StarBurst
StarBurst is a SmallSat that will detect high-energy gamma rays from events such as the mergers of dense stellar remnants called neutron stars.
active Mission

Featured Story
NASA Selects 4 Concepts for Small Missions to Study Universe’s Secrets
NASA has chosen four small-scale astrophysics missions for further concept development in a new program called Pioneers. Through small satellites and…
Read the Story
Images to Download
Fermi
active Mission
Overview Fermi observes light with energies thousands to hundreds of billions of times greater than what our eyes can detect. The energy of the light we can see ranges from…
Learn More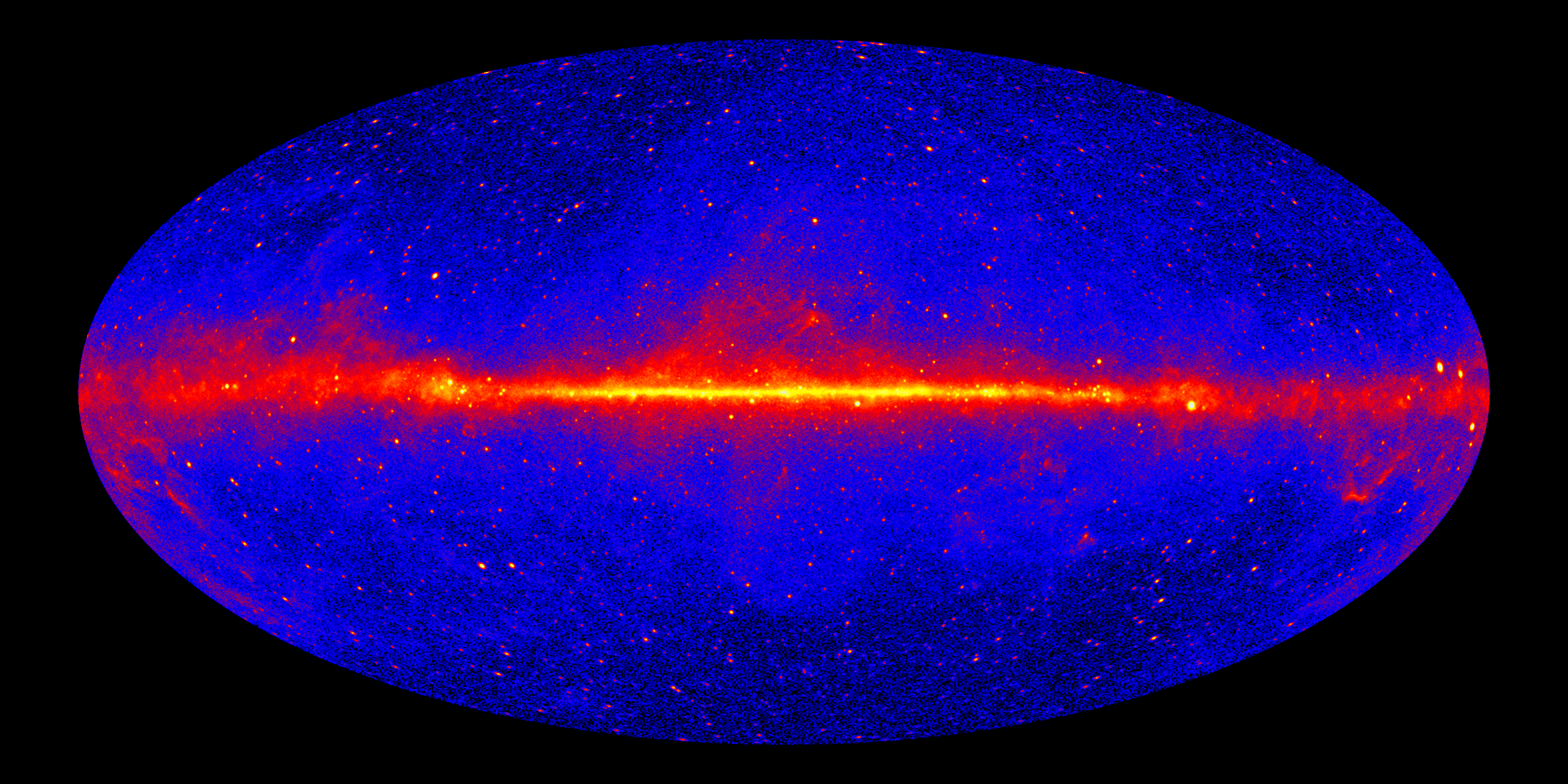
This image shows the entire sky as seen by Fermi's Large Area Telescope. The most prominent feature is the bright, diffuse glow running along the middle of the map, which marks the central plane of our Milky Way galaxy. The gamma rays there are mostly produced when energetic particles accelerated in the shock waves of supernova remnants collide with gas atoms and even light between the stars. Many of the star-like features above and below the Milky Way plane are distant galaxies powered by supermassive black holes. Many of the bright sources along the plane are pulsars. The image was constructed from 12 years of observations using front-converting gamma rays with energies greater than 1 GeV. Hammer projection.
Keep Exploring