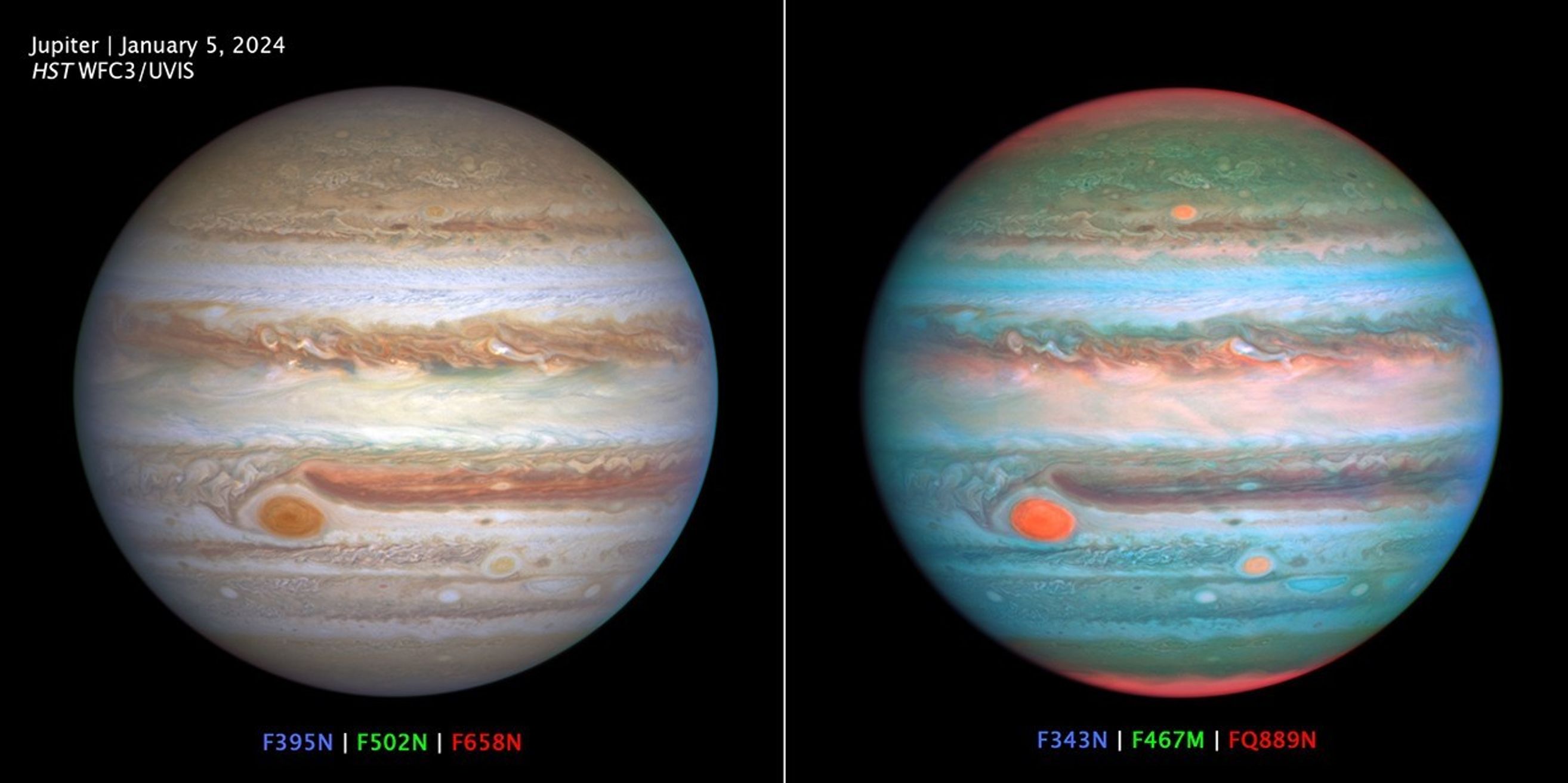
Hubble Multiwavelength OPAL Jupiter
Two views of Jupiter showcase the wealth of information provided by the spectral filters on the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) science instrument. At left, the RGB composite is created using three filters at wavelengths similar to the colors seen by the human eye. At right, the wavelength bounds are widened beyond the visible range to extend just into the ultraviolet (UV) and infrared regimes. Humans cannot perceive these extended wavelengths, but some animals (such as mantis shrimp, whose eyes function similarly to certain sensors on some NASA missions) are able to detect infrared and ultraviolet light. The result is a vivid disk that shows UV-absorbing lofty hazes as orange (over the poles and in three large storms, including the Great Red Spot), and freshly-formed ice as white (compact storm plumes just north of the equator). Astronomers, including the OPAL team, use these filters (and others not shown here) to study differences in cloud thickness, altitude, and chemical makeup.
- X