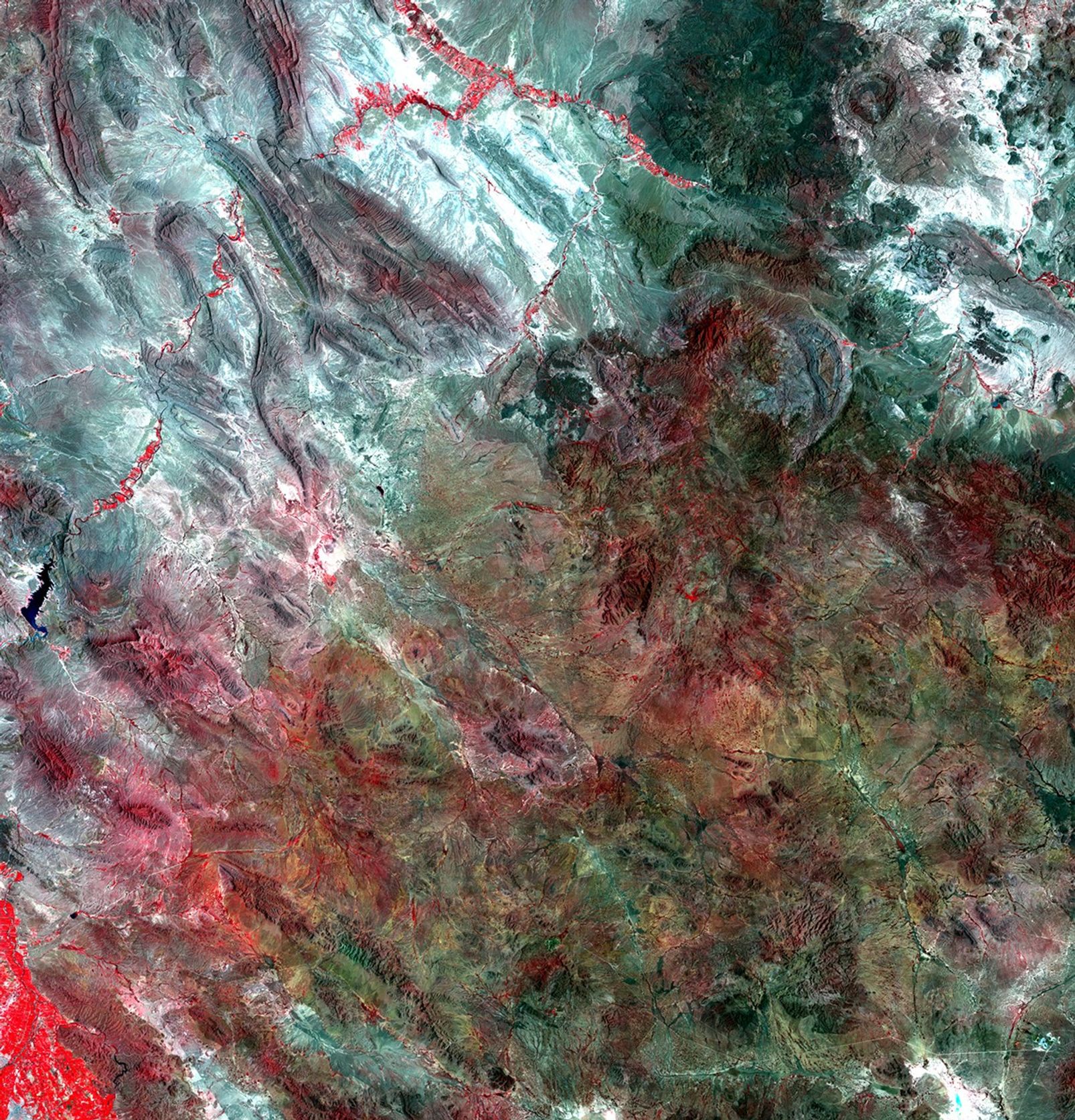
These images illustrate major changes in agricultural practices in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. Increased diversion of water from the Luis L. Leon Reservoir for agricultural irrigation has affected vegetation patterns in the northeastern part of Chihuahua and significantly reduced the amount of water reaching the Rio Grande River. Farmers use center pivot irrigation systems (marked by red circles) to grow alfalfa and sorghum for dairy farms and cattle feedlots. The drop in water supplying the Rio Grande seriously threatens wildlife habitat and natural vegetation. Images taken by the Thematic Mapper sensor onboard Landsat 5. Source: USGS Landsat Missions Gallery, "Irrigation Expansion in Mexico," U.S. Department of the Interior / U.S. Geological Survey.
NASA/USGS
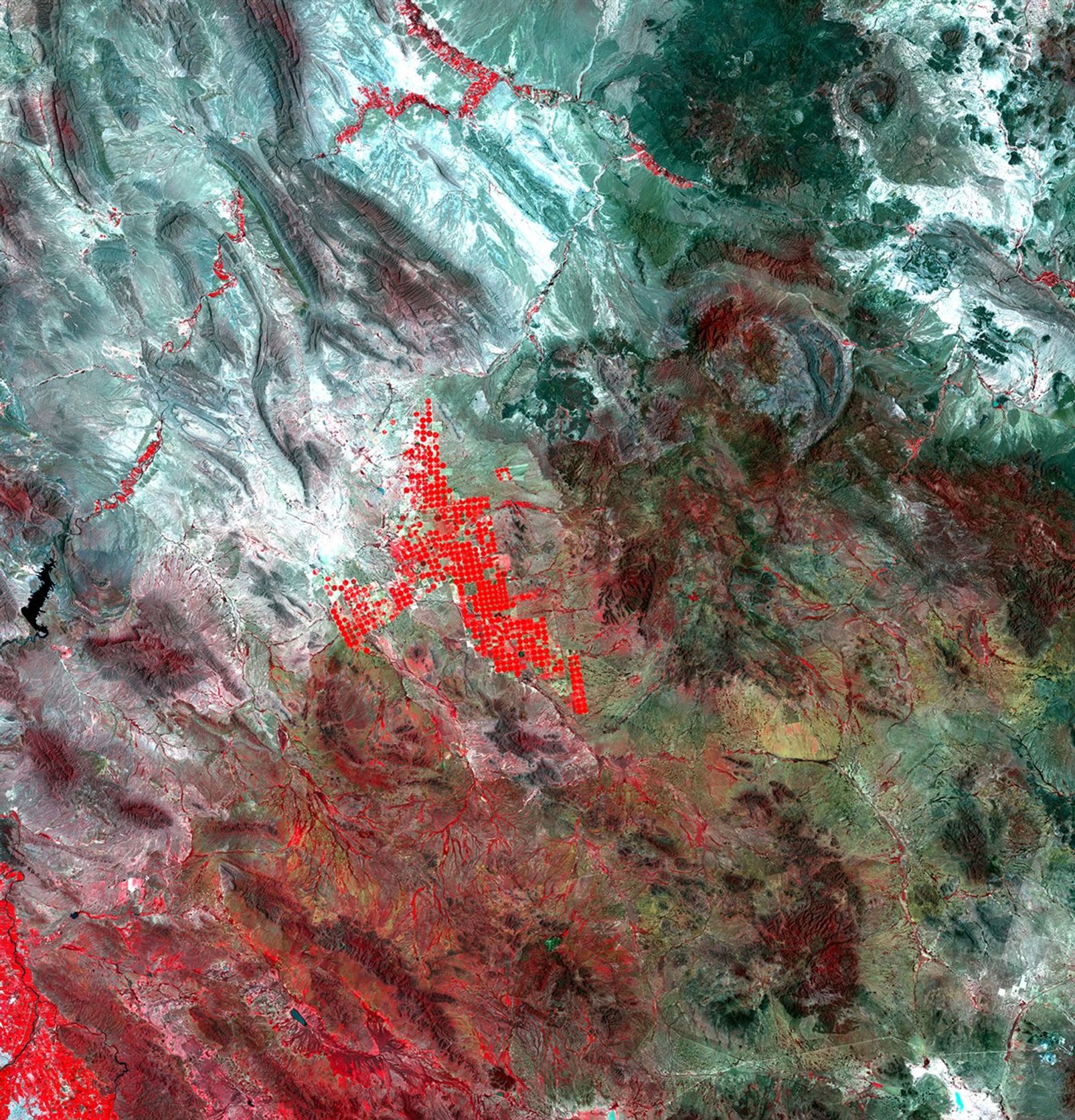
These images illustrate major changes in agricultural practices in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. Increased diversion of water from the Luis L. Leon Reservoir for agricultural irrigation has affected vegetation patterns in the northeastern part of Chihuahua and significantly reduced the amount of water reaching the Rio Grande River. Farmers use center pivot irrigation systems (marked by red circles) to grow alfalfa and sorghum for dairy farms and cattle feedlots. The drop in water supplying the Rio Grande seriously threatens wildlife habitat and natural vegetation. Images taken by the Thematic Mapper sensor onboard Landsat 5. Source: USGS Landsat Missions Gallery, "Irrigation Expansion in Mexico," U.S. Department of the Interior / U.S. Geological Survey.
NASA/USGS
Before and After
Irrigation impact in Chihuahua, Mexico
August 17, 1992 - August 3, 2010
These images illustrate major changes in agricultural practices in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. Increased diversion of water from the Luis L. Leon Reservoir for agricultural irrigation has affected vegetation patterns in the northeastern part of Chihuahua and significantly reduced the amount of water reaching the Rio Grande River. Farmers use center pivot irrigation systems (marked by red circles) to grow alfalfa and sorghum for dairy farms and cattle feedlots. The drop in water supplying the Rio Grande seriously threatens wildlife habitat and natural vegetation. Images taken by the Thematic Mapper sensor onboard Landsat 5. Source: USGS Landsat Missions Gallery, "Irrigation Expansion in Mexico," U.S. Department of the Interior / U.S. Geological Survey.