Spectrometer Characteristics
Spectrometer Specifications
| Spectral | Range | 349.9 – 1053.5 nm |
| Spectral | Sampling | 2.83 nm |
| Spectral | Resolution (FWHM) | 3.5 nm typ |
| Spectral | Calibration uncertainty | <0.1 nm |
| Spatial | Field of view | 30.7° |
| Spatial | Instantaneous FOV sampling | 0.882 mrad |
| Spatial | IFOV resolution (FWHM) | 0.97 mrad |
| Spatial | Cross-track spatial pixels | 608 |
| Radiometric | Range | 0 – 99% R |
| Radiometric | Sampling | 14 bit |
| Radiometric | Calibration uncertainty | <2% |
| Radiometric | Signal to Noise Ratio * | 500 @ 450 nm |
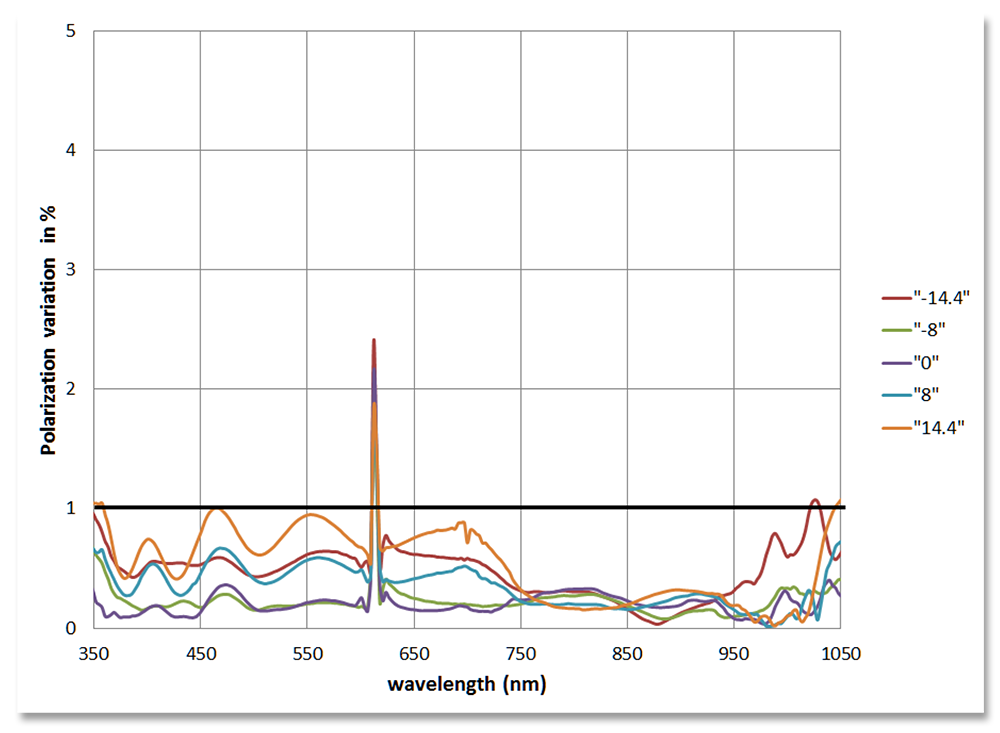
| Radiometric | Polarization variation | <1% |
| Uniformity | Spectral cross-track uniformity | >95% |
| Uniformity | Spectral IFOV mixing uniformity | >95% |
* : at a single integration (167 Hz rate) and three-band aggregate (8.5 nm), 5% reflectance, 45° solar zenith, MODTRAN standard atmosphere
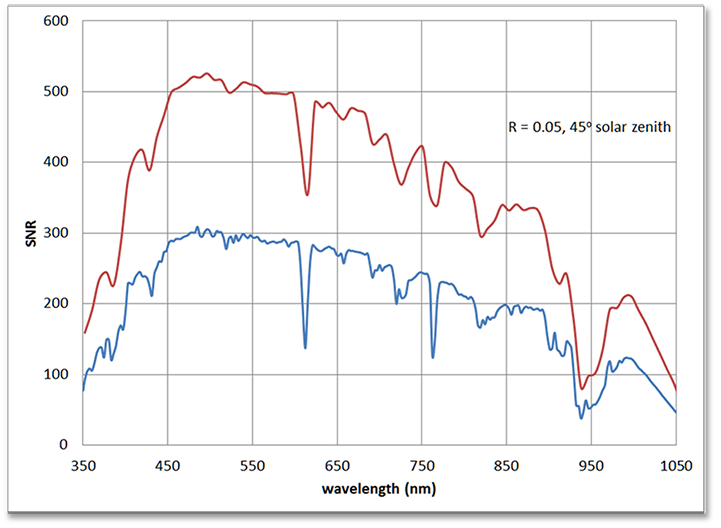
Signal to noise ratio through wavelength for low R (0.05) reference surface including standard atmosphere. Bottom curve is for a single 6ms integration and one spectral channel (2.83 nm). Top curve aggregates three spectral channels (8.5 nm). PRISM SNR is normally even higher due to forward oversampling (see flight envelope under “platforms.”)
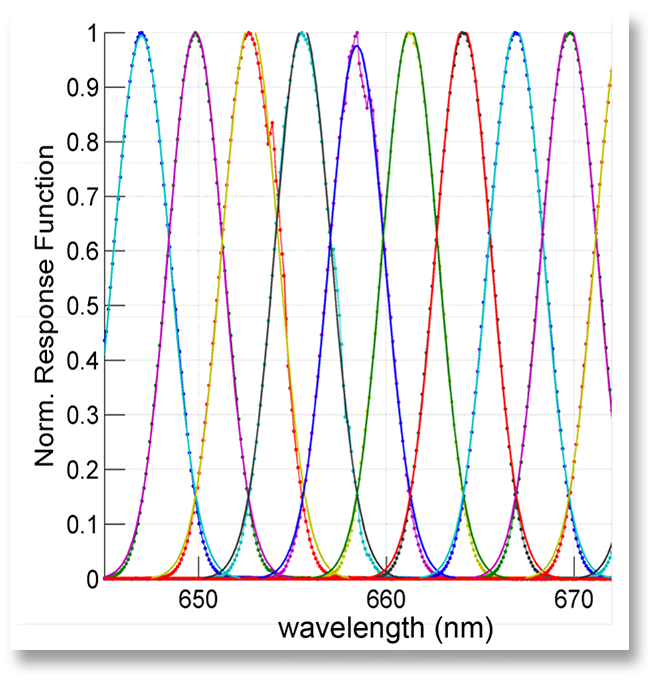
Typical spectral response functions obtained with a scanning monochromator, shown with interpolated Gaussian curves. PRISM has well-behaved nearly Gaussian spectral response.
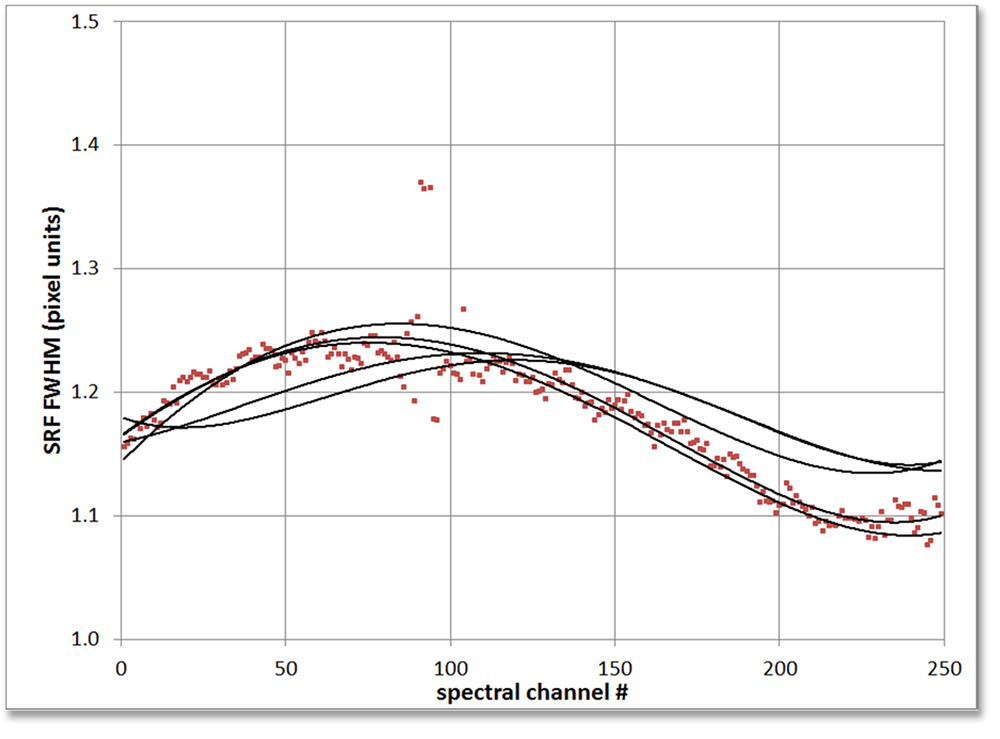
SRF FWHM from Gaussian fit as a function of wavelength (spectral channel #) for five field points across the PRISM field of view. Five interpolated lines are shown and one set of raw points. The field points are ±14.4°, ±8°, and 0°. The SRF width and shape is nearly independent of field location for any one wavelength.
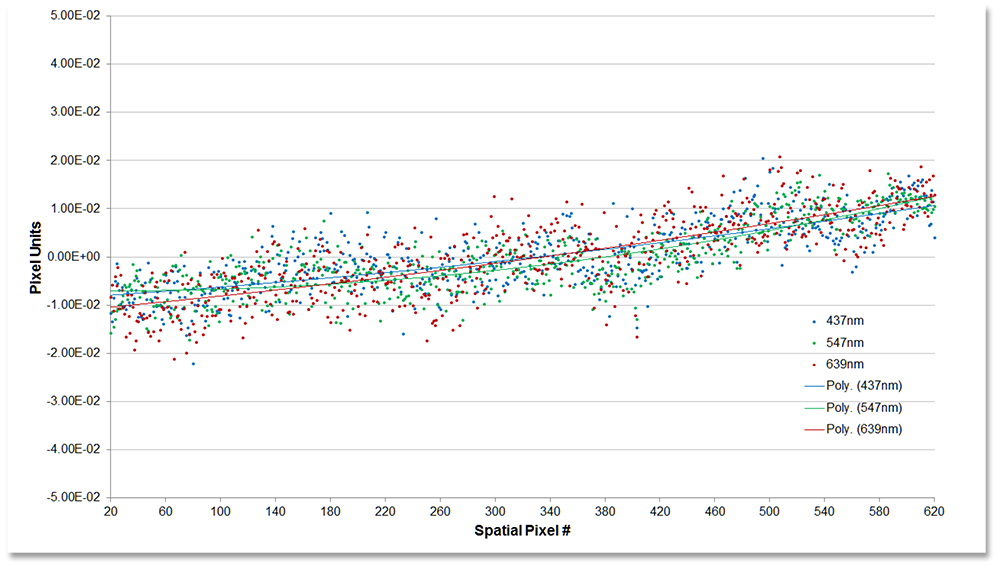
Scatter plot of spectral channel centroids as a function of spatial location for three isolated wavelengths (Hg lamp 437 nm and 547 nm, and laser at 632.8 nm). The centers of the SRF through field are aligned with the detector within 2% of a pixel (0.057 nm).
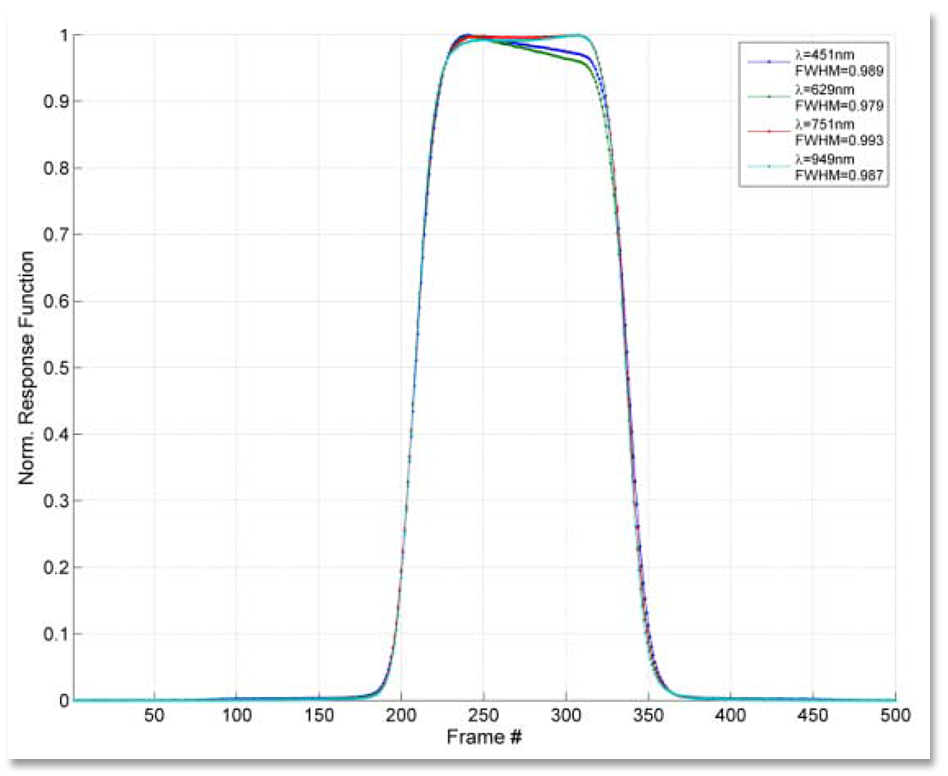
Along-track spatial response functions (ARF) for several wavelengths, without motion blur. The vertical axis is normalized to unity. The width is 1.1x sampling (slit width). The ARF is practically independent of wavelength.
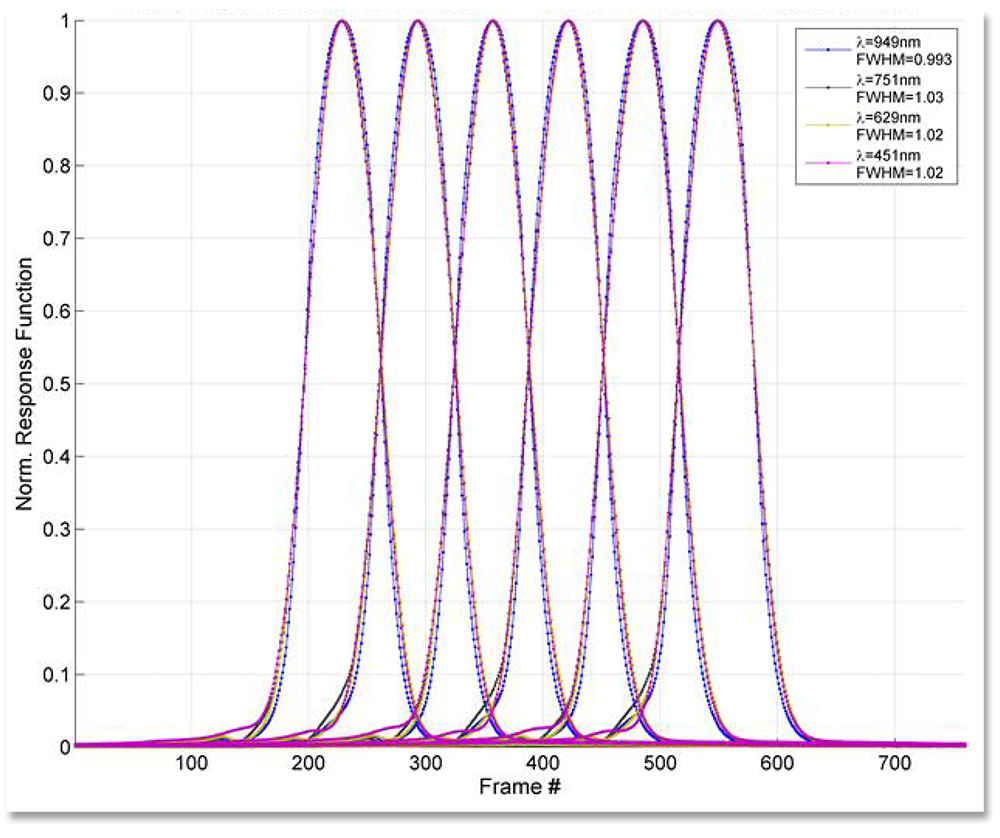
Typical cross-track spatial response functions (CRF) for adjacent pixels and several wavelengths. The vertical axis is normalized to unity. The total CRF variation with wavelength (non-uniformity) is ≤5% of a pixel.
Polarization variation throughout the spectral range for five positions spanning the field of view. With the exception of the filter seam location, polarization variation remains at or below 1%.