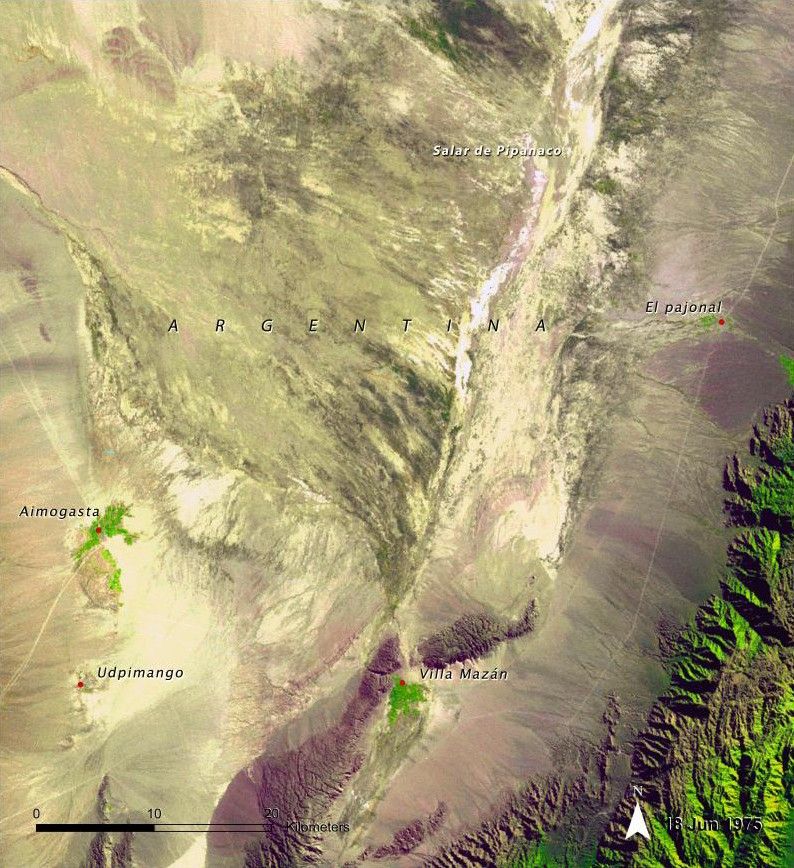
Aimogasta is a regional center of olive production, trade and tourism. Expansion of the agricultural frontier in this region has led to increased wind and water erosion, salinization, and loss of biodiversity. In the 2008 image, cultivated fields that did not exist in 1975 are visible around Aimogasta, Villa Mazán and El Pajonal (seen as green areas with regular geometric patterns). Source: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). From Latin America and the Caribbean Atlas of our Changing Environment (2010).
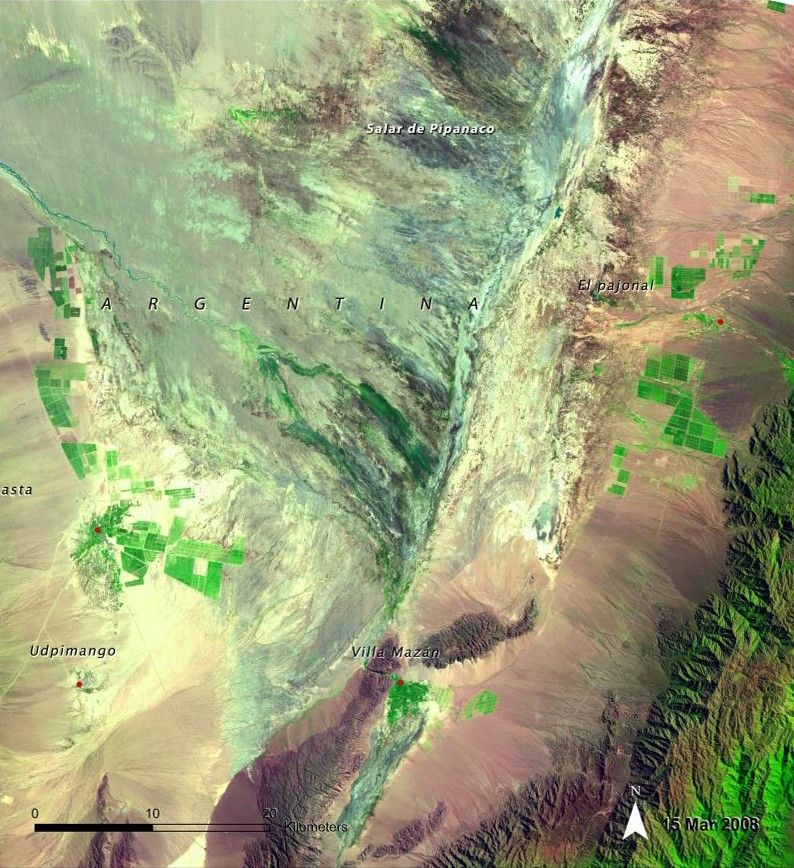
Aimogasta is a regional center of olive production, trade and tourism. Expansion of the agricultural frontier in this region has led to increased wind and water erosion, salinization, and loss of biodiversity. In the 2008 image, cultivated fields that did not exist in 1975 are visible around Aimogasta, Villa Mazán and El Pajonal (seen as green areas with regular geometric patterns). Source: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). From Latin America and the Caribbean Atlas of our Changing Environment (2010).

Aimogasta is a regional center of olive production, trade and tourism. Expansion of the agricultural frontier in this region has led to increased wind and water erosion, salinization, and loss of biodiversity. In the 2008 image, cultivated fields that did not exist in 1975 are visible around Aimogasta, Villa Mazán and El Pajonal (seen as green areas with regular geometric patterns). Source: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). From Latin America and the Caribbean Atlas of our Changing Environment (2010).

Aimogasta is a regional center of olive production, trade and tourism. Expansion of the agricultural frontier in this region has led to increased wind and water erosion, salinization, and loss of biodiversity. In the 2008 image, cultivated fields that did not exist in 1975 are visible around Aimogasta, Villa Mazán and El Pajonal (seen as green areas with regular geometric patterns). Source: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). From Latin America and the Caribbean Atlas of our Changing Environment (2010).
before
after
Before and After
Agricultural impact in Aimogasta, Argentina
June 18, 1975 - March 15, 2008
Aimogasta is a regional center of olive production, trade and tourism. Expansion of the agricultural frontier in this region has led to increased wind and water erosion, salinization, and loss of biodiversity. In the 2008 image, cultivated fields that did not exist in 1975 are visible around Aimogasta, Villa Mazán and El Pajonal (seen as green areas with regular geometric patterns). Source: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). From Latin America and the Caribbean Atlas of our Changing Environment (2010).


























