Cold Atom Laboratory
CAL
About the mission
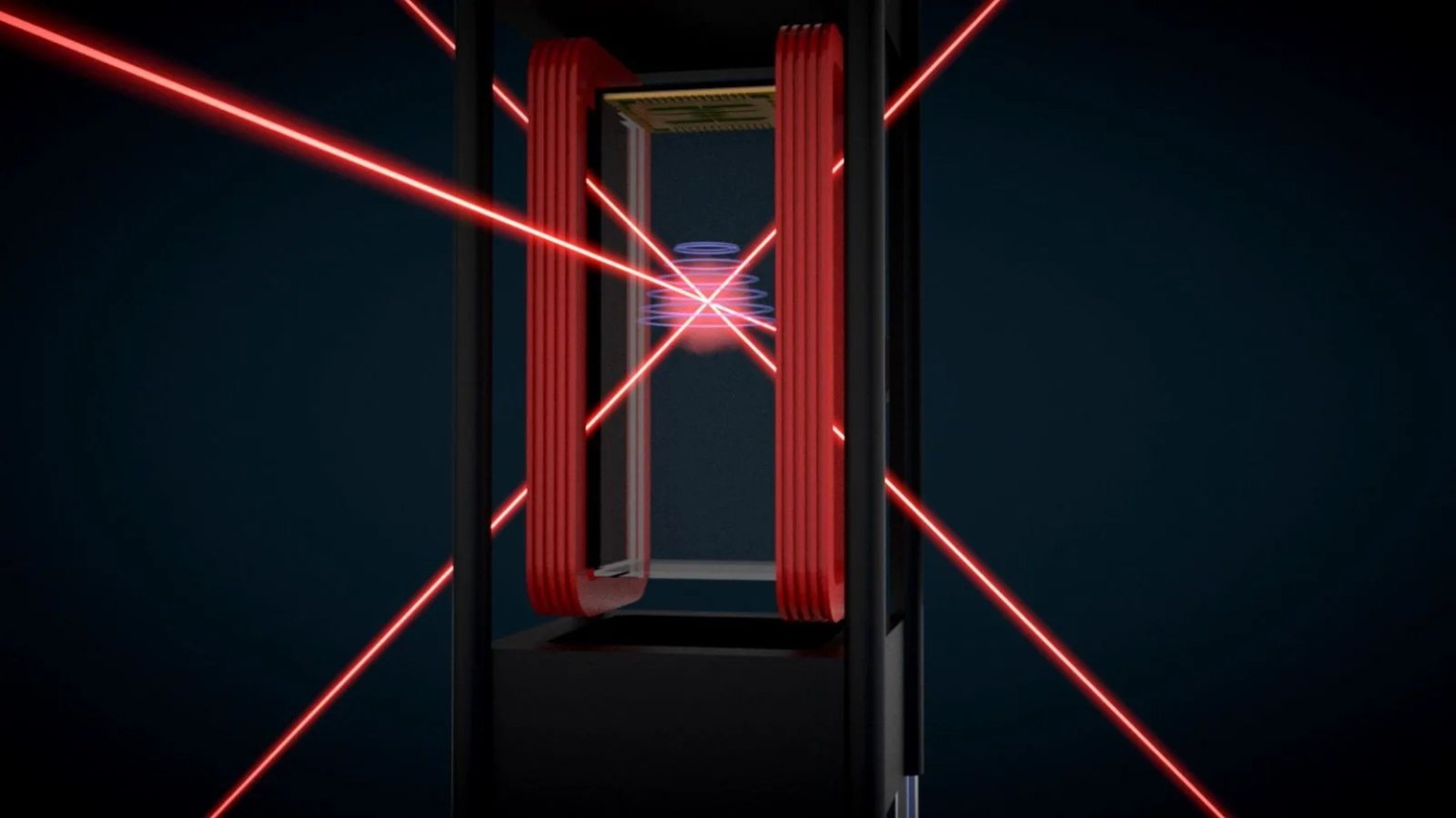
The Cold Atom Laboratory launched to the International Space Station in May 2018 and was installed a few months later. The facility uses lasers to cool atoms down to less than a degree above absolute zero. When clouds of atoms reach these ultracold temperatures they may form a fifth state of matter called a Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC). Distinct from gasses, liquids, solids and plasmas, a BEC makes the quantum properties of atoms macroscopic, so scientists can more easily observe them. Cold Atom Lab produced the first BECs in Earth orbit.
Multiple groups are conducting experiments inside Cold Atom Lab, which is operated completely remotely from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The primary goal of Cold Atom Lab is to utilize the microgravity environment to open up new avenues of fundamental research into the nature of atoms and quantum science. Many technologies that impact our everyday lives are based on quantum phenomena, including transistors and microchips.



























