Hubble Spies a Cosmic Eye
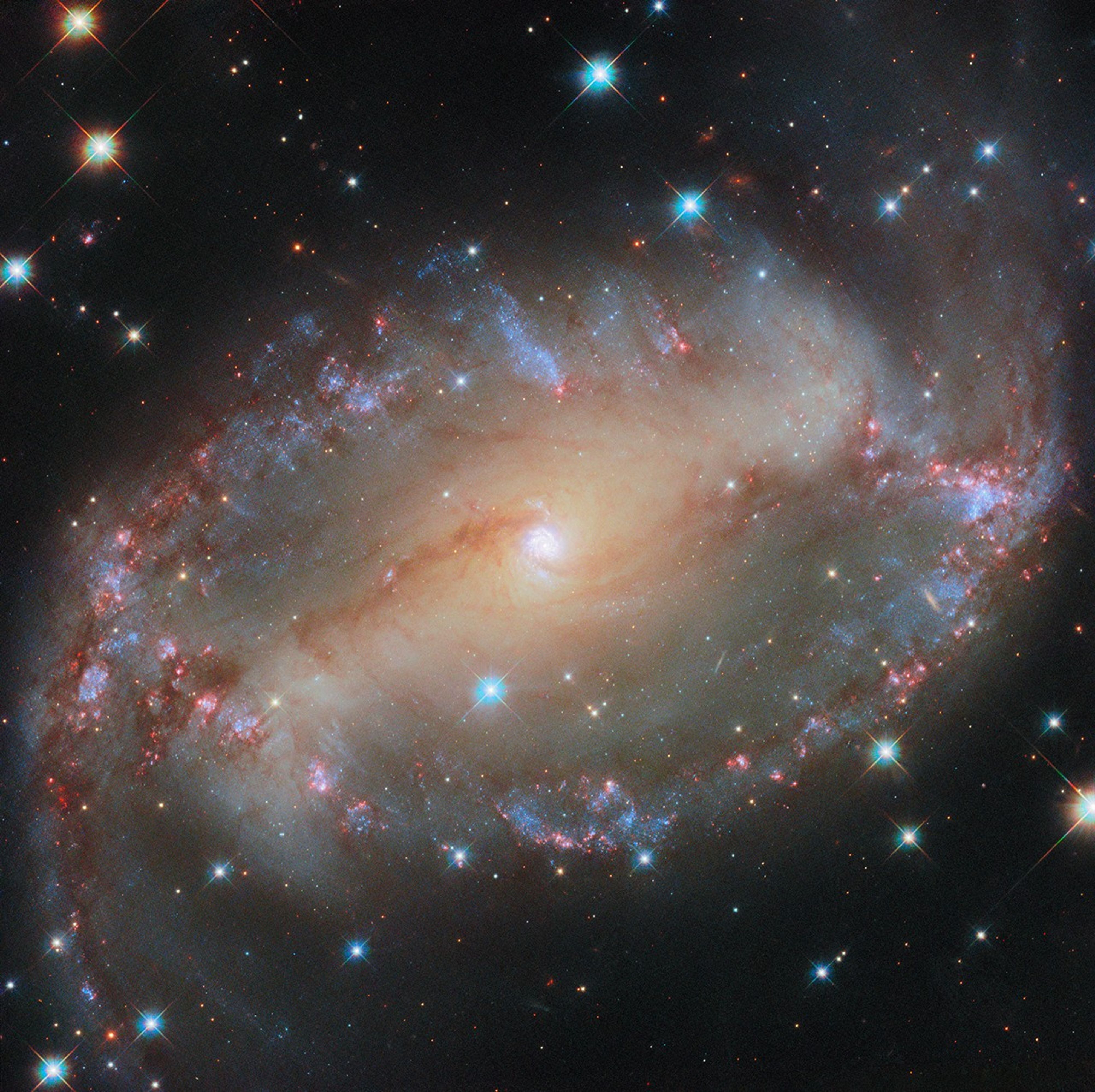
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image features the spiral galaxy NGC 2566, which sits 76 million light-years away in the constellation Puppis. A prominent bar of stars stretches across the center of this galaxy, and spiral arms emerge from each end of the bar. Because NGC 2566 appears tilted from our perspective, its disk takes on an almond shape, giving the galaxy the appearance of a cosmic eye. As NGC 2566 appears to gaze at us, astronomers gaze right back, using Hubble to survey the galaxy’s star clusters and star-forming regions. The Hubble data are especially valuable for studying stars that are just a few million years old; these stars are bright at the ultraviolet and visible wavelengths to which Hubble is sensitive. Using these data, researchers can measure the ages of NGC 2566’s stars, which helps piece together the timeline of the galaxy’s star formation and the exchange of gas between star-forming clouds and the stars themselves.
- X