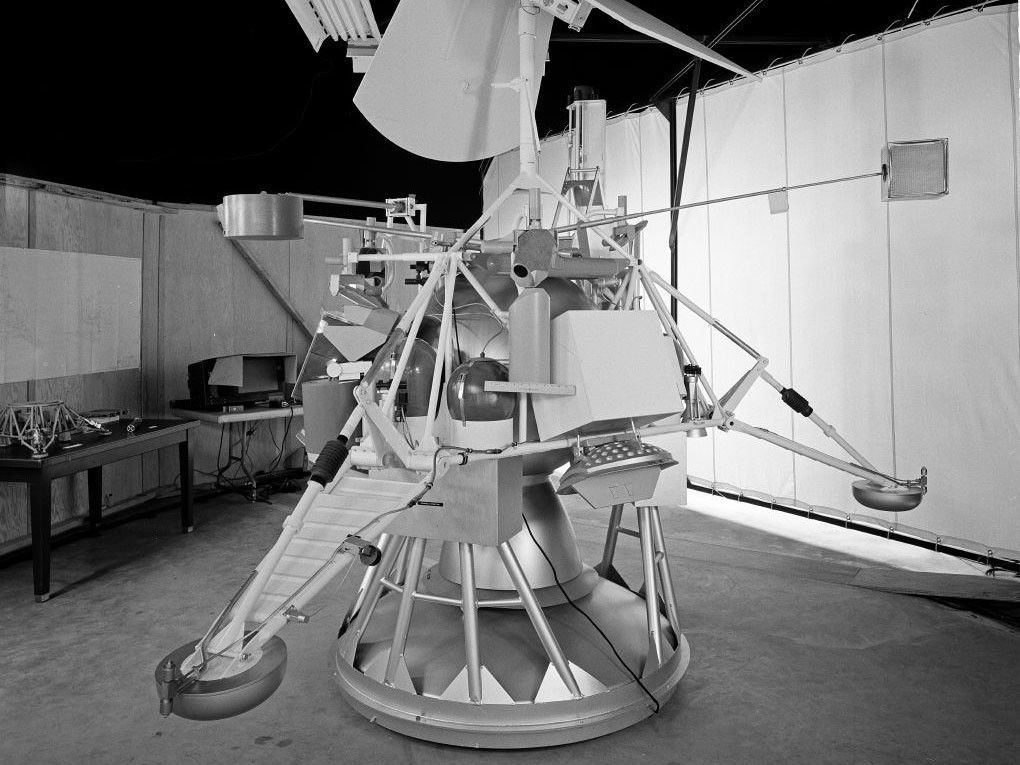
Surveyor 2
Type
Launch
Target
Objective
What was Surveyor 2?
NASA's Surveyor 2 was supposed to make a soft landing on the Moon, but a thruster failed to ignite, putting the spacecraft into a spin. The lander crashed on the Moon.
| Nation | United States of America (USA) |
| Objective(s) | Lunar Soft-Landing |
| Spacecraft | Surveyor-B |
| Spacecraft Mass | 2,194 pounds (995.2 kilograms) |
| Mission Design and Management | NASA / JPL |
| Launch Vehicle | Atlas Centaur (AC-7 / Atlas D no. 194 / Centaur D) |
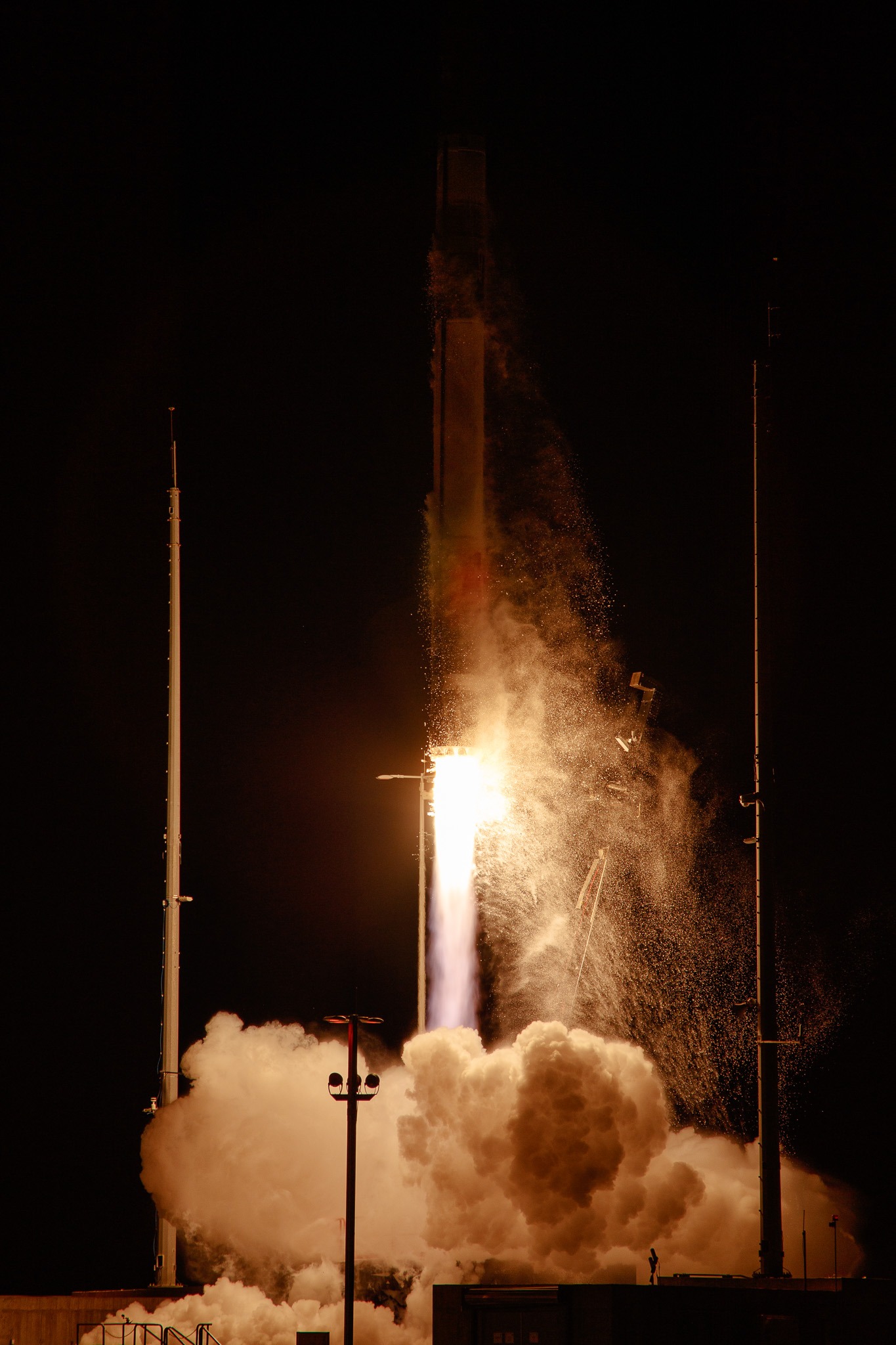
| Launch Date and Time | Sept. 20, 1966 / 12:32:00 UT |
| Launch Site | Cape Canaveral, Fla. / Launch Complex 36A |
| Scientific Instruments | Imaging System |
Key Dates
Sept. 20, 1966: Launch
Sept. 23, 1966: Lander crashed on the Moon
In Depth: Surveyor 2
Surveyor 2, similar in design to its predecessor, was aimed for a lunar soft-landing in Sinus Medii. During the coast to the Moon, at 05:00 UT Sept. 21, 1966, one of three thrusters failed to ignite for a 9.8-second course correction, and as a result, put the spacecraft into an unwanted spin.
Despite as many as 39 repeated attempts to fire the recalcitrant thruster, the engine failed to ignite, and Surveyor 2 headed to the Moon without proper control.
Just 30 seconds after retro-fire ignition at 09:34 UT Sept. 22, 1966, communications ceased, and the spacecraft crashed on the surface of the Moon at 5 degrees 30 minutes north latitude and 12 degrees west longitude, just southeast of Copernicus crater.
Key Source
Siddiqi, Asif A. Beyond Earth: A Chronicle of Deep Space Exploration, 1958-2016. NASA History Program Office, 2018.