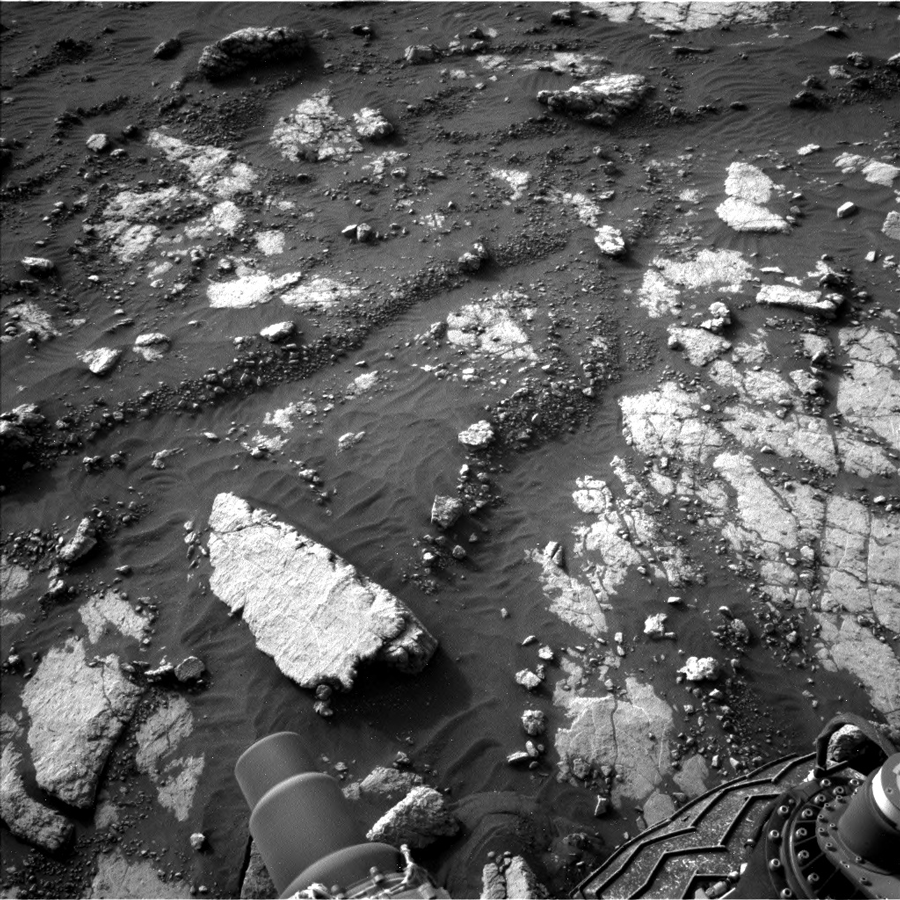
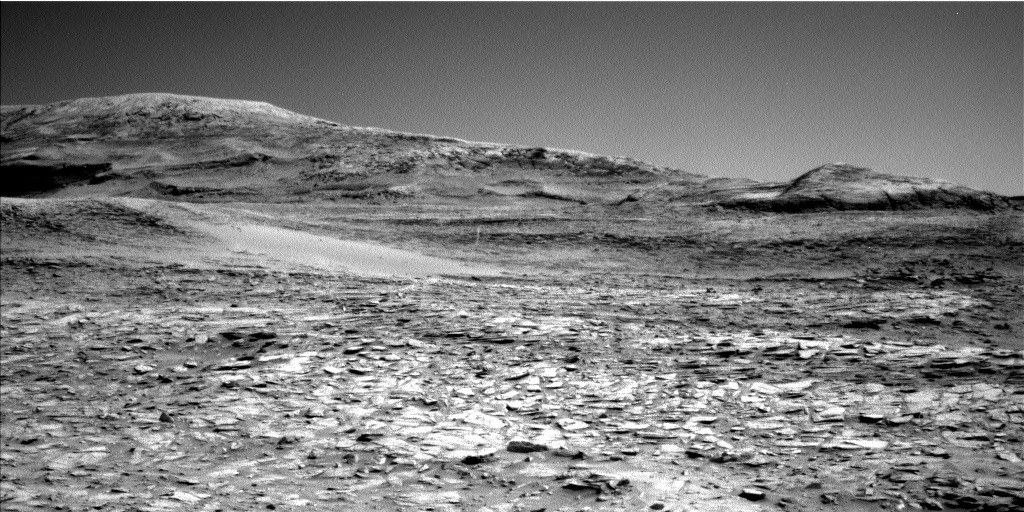
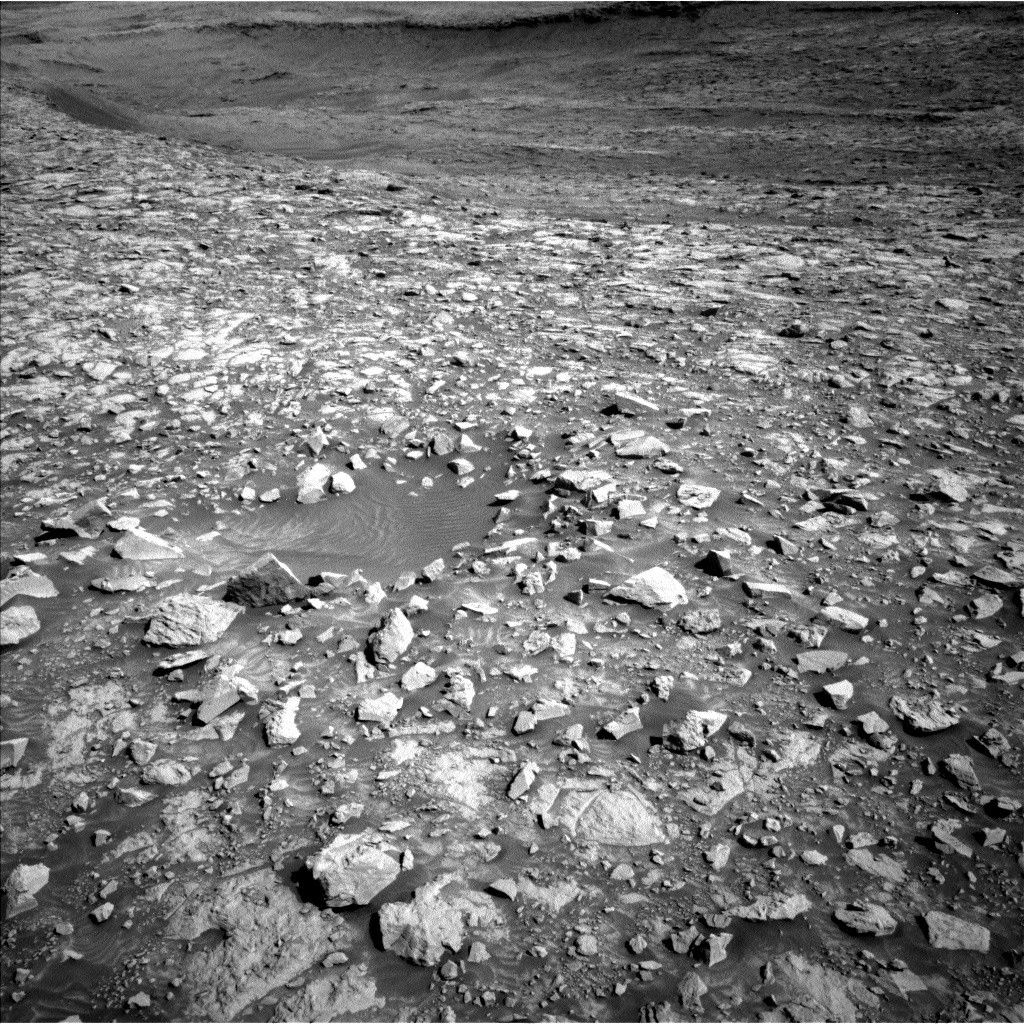
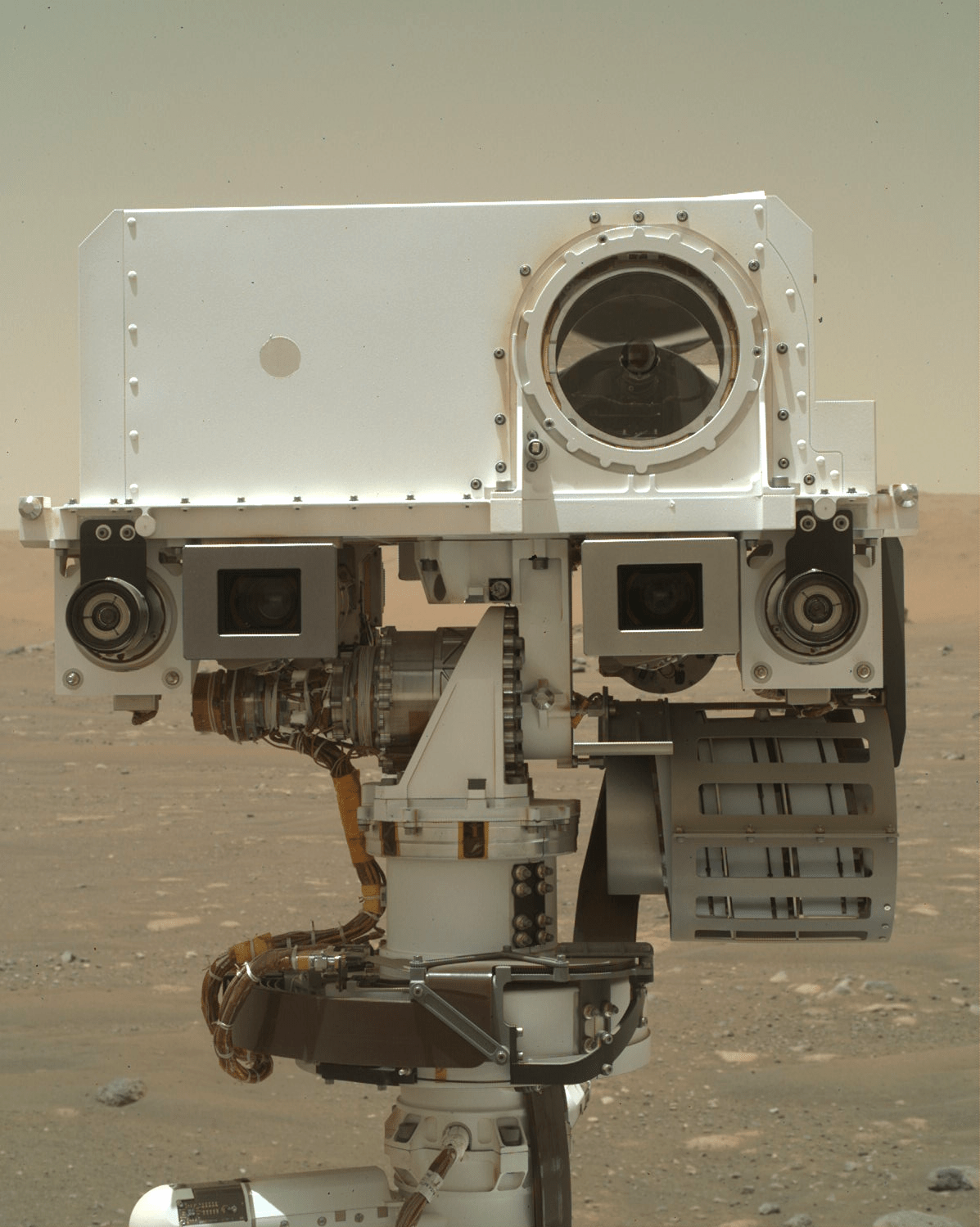
Curiosity is continuing her trek towards the sulfate-bearing unit while studying the local bedrock and environment along the way. The previous drive placed Curiosity in front of several bedrock exposures (see above image), which will be analyzed extensively before the rover continues driving in this weekend’s three-sol plan.
The star of the plan is the “Heather Island” target (the slab at the very left of the above image), which will be studied by four(!) of the rover’s instruments. First, ChemCam will take an extended 20-point raster observation across Heather Island. Having more ChemCam data points on this target will enable better comparison with the high-resolution MAHLI imaging that comes next, and will help us better understand small-scale chemical variations in the bedrock. The rover will then use the Dust Removal Tool (DRT) to clear dust from Heather Island’s surface so that APXS can better measure the composition of the underlying bedrock. Finally, Mastcam will take a multispectral observation over the same spot. This is really a great opportunity to leverage the unique capabilities of multiple instruments to characterize different aspects of the same target.
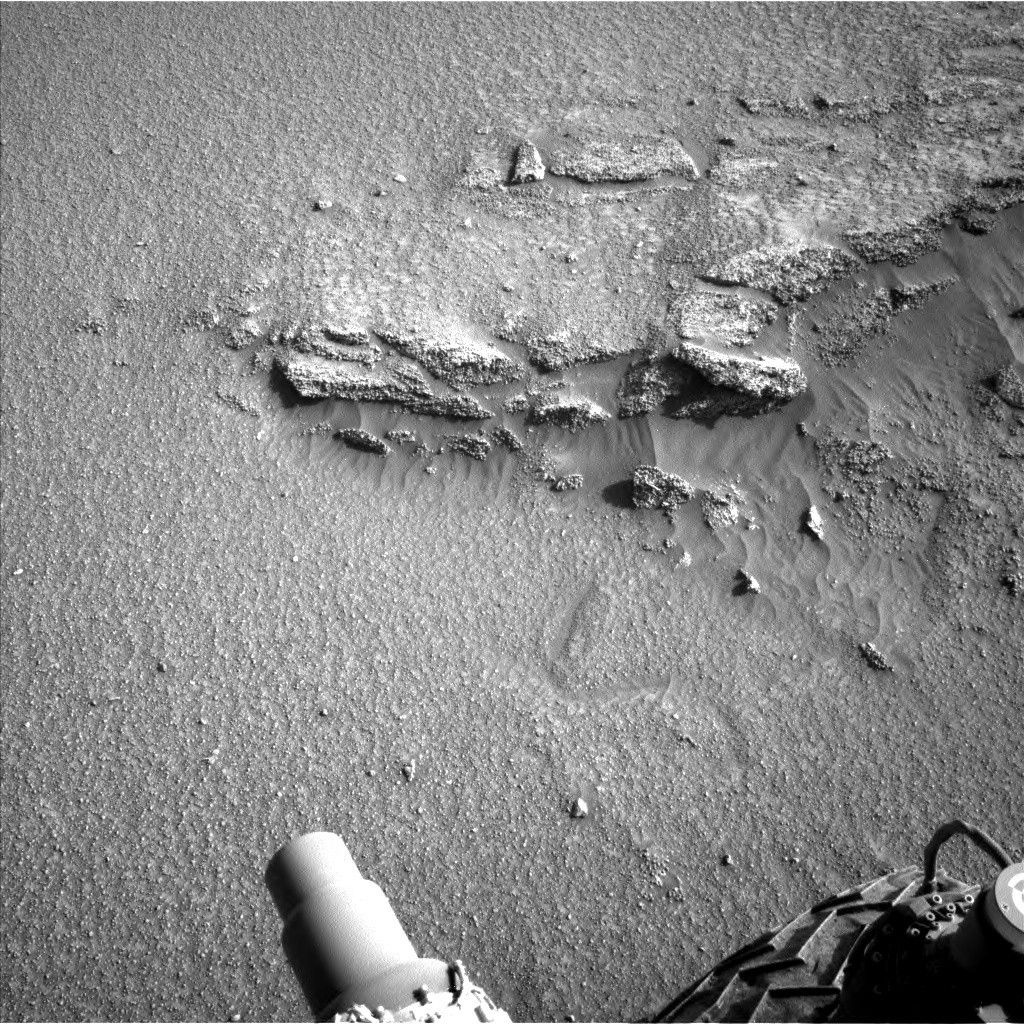
The rest of the plan is also packed with other observations. ChemCam will observe “Glame,” a nodular target that will add to our characterization of nodular features in this region. Mastcam will also keep busy with four mosaics focused on the pediment and local landscape, and a suite of atmospheric monitoring activities and dust devil observations are also included throughout the plan. Curiosity will then drive and take two post-drive ChemCam observations using the AEGIS mode, which will autonomously select bedrock targets at our next stop so that we can get a head start on characterizing the next location.
Written by Vivian Sun, Planetary Geologist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory