Live From the Clean Room at JPL
Watch Us Build Two New Missions
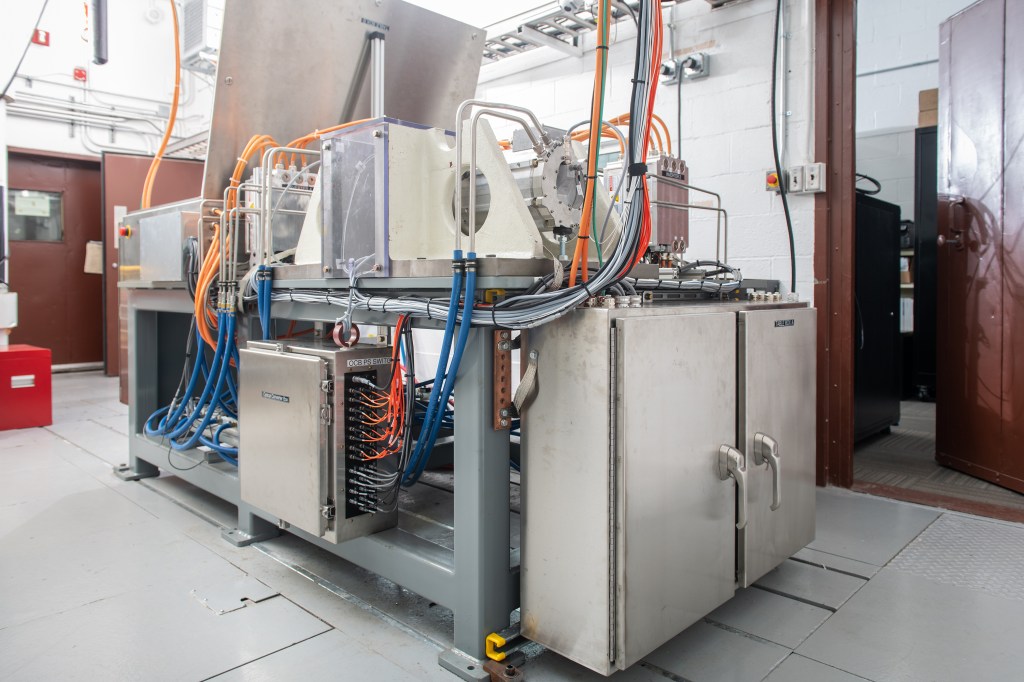
Welcome to the High Bay 1 clean room in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Many of NASA's most famous robotic spacecraft were assembled and tested in High Bay 1, including most of the Ranger and Mariner spacecraft; Voyager 1; the Galileo and Cassini orbiters; and all of NASA's Mars rovers. Currently, we have a special treat; two missions are sharing the room — NEO Surveyor and ASTHROS. Here is what you're seeing on the live cam:
Hello, Roomies!
-
On the Right: ASTHROS
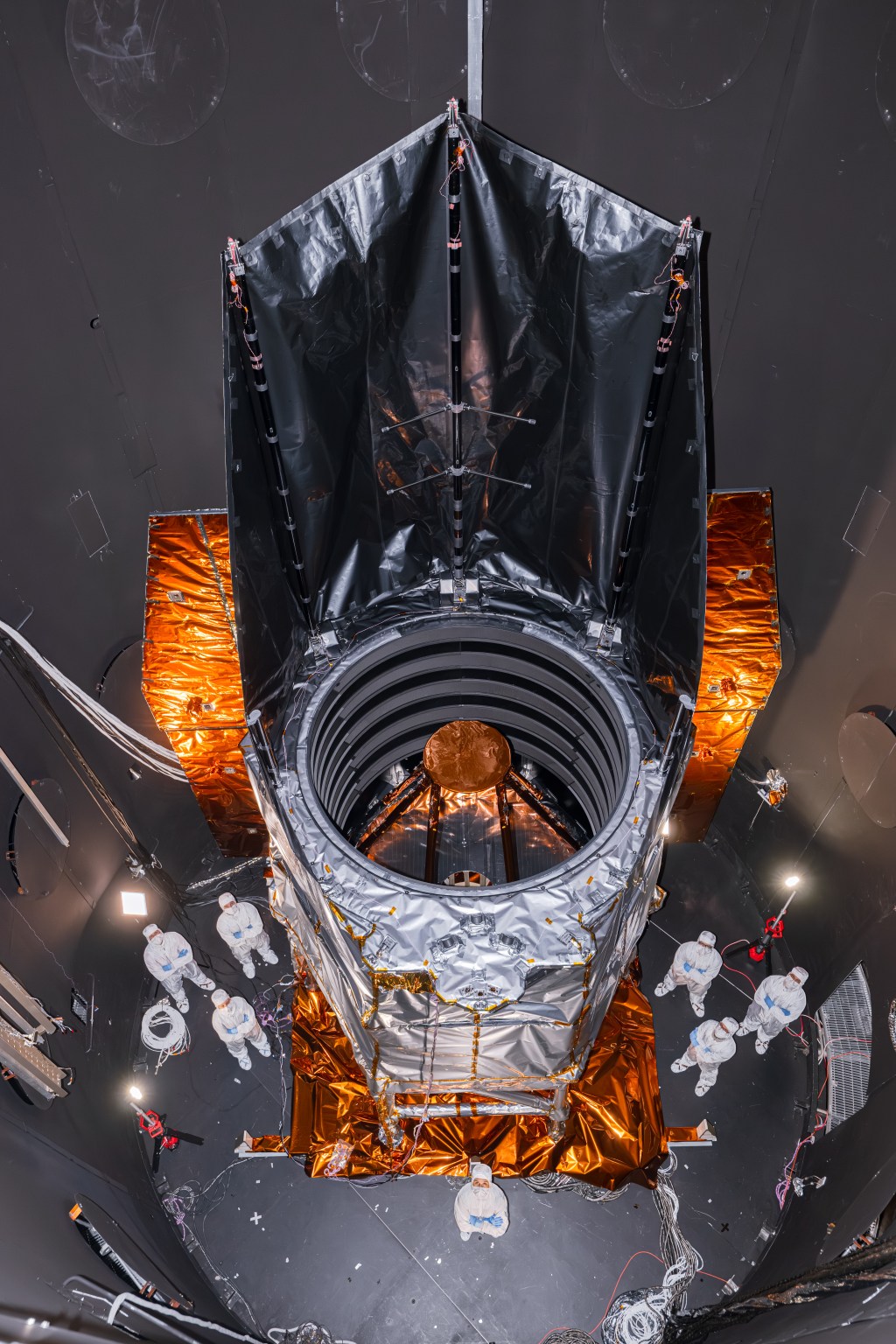
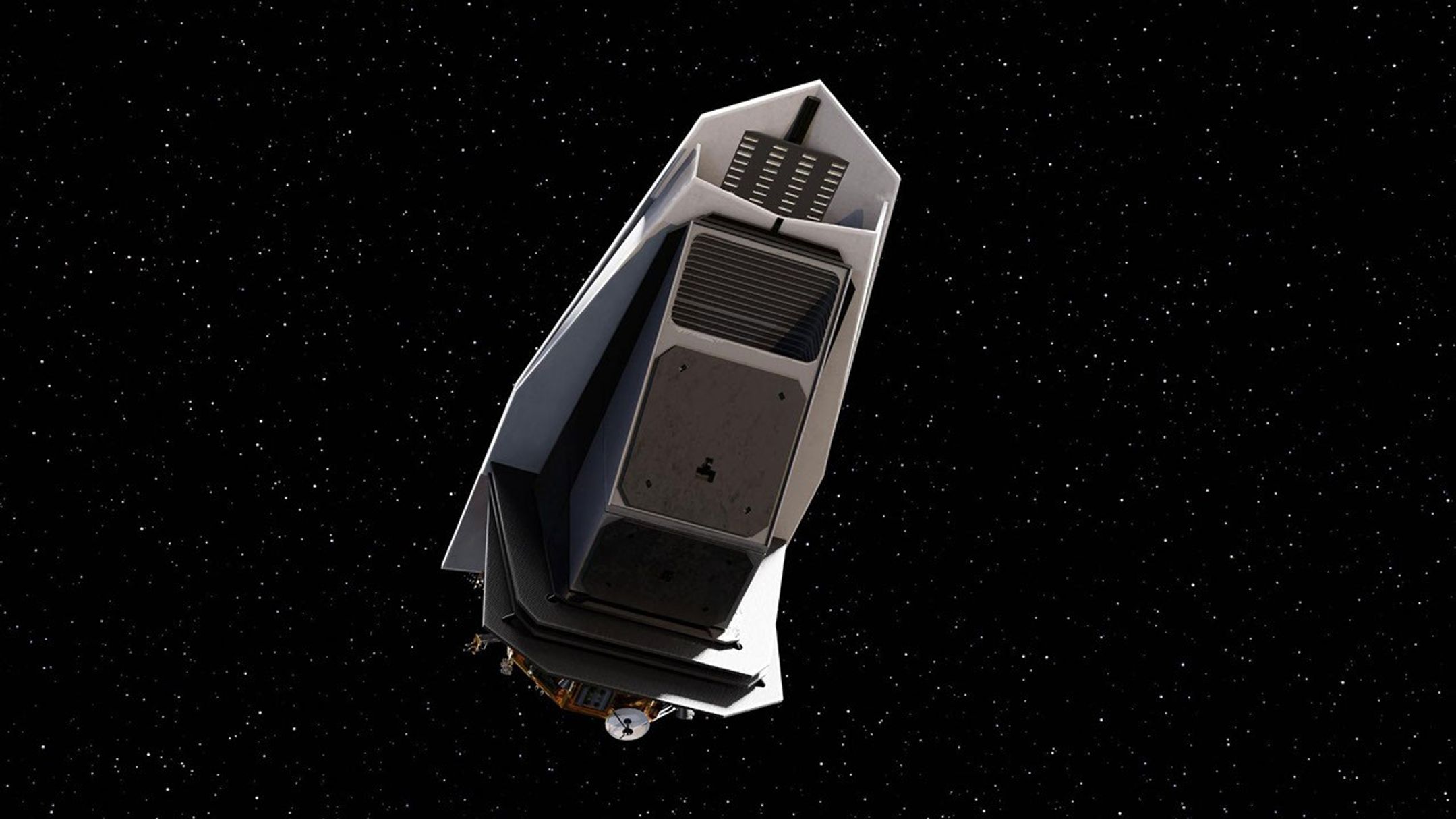
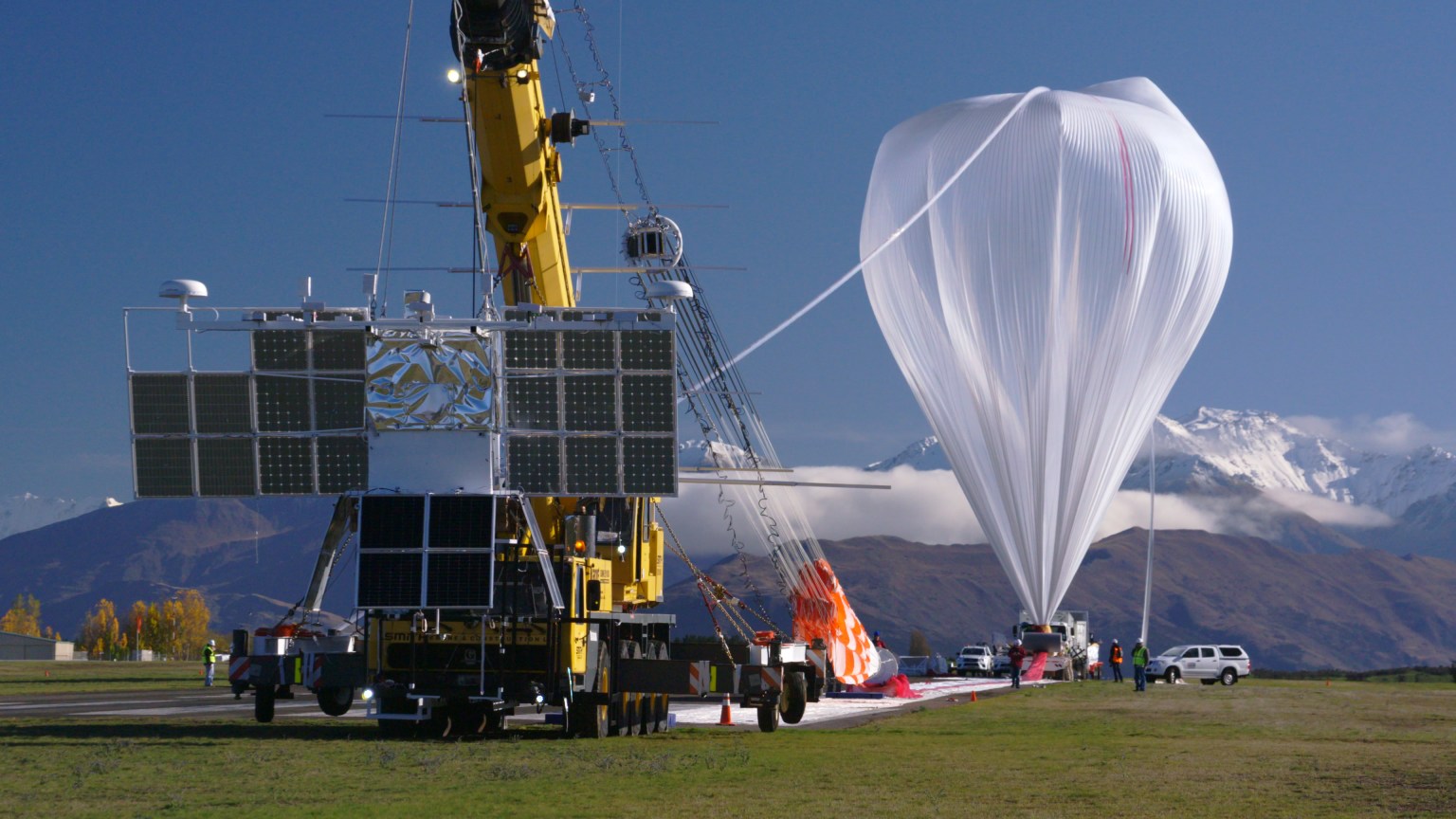
ASTHROS (Astrophysics Stratospheric Telescope for High Spectral Resolution Observations at Submillimeter-wavelengths) is a high-altitude astrophysics balloon mission. It will be able to detect wavelengths of light blocked by Earth’s atmosphere, and observe cosmic phenomena not visible from the ground. On the Live Cam, you can see its lightweight 8.2-foot (2.5-meter) gold-coated primary mirror — one of the largest ever to fly on a high-altitude balloon. Carried beneath a balloon the size of a football stadium, ASTHROS will rise to an altitude of 130,000 feet (about 40 kilometers) above Antarctica. For up to one month, it will ride a polar vortex around the center of the continent.
 The ASTHROS mission's primary mirror, shown here, is one of the largest ever flown on a high-altitude balloon. This lightweight mirror is coated with gold and nickel to make it more reflective in far-infrared wavelengths.Credit: Media Lario
The ASTHROS mission's primary mirror, shown here, is one of the largest ever flown on a high-altitude balloon. This lightweight mirror is coated with gold and nickel to make it more reflective in far-infrared wavelengths.Credit: Media Lario -
On the Left: NEO Surveyor
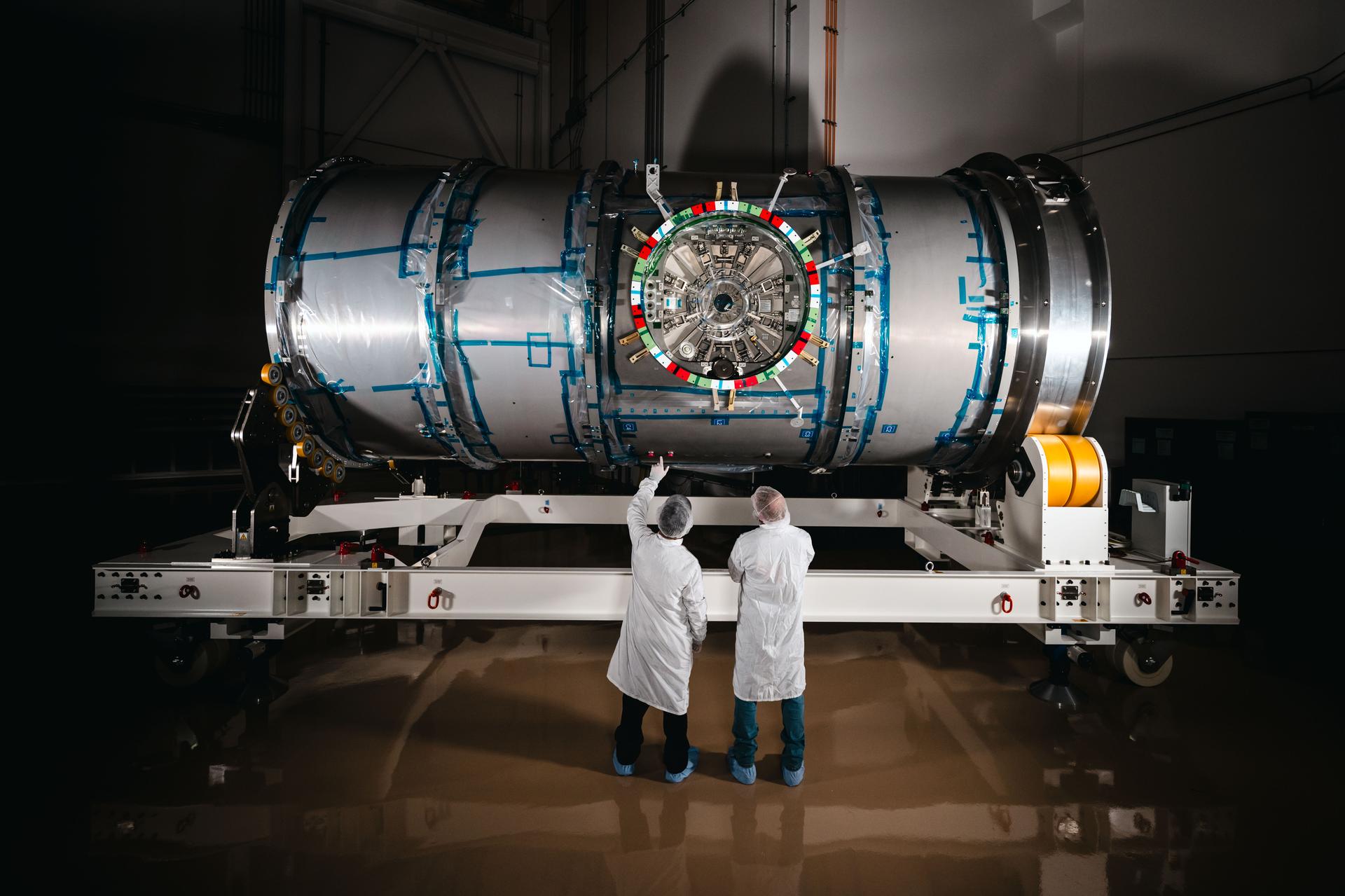
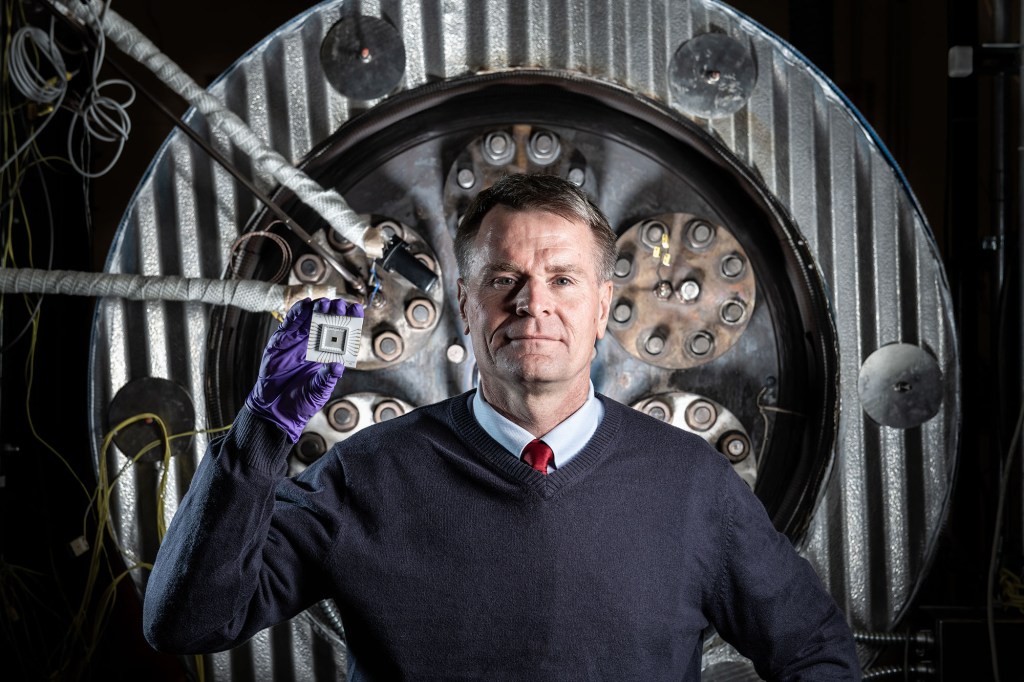
Near-Earth Object (NEO) Surveyor is the first space telescope specifically designed to detect asteroids and comets that may be potential hazards to Earth. The NEO Surveyor instrument enclosure is on the left side of the room inside a large white box. The enclosure is a key part of the spacecraft. It will house NEO Surveyor’s powerful infrared telescope. When completed and tested, the enclosure will be mounted to the back of the spacecraft’s large sunshield and avionics for the mission. NEO Surveyor is scheduled to launch no earlier than September 2027.
NEO Surveyor's instrument enclosure is to the far left in the large white box. The gold dish to the right is primary mirror for ASTHROS, a high-altitude balloon mission.NASA/JPL-Caltech