Hubble Images Messier 96
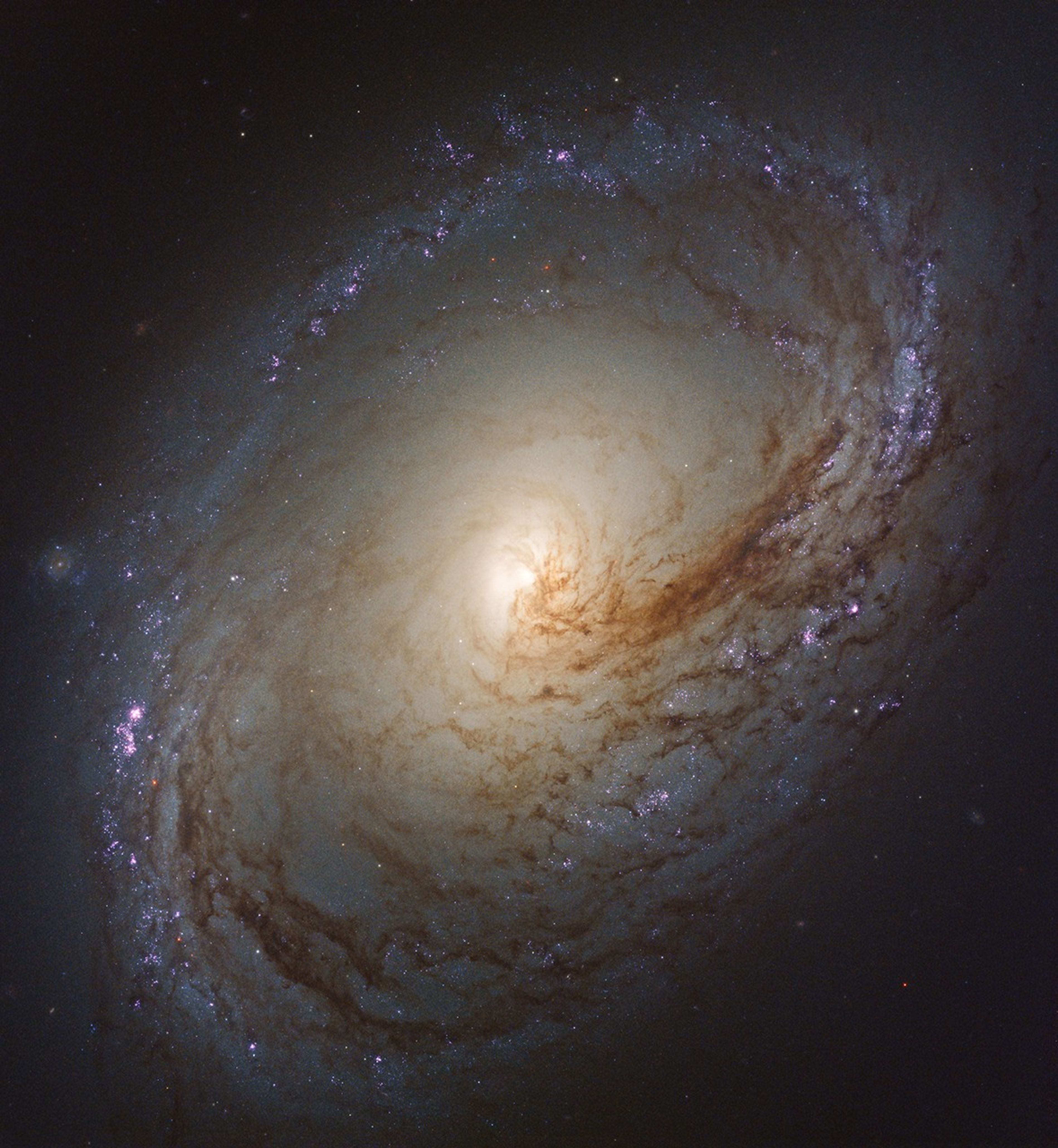
Messier 96, also known as NGC 3368, is a spiral galaxy about 35 million light-years away in the constellation of Leo (the Lion). It has roughly the same mass and size as our own Milky Way galaxy. It was first discovered by astronomer Pierre Méchain in 1781 and added to Charles Messier’s famous catalog of astronomical objects just four days later. There is a wave of star formation occurring along the dark filaments that make up the galaxy’s spiral arms. The fledgling stars illuminate the surrounding hydrogen gas, making the stars appear pink. Star birth begins at the inner spiral arms and moves outward. The milky-white region in the center represents the glow of countless stars.
- X
https://science.nasa.gov/image-detail/amf-6f64bd7b-8113-4ca6-9b9b-504eb1546b6d/
TakenMay 17, 2018
Size3799x4123px