NASA pushes the frontiers of engineering, taking smart risks and pursuing innovative ways to explore our planet and the solar system. As an innovation hub for Earth science, we develop new technologies to observe the unseen and answer critical questions about our planet.
Together with industry partners, we conceive and build the next generation of remote sensing tools, enabling NASA missions and charting a path for operational agencies and businesses. By testing and proving cutting-edge technologies — from advanced sensors to predictive models — NASA Earth Science creates jobs, drives innovation, and sustains U.S. leadership in the exploration of Earth and other planets.
Why it matters
By investing in Earth observation technology, we're strengthening America's industrial base and creating new opportunities in the rapidly growing commercial space sector. These innovations protect American lives and property while maintaining our nation's technological edge over global competitors.
These investments also advance America's space exploration goals. The same satellite technologies that track Earth's weather and surface features today are proving grounds for systems we’ll need for sustainable presence on Mars.
From Orbit to A.I. - Harnessing Machine Learning with Landsat Data
Over the last few years, machine learning techniques have been increasingly used to analyze the vast amount of data collected by the Landsat mission, which has been circling the globe for over 50 years.
Learn MoreHow NASA Earth Science Technology Helps
- We accelerate innovation by partnering with American companies and universities to develop next-generation Earth observation capabilities.
- We ensure U.S. technological leadership by pioneering advanced solutions that combine satellite engineering, data processing, and artificial intelligence.
- We create opportunities for American businesses that transition NASA innovations into commercial products, fueling growth in the space sector and other private sectors.
NASA proves out the technology and the instrument.... That is a huge enabler for companies like ours because we can adopt it knowing that much of the physics risk has been retired.
Jonathan Dyer
CEO of Muon Space
What We Do
-
Develop Next-Generation Earth Observation Capabilities
Working with technologists and engineers at companies, universities, and federal labs nationwide, we’re creating next-generation satellites and sensors that deliver precise data about our nation's resources, from freshwater supplies to rare Earth minerals critical for domestic technology manufacturing.
For example, the American weather company Tomorrow.io is leveraging breakthrough miniaturized radar technology first proven by NASA’s RainCube — a shoebox-sized satellite that successfully observed major storms using radar 100 times smaller than traditional systems.
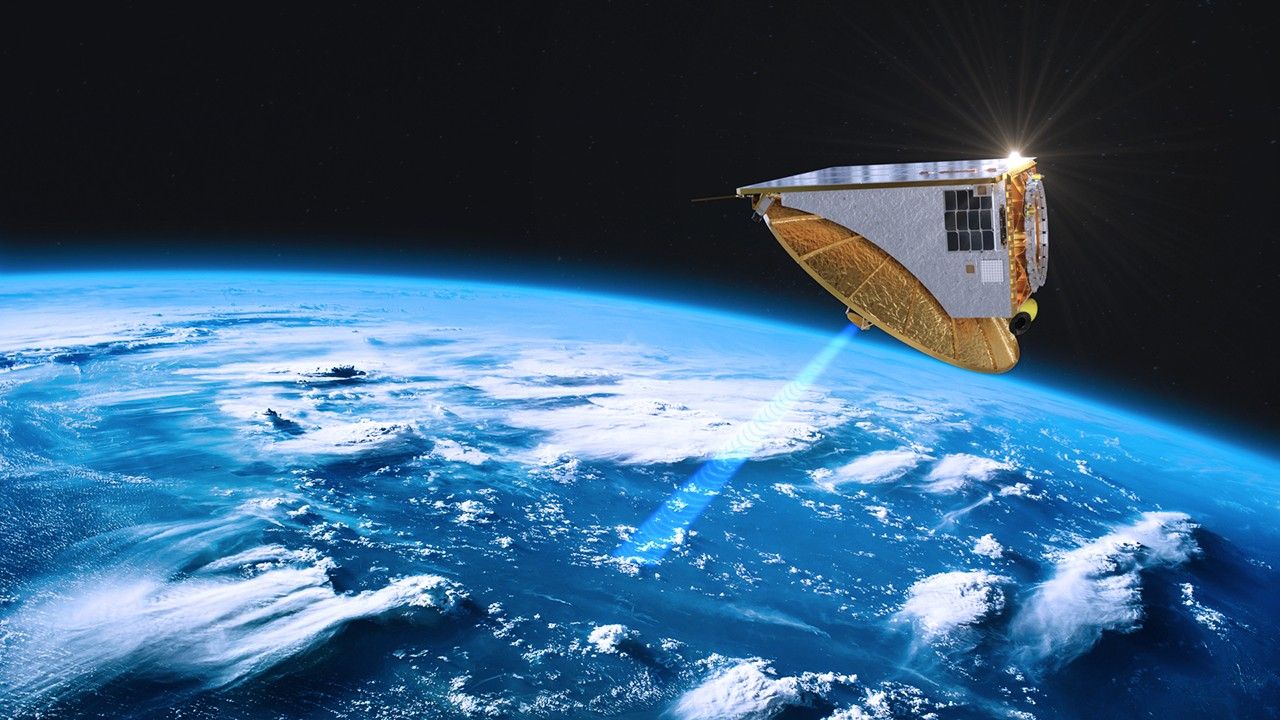 Tomorrow.io is building a constellation of small satellites equipped with proprietary radar technology that leans on previous NASA development such as RainCube.Tomorrow.io
Tomorrow.io is building a constellation of small satellites equipped with proprietary radar technology that leans on previous NASA development such as RainCube.Tomorrow.io -
Maintain American Leadership in Space Technology
Our Earth Science Technology Office (ESTO) provides funding opportunities and technical management to develop and demonstrate the advanced Earth observation capabilities that maintain U.S. leadership in space.
For example, NASA Earth Science's investment in quantum technology aims to position the nation at the forefront of this revolutionary field. Advances in sensors such as the Quantum Gravity Gradiometer will help America better track crucial resources like underground water supplies and changing sea levels, while ensuring the U.S. stays ahead of global competitors in this cutting-edge technology.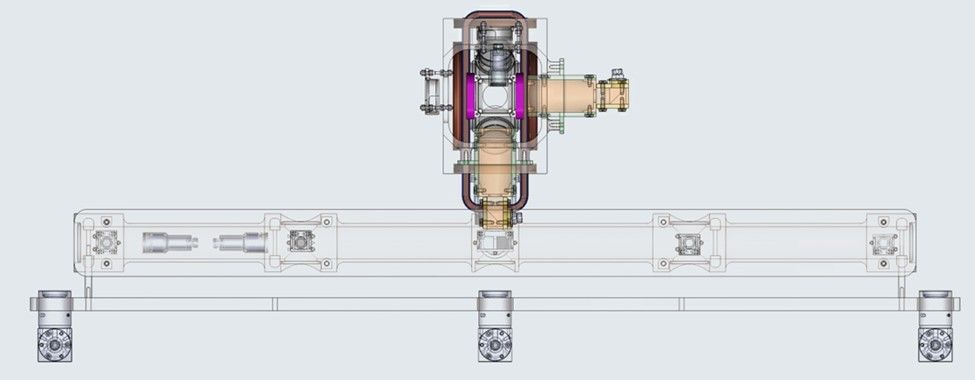 NASA is developing a Quantum Gravity Gradiometer to enhance Earth's gravity measurements, improving water monitoring.NASA/JPL
NASA is developing a Quantum Gravity Gradiometer to enhance Earth's gravity measurements, improving water monitoring.NASA/JPL
-
Create Opportunities for Businesses
NASA’s investment in technology fuels innovation and creates new opportunities for U.S. industry.
For instance, the American space company Muon Space is using NASA-developed radar technology to turn GPS signals into powerful tools for tracking storms and floods. With a system that uses existing GPS satellites to do half the work, these American-designed receivers are compact and affordable enough to launch on small satellites.
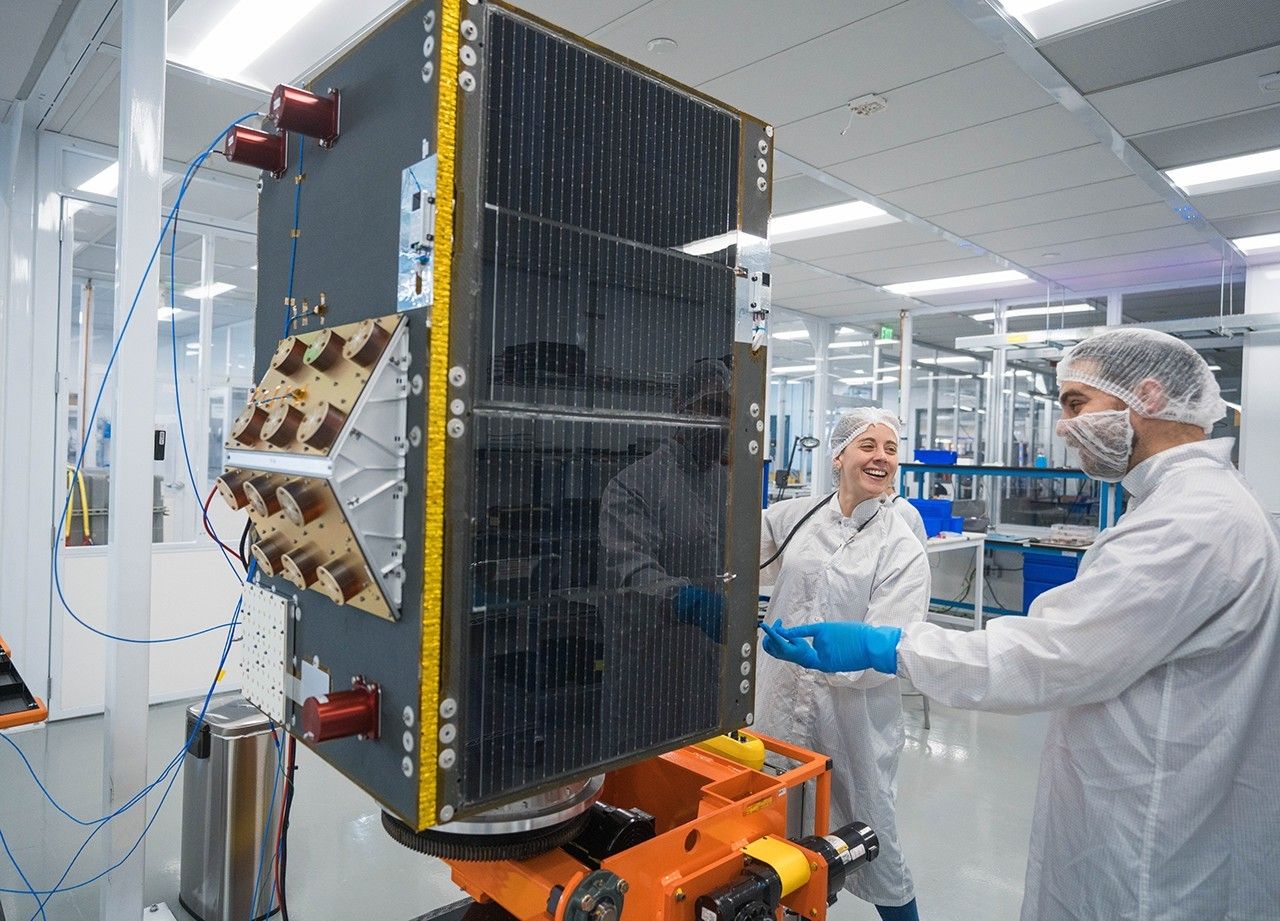 Muon Space's MuSat2 satellite launched in March 2024 that includes a NASA-developed radar technology, shown at the Muon Space headquarters in Mountain View, CaliforniaMuon Space
Muon Space's MuSat2 satellite launched in March 2024 that includes a NASA-developed radar technology, shown at the Muon Space headquarters in Mountain View, CaliforniaMuon Space -
Protect Lives, Property, and the Economy
NASA’s technological innovations enable monitoring of hazards, such as wildfires, providing crucial data to help emergency responders and government officials safeguard lives and property and efficiently allocate resources during crises.
Through its innovative FireSense program, NASA is testing new ways to track and assess wildfires using specialized aircraft and with advanced sensors. These tools can help firefighters and emergency managers better understand and respond to fire threats.
Beyond fire monitoring, NASA-funded technology has also led to unexpected benefits, such as adapting space-based laser technology into a precise medical tool for removing kidney stones.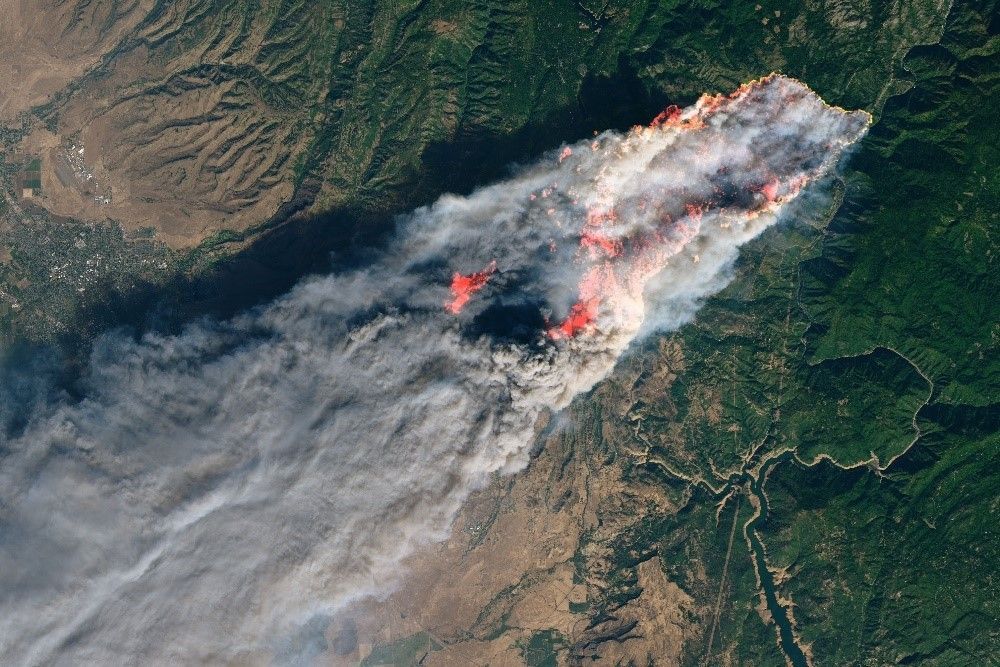 Multiple fast-moving fires are producing huge plumes of smoke and threatening several communities.NASA Earth Observatory
Multiple fast-moving fires are producing huge plumes of smoke and threatening several communities.NASA Earth Observatory
NASA Tech and Innovation in Action
‘Current’ Events: NASA and USGS Find a New Way to Measure River Flows

NASA Laser Reflecting Instruments to Help Pinpoint Earth Measurements
NASA and Forest Service Use Balloon to Help Firefighters Communicate

NASA JPL Developing Underwater Robots to Venture Deep Below Polar Ice

NASA-developed Technology Supports Ocean Wind Speed Measurements from Commercial Satellite

New NASA Instrument for Studying Snowpack Completes Airborne Testing

How New NASA, India Earth Satellite NISAR Will See Earth

NASA Flight Tests Wildland Fire Tech Ahead of Demo

PACE's Instruments Reveal a New Dimension of Atmospheric Info
Two instruments on NASA’s PACE satellite mission will look at aerosols and clouds – the A and C in the mission’s name, Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem – to help scientists learn more about their characteristics and interactions in Earth’s systems.
Learn More































