IMAGE
Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration
Type
Launch
Target
Objective
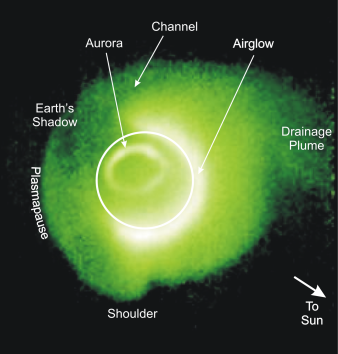
The Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration, or IMAGE, studied the response of Earth’s global magnetic environment — the magnetosphere — to changes in the Sun’s constant outflow of material in all directions, called the solar wind. Changes in this flow of material, which contains frozen-in magnetic fields, can set off a chain reaction in Earth’s magnetosphere that can lead to everything from auroras to disrupted power grids in the most extreme cases. IMAGE tracked these changes by quantifying neutral particles, as well as imaging the magnetosphere in radio and ultraviolet wavelengths of light. Before IMAGE, Earth’s magnetosphere was typically characterized by direct measurements of local particle flux and electric and magnetic fields. IMAGE collected most of its data remotely, making it the first mission dedicated to this type of study of Earth’s magnetosphere.