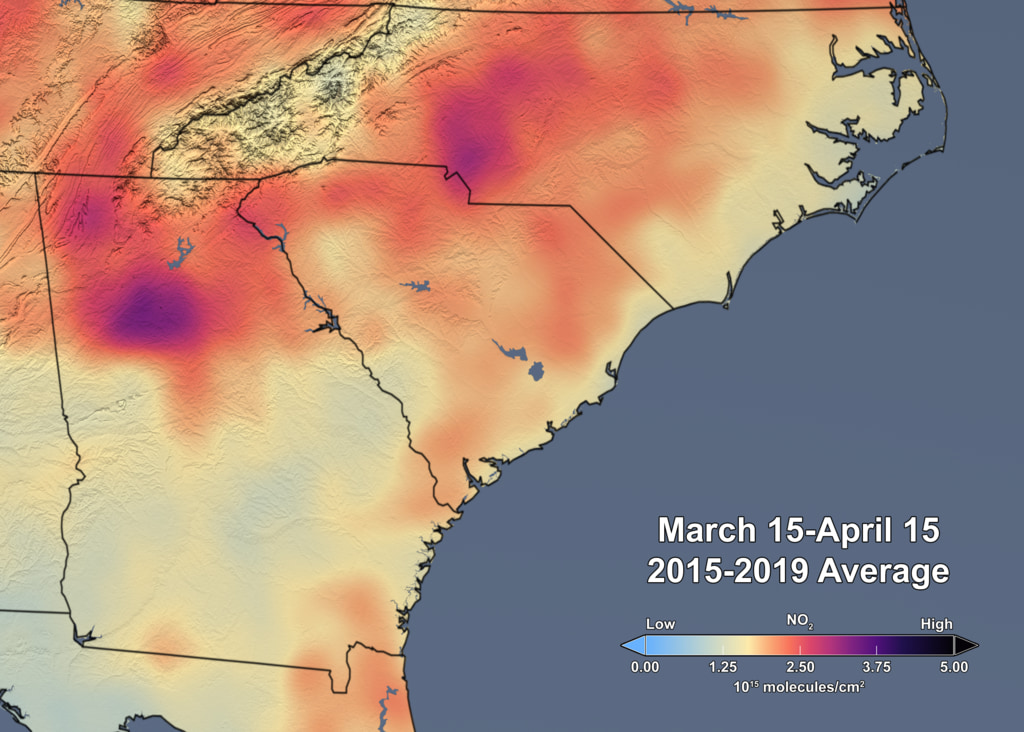
Scientists are using information from NASA’s Earth-observing satellites, on-the-ground sensors and computer-based datasets to study the environmental, economic and societal impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, the agency’s Earth Science Division recently sponsored new projects to examine how the…
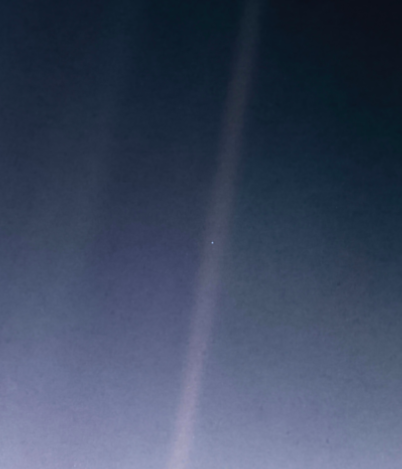

Earth is a pale, blue dot when seen from space. Its blue color is due to our home planet being 71% covered in water. NASA monitors Earth’s water from space, the skies, ground stations on land, ships sailing the seas…
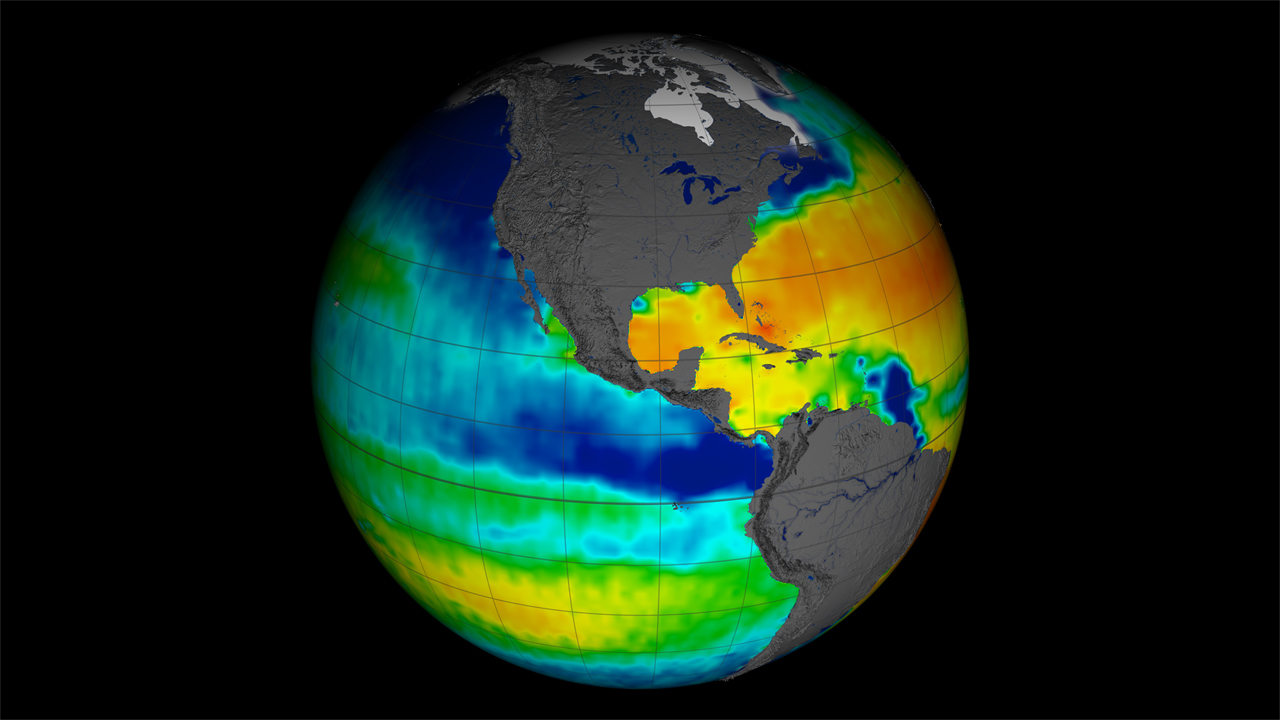
When modeling the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) ocean-climate cycle, adding satellite sea surface salinity — or saltiness — data significantly improves model accuracy, according to a new NASA study. ENSO is an irregular cycle of warm and cold climate events…

SMAP satellite soil moisture measurements now increase the accuracy of Army and Air Force weather forecasts and advisories.