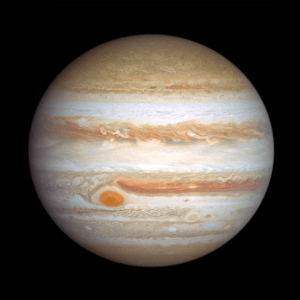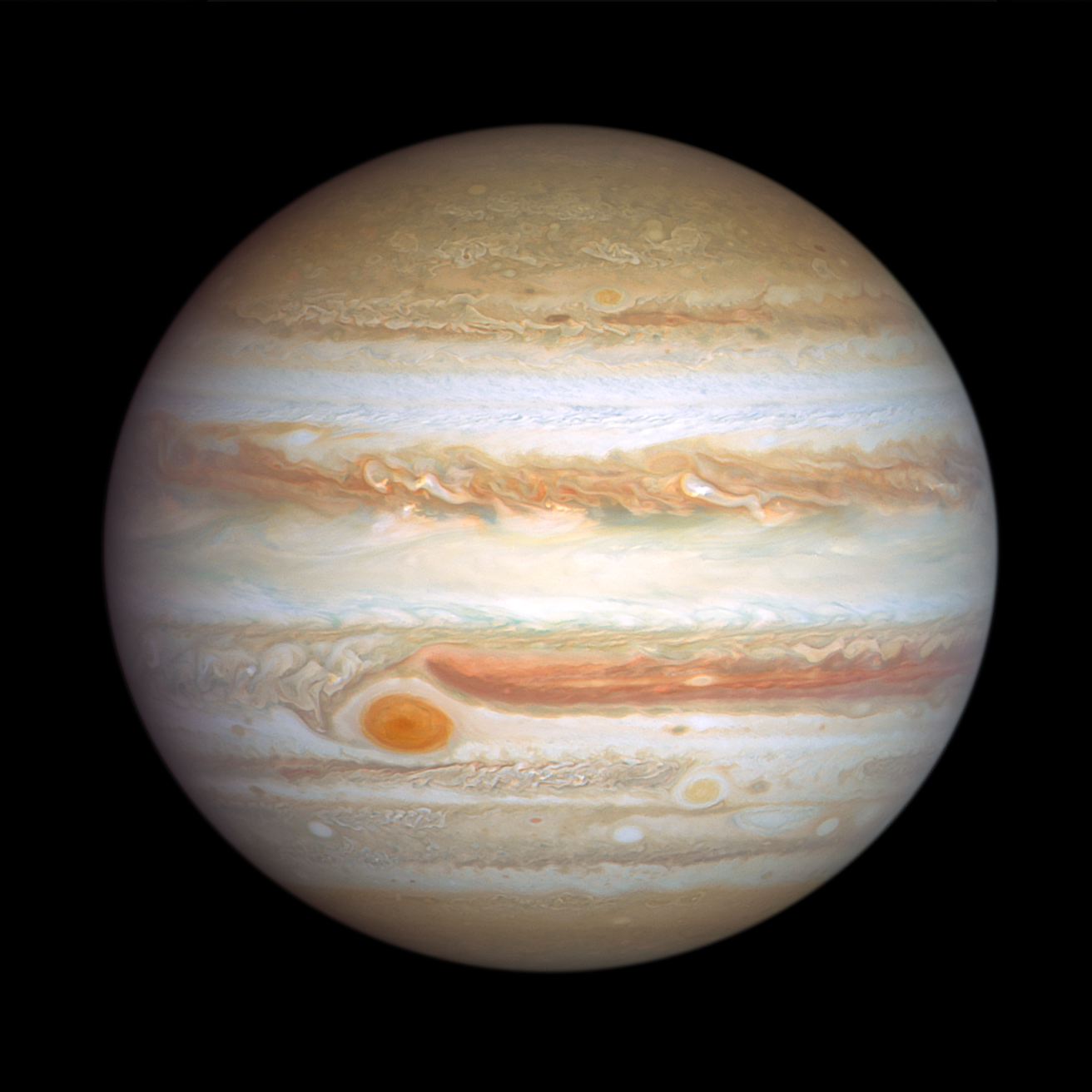
Hubble Image of Jupiter Taken January 5, 2024
Big enough to swallow Earth, the classic Great Red Spot stands out prominently in Jupiter's atmosphere. To its lower right, at a more southerly latitude, is a feature sometimes dubbed Red Spot Jr. This anticyclone was the result of storms merging in 1998 and 2000, and it first appeared red in 2006 before returning to a pale beige in subsequent years. This year it is somewhat redder again. The source of the red coloration is unknown but may involve a range of chemical compounds: sulfur, phosphorus, or organic material. Staying in their lanes, but moving in opposite directions, Red Spot Jr. passes the Great Red Spot about every two years. Another small red anticyclone appears in the far north.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC)
- X
https://science.nasa.gov/image-detail/hubble-jupiter-5jan2024-stsci-01hpmmsxbevgs2hk67vyvnveg5/
Image CreditNASA, ESA, STScI, Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC)
Size1024x1024px