The Electromagnetic Spectrum Unit Activities
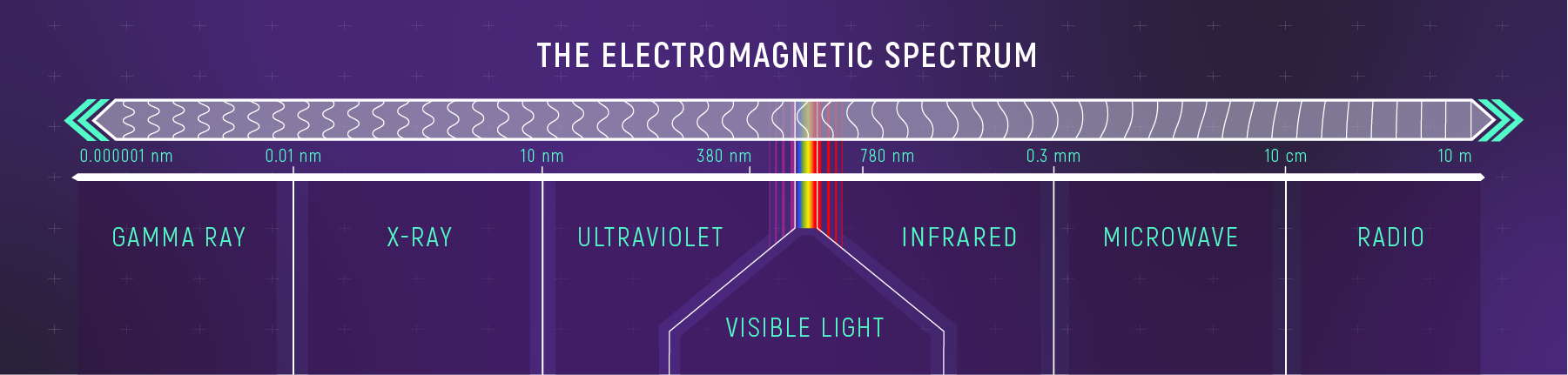
Gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible light (the visible rainbow), infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves are all forms of light (also called electromagnetic radiation). Together, they make up the electromagnetic spectrum. Each band of light has a different range of wavelengths: Gamma rays are the shortest and radio waves are the longest.
NASA, ESA, Leah Hustak (STScI)
| Levels |
|
|---|---|
| Material Type |
|
| Heliophysics Topics |
|
| Related Missions |
|
| Material Cost per Learner | Free |
| Language | English |
In these activities, students build simple spectroscopes to study visible light through multiple hands-on lesson plans and construction projects. The collection includes six different lessons: Simple Spectroscope, Project Visible Spectra, Cereal Box Spectroscope, Red Shift Blue Shift, Wavelength and Energy, and Resonating Atmosphere. Students learn about light analysis and spectroscopy principles while creating functional scientific instruments using everyday materials. These activities demonstrate how scientists use spectroscopes to analyze light and understand the composition of distant objects.























