The Ocean and Climate Change
Our ocean is changing. With 70 percent of the planet covered in water, the seas are important drivers of the global climate. Yet increasing greenhouse gases from human activities are altering the ocean before our eyes. NASA and its partners are on a mission to find out more.
-
The ocean is warming
Rising greenhouse gas concentrations not only warm the air, but the ocean, too. Research shows that around 90 percent of the excess heat from global warming is being absorbed by the ocean. Ocean heat has steadily risen since measurements began in 1955, breaking records in 2023. All this added heat has led to more frequent and intense marine heat waves.
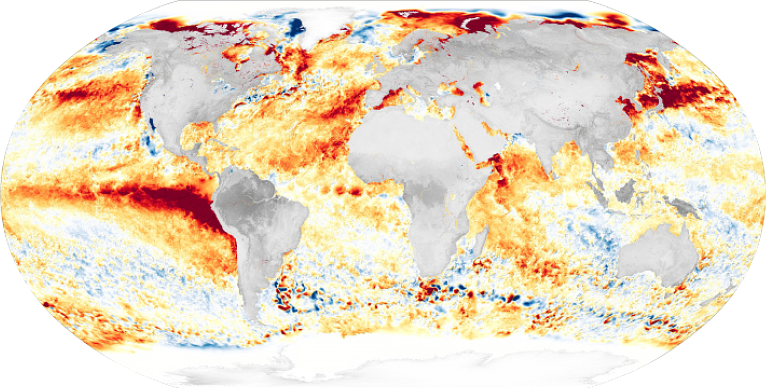 The image visualizes sea surface temperature anomalies in August 2023. Warm colors (red, orange) show where the ocean was warmer than normal. Cool colors (blues) show where temperatures were cooler. The red swath in the Eastern Pacific was due to an El Niño event. El Niño is a climate phenomenon in the tropical Pacific that results in warmer than normal sea surface temperatures leading to weather impacts across the planet.Credit: NASA
The image visualizes sea surface temperature anomalies in August 2023. Warm colors (red, orange) show where the ocean was warmer than normal. Cool colors (blues) show where temperatures were cooler. The red swath in the Eastern Pacific was due to an El Niño event. El Niño is a climate phenomenon in the tropical Pacific that results in warmer than normal sea surface temperatures leading to weather impacts across the planet.Credit: NASA -
Sea levels are rising
Global sea levels have risen more than 4 inches (101 millimeters) since measurements began in 1992, increasing coastal flooding in some places. As ocean water warms, it expands and takes up more space. The added heat in the air and ocean is also melting ice sheets and glaciers, which adds freshwater to the ocean and further raises sea levels. The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission, launched in 2022, and Sentinel 6 Michael Freilich, launched in 2020, are providing unparalleled views of sea level rise on top of decades of data from other missions.
The video shows a 21-day average of sea surface height anomalies highlighting ocean eddies and currents as imaged by the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite. The red and orange colors indicate where the sea surface was higher than normal and the blues are where it was lower than normal.Credit: NASA
The ocean is getting a little greener
Recent research found that over the past 20 years, the tropical ocean turned greener. Ocean color reflects the life that is found in it. Green colors often correspond to phytoplankton, microscopic plant-like organisms that form the center of the ocean's food web. Observations of changes in phytoplankton populations due to climate change are a key part of the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, and ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission, which launched in 2024.
Learn More About PACE about The ocean is getting a little greener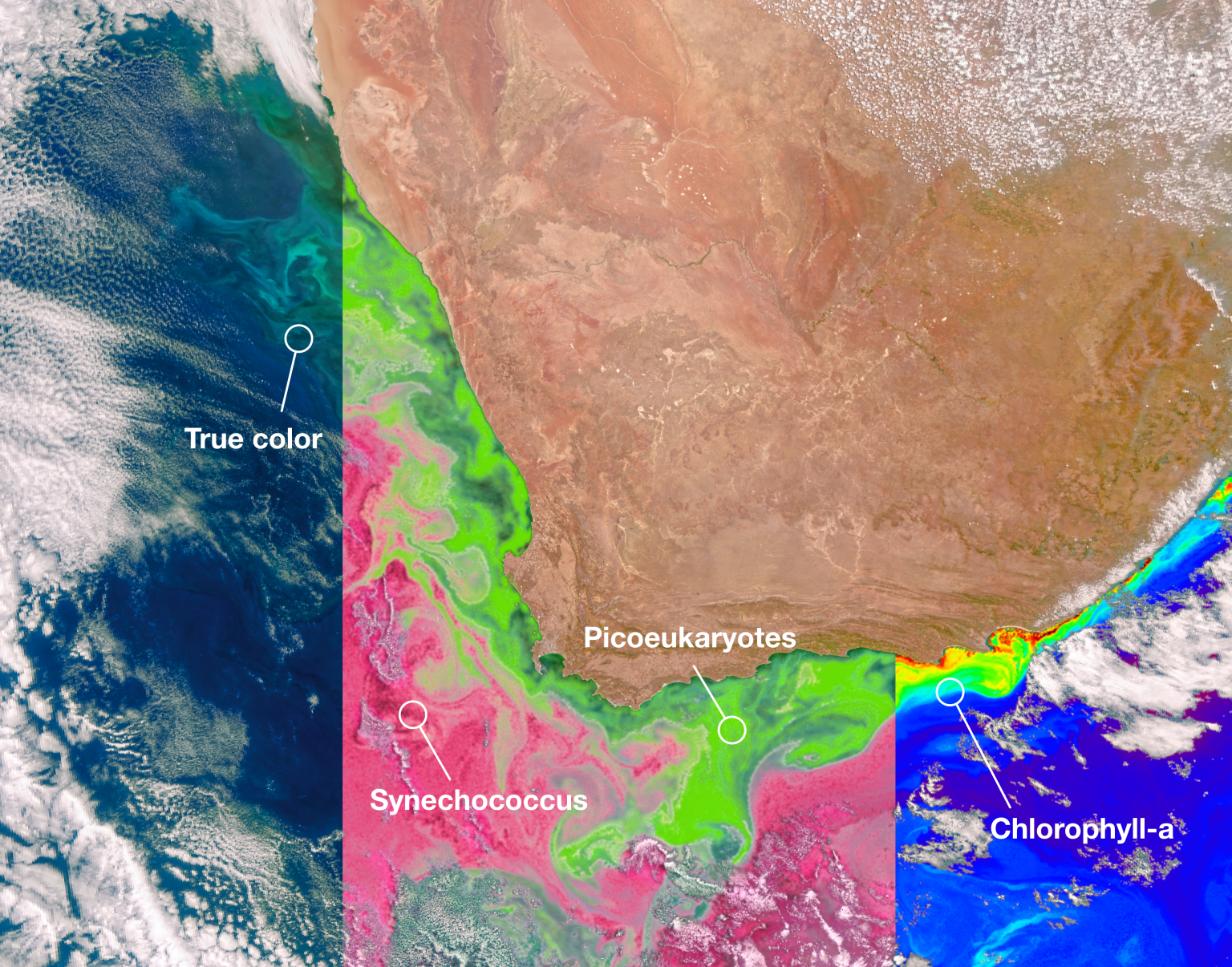
-
Ocean warming is altering hurricanes
Hurricanes need warm water to form and strengthen. Recent research points to warmer ocean temperatures as a key factor causing more storms to rapidly intensify. One way to detect rapid intensification before it happens may be through a change in lightning around the eye of the storm. Plus, higher sea levels worsen storm surge flooding when a storm travels over a coastline.
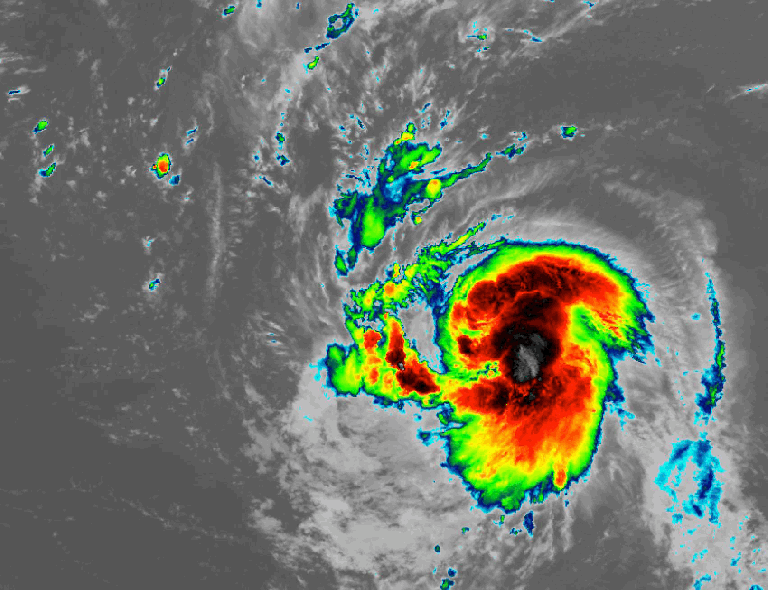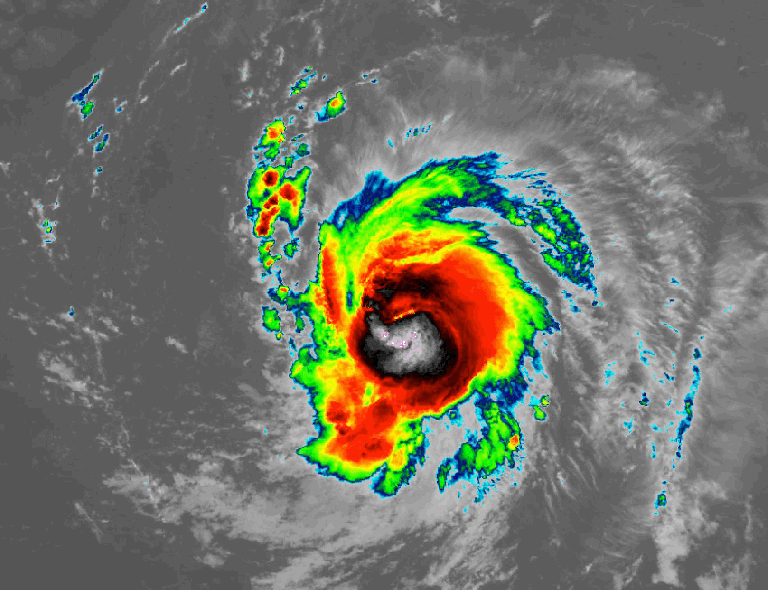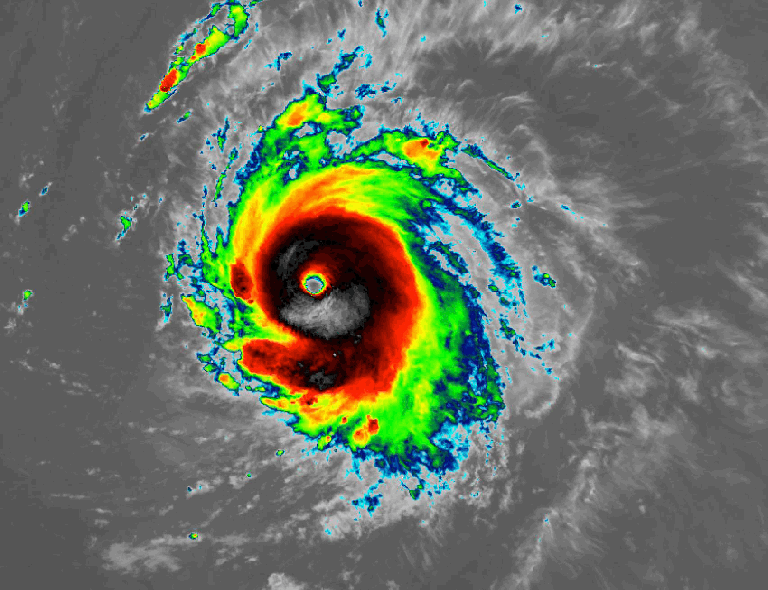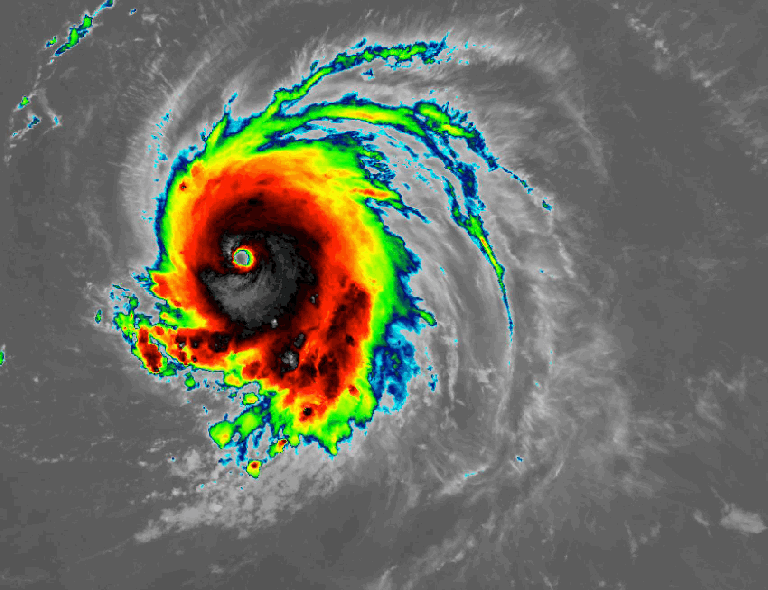 NOAA’s GOES-East satellite captures the rapid intensification of Hurricane Lee on Sept. 7, 2023.Credit: NASA/NOAA
NOAA’s GOES-East satellite captures the rapid intensification of Hurricane Lee on Sept. 7, 2023.Credit: NASA/NOAA -
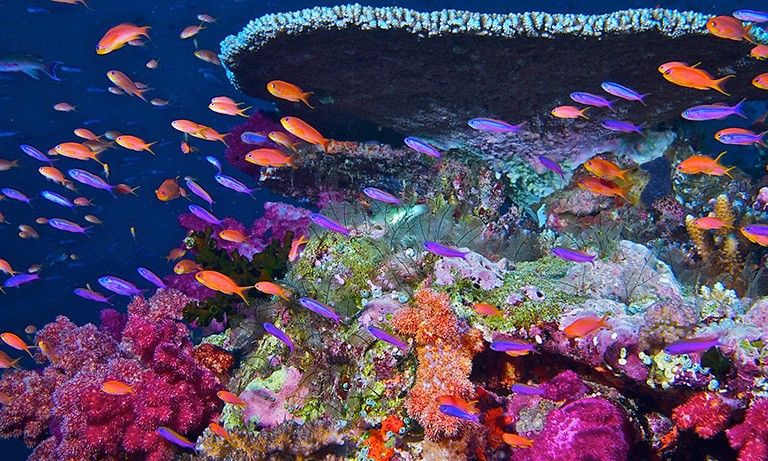
Ocean acidification and heating are altering marine ecosystems
Carbon dioxide and heat are both absorbed by the ocean as greenhouse gas levels increase. When carbon dioxide is dissolved in the ocean, the water becomes more acidic. This makes it harder for corals and some other marine life to grow shells and protect themselves. Marine heat waves are complicating the matter by making it too warm for many corals to survive. Satellites are providing important data to scientists measuring such changes in ocean environments.
 When corals are stressed from changes in their environment, they turn white, or "bleach." Sometimes the coral is able to recover, but other times the bleaching event leads to its death. This image shows the decay of a healthy coral reef to a reef between 2014 and 2015 in the National Marine Sanctuary of American Samoa.
When corals are stressed from changes in their environment, they turn white, or "bleach." Sometimes the coral is able to recover, but other times the bleaching event leads to its death. This image shows the decay of a healthy coral reef to a reef between 2014 and 2015 in the National Marine Sanctuary of American Samoa. -
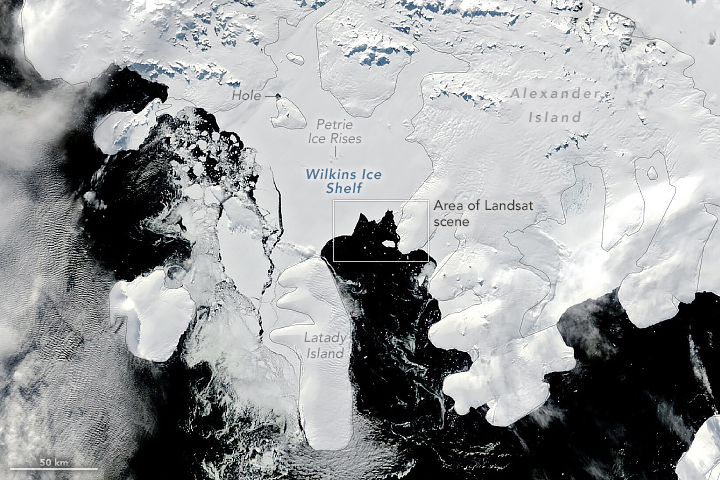
Sea ice is thinning and shrinking
Melting sea ice does not affect sea levels, but it does impact global temperatures. Sea ice is light-colored and reflects sunlight back into space; open water is darker and absorbs more sunlight. Warming ocean waters melt sea ice from below, and warmer air helps melt it from above. As ice cover thins and shrinks, more ocean is exposed and less sunlight is reflected, further warming the water and air. Satellites help monitor changes in sea ice which is an area of research for upcoming missions in the Earth Systems Observatory.
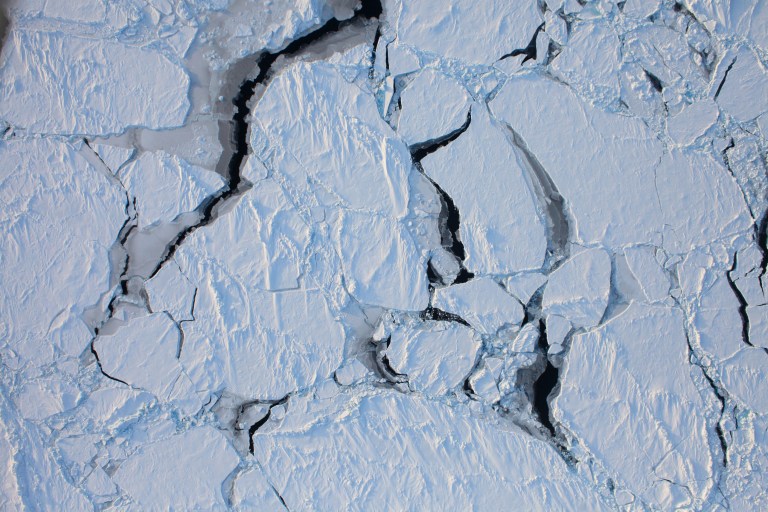 A photograph of Arctic sea ice breaking up as seen during an overhead flight during NASA’s Operation IceBridge in March 2011.Credit: NASA
A photograph of Arctic sea ice breaking up as seen during an overhead flight during NASA’s Operation IceBridge in March 2011.Credit: NASA -
El Niño can add to the heat
El Niño occurs when the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean become warmer than normal. This periodic ocean warming can add to the long-term global warming that has already accumulated, making a hot year even hotter. That’s because ocean temperatures are major drivers of global temperatures, as seen in 2023.
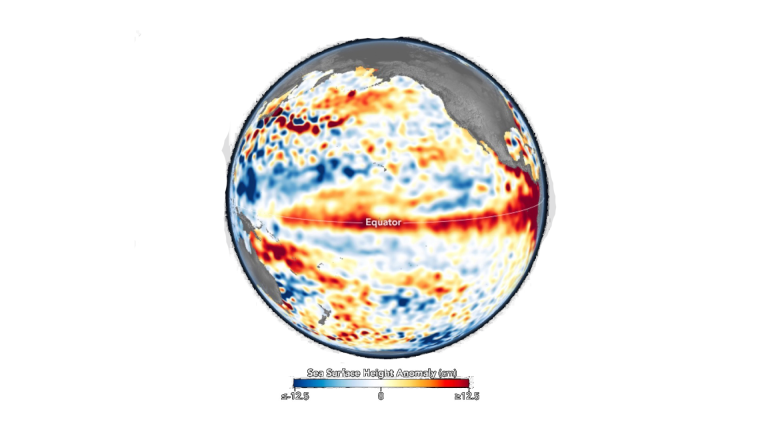 A visualization showing sea surface height anomalies in the Pacific Ocean in June 2023 based on satellite data. The red and orange colors show a higher-than-normal sea surface height. The blue areas were lower than normal.Credit: NASA
A visualization showing sea surface height anomalies in the Pacific Ocean in June 2023 based on satellite data. The red and orange colors show a higher-than-normal sea surface height. The blue areas were lower than normal.Credit: NASA -
Ocean circulation may be changing
Ocean currents are vital transporters of heat around the planet. As the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets melt, the excess fresh water running into the ocean could disrupt the balance of temperature and salinity that drive deep ocean currents. NASA satellite missions are monitoring the ocean for changes in heat transport as glaciers continue to melt and the ocean warms.
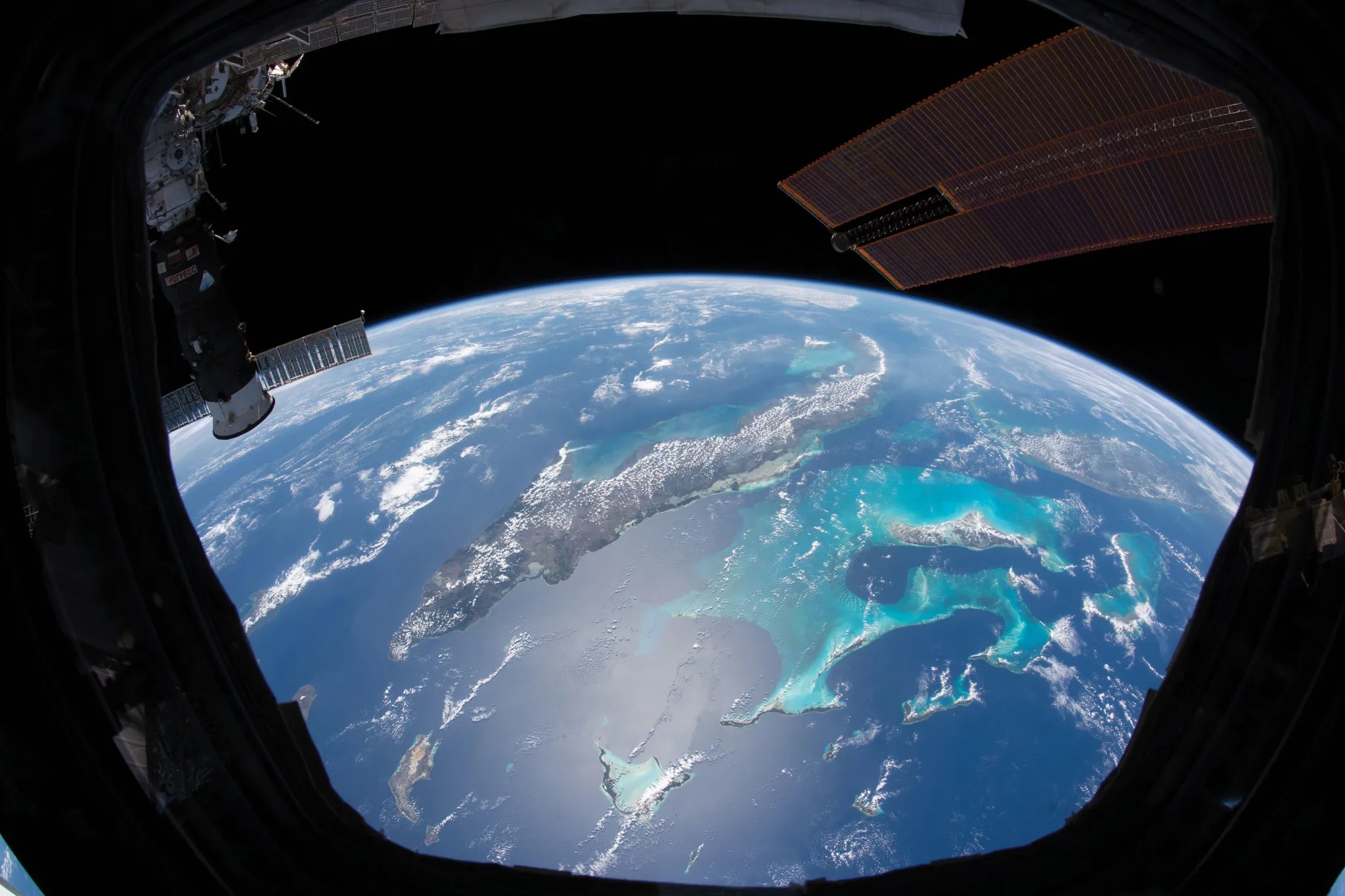 Clouds trace out islands in the Caribbean Sea in this photo taken by an astronaut aboard the International Space Station.Credit: NASA
Clouds trace out islands in the Caribbean Sea in this photo taken by an astronaut aboard the International Space Station.Credit: NASA
Key Satellites and Missions
Latest News and Research
Key Ocean and Climate Resources
Climate Kids
The ocean covers about 70% of Earth’s surface. So, it’s not surprising that it plays a large part in Earth’s environment. As Earth warms, water in the ocean soaks up energy (heat) and distributes it more evenly across the planet. The ocean also absorbs carbon dioxide from Earth’s atmosphere. The additional heat and carbon dioxide in the ocean can change the environment for the many plants and animals that live there.
How Does Climate Change Affect the Ocean?