Hinode (Solar-B)
Active Mission

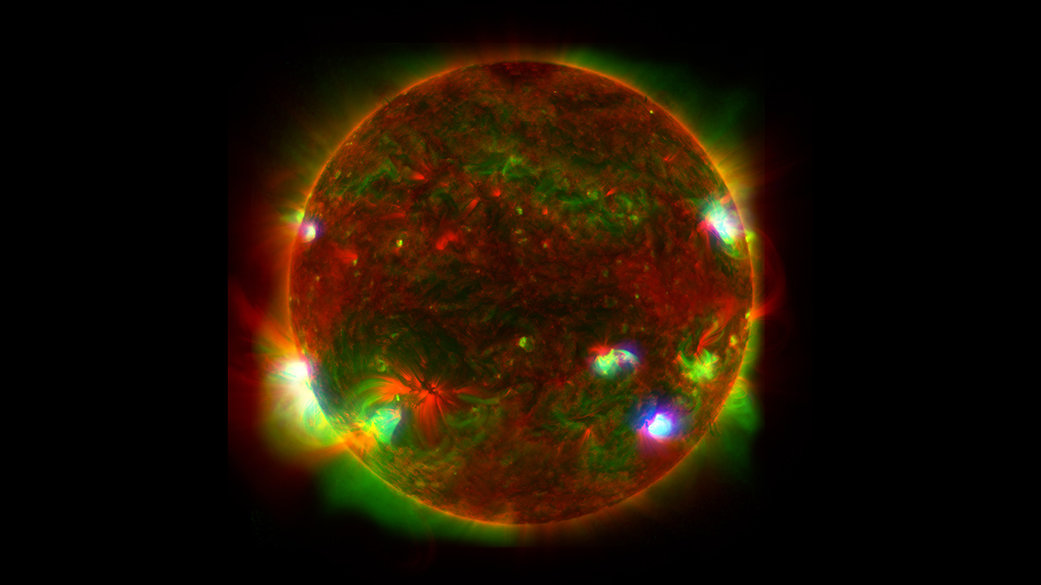
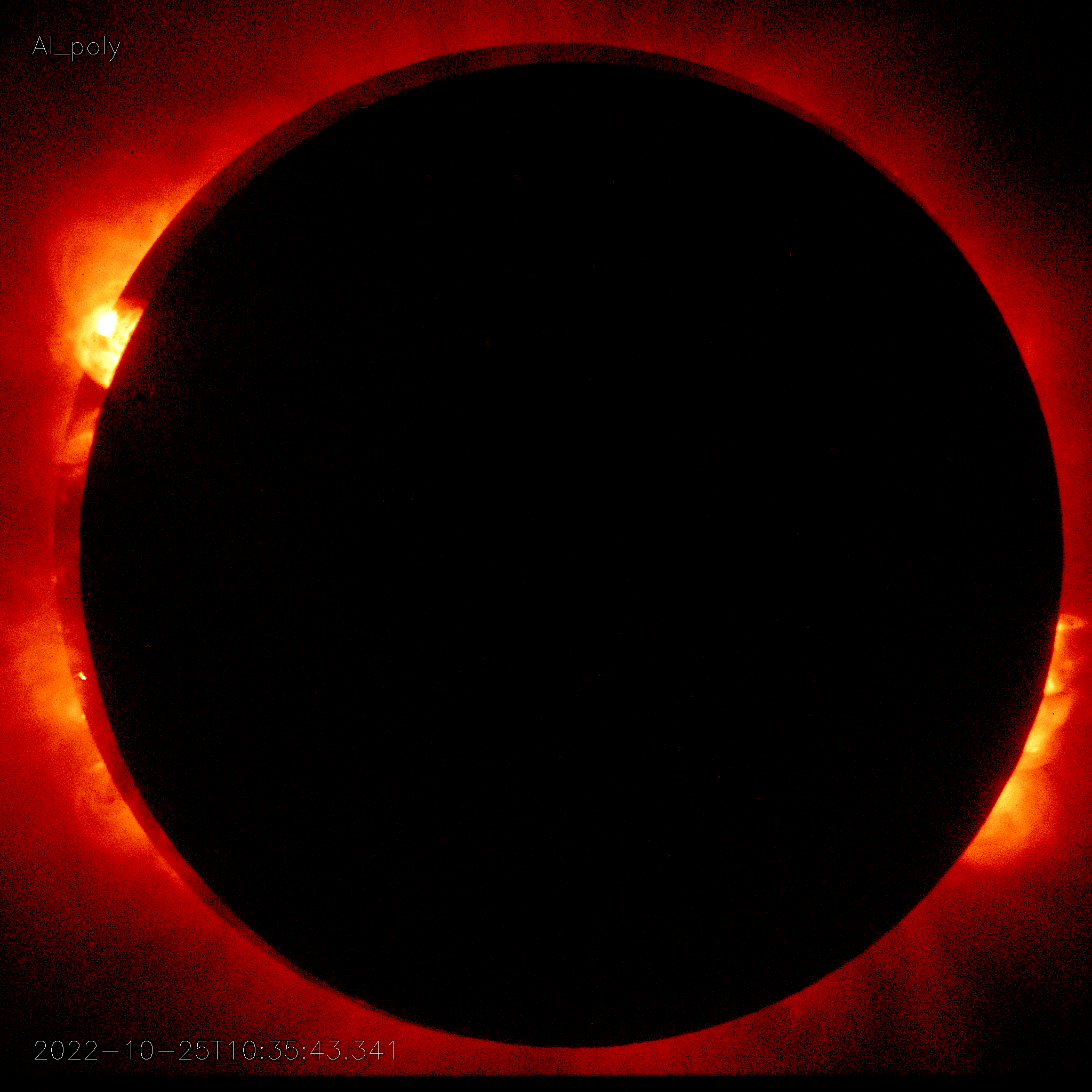
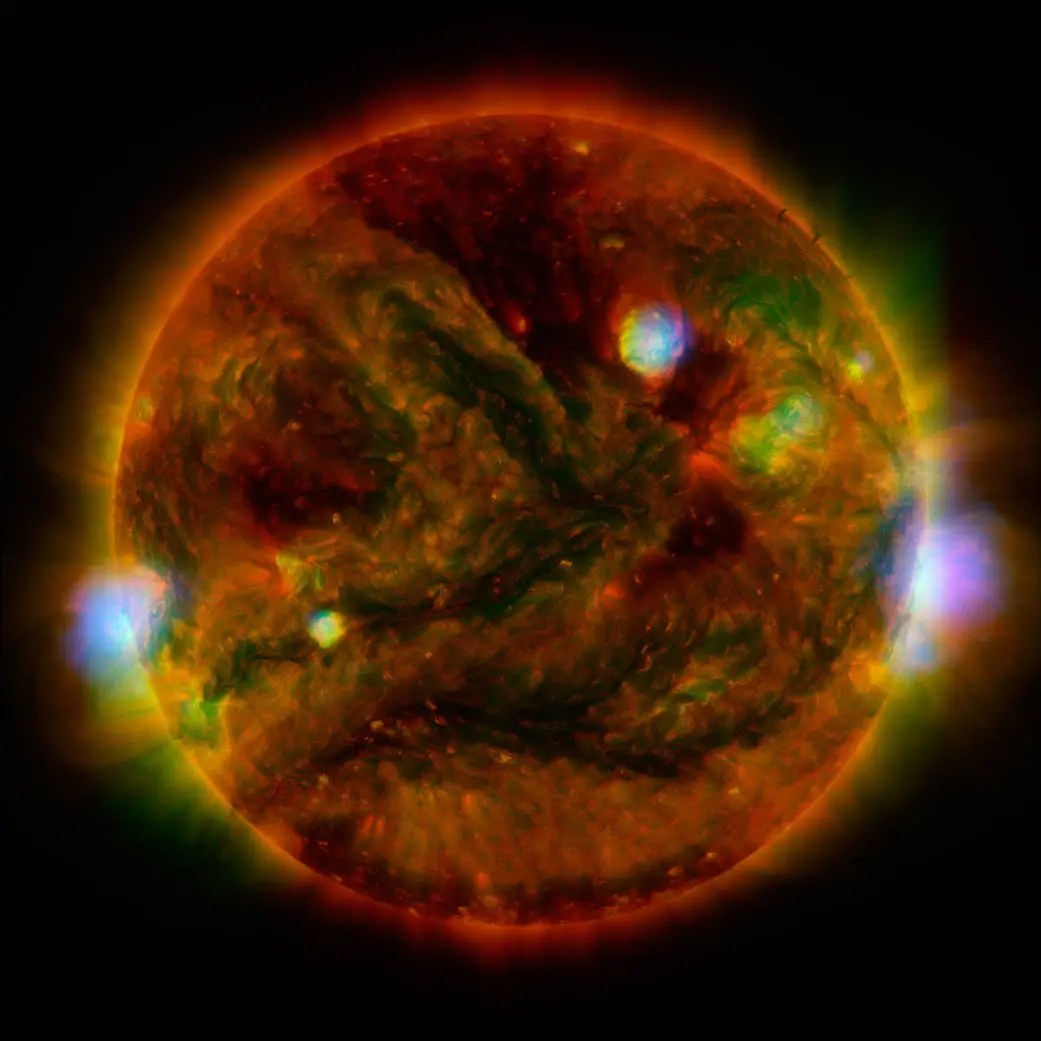
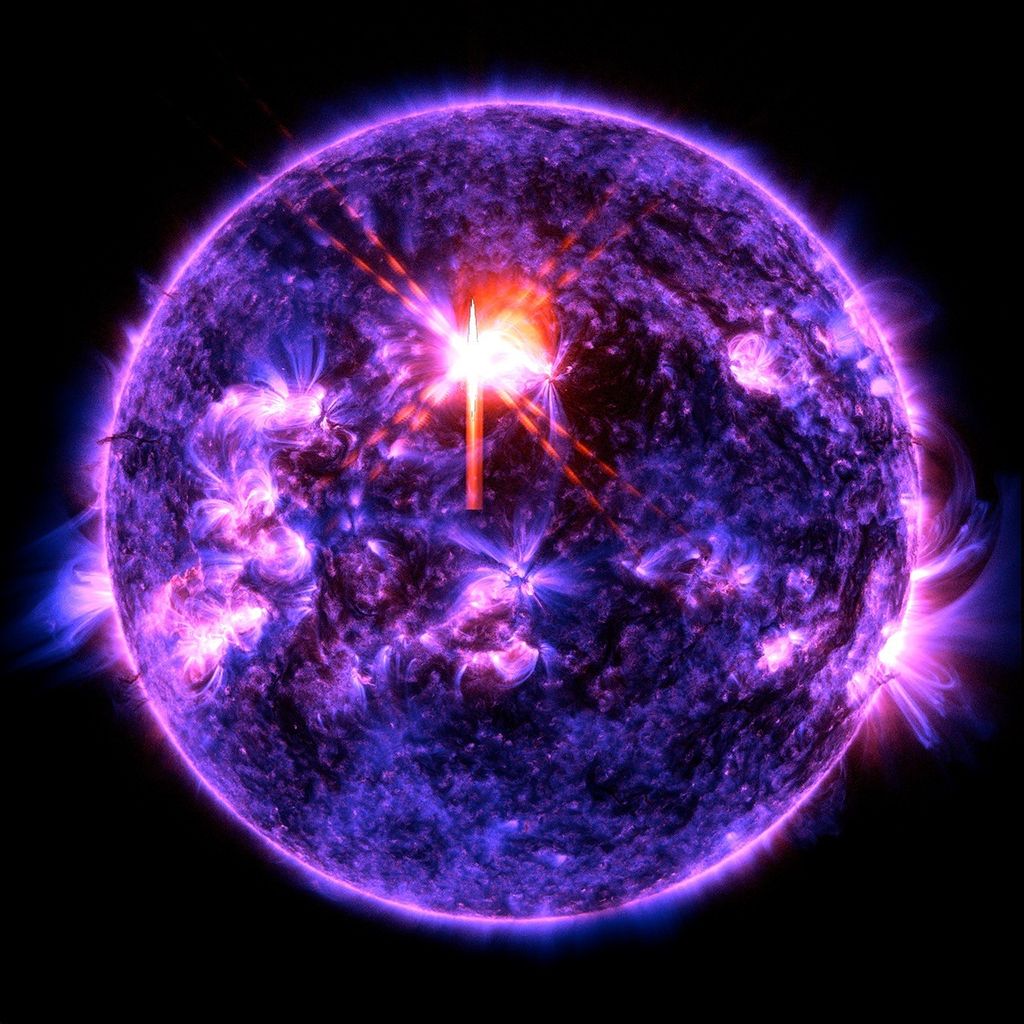
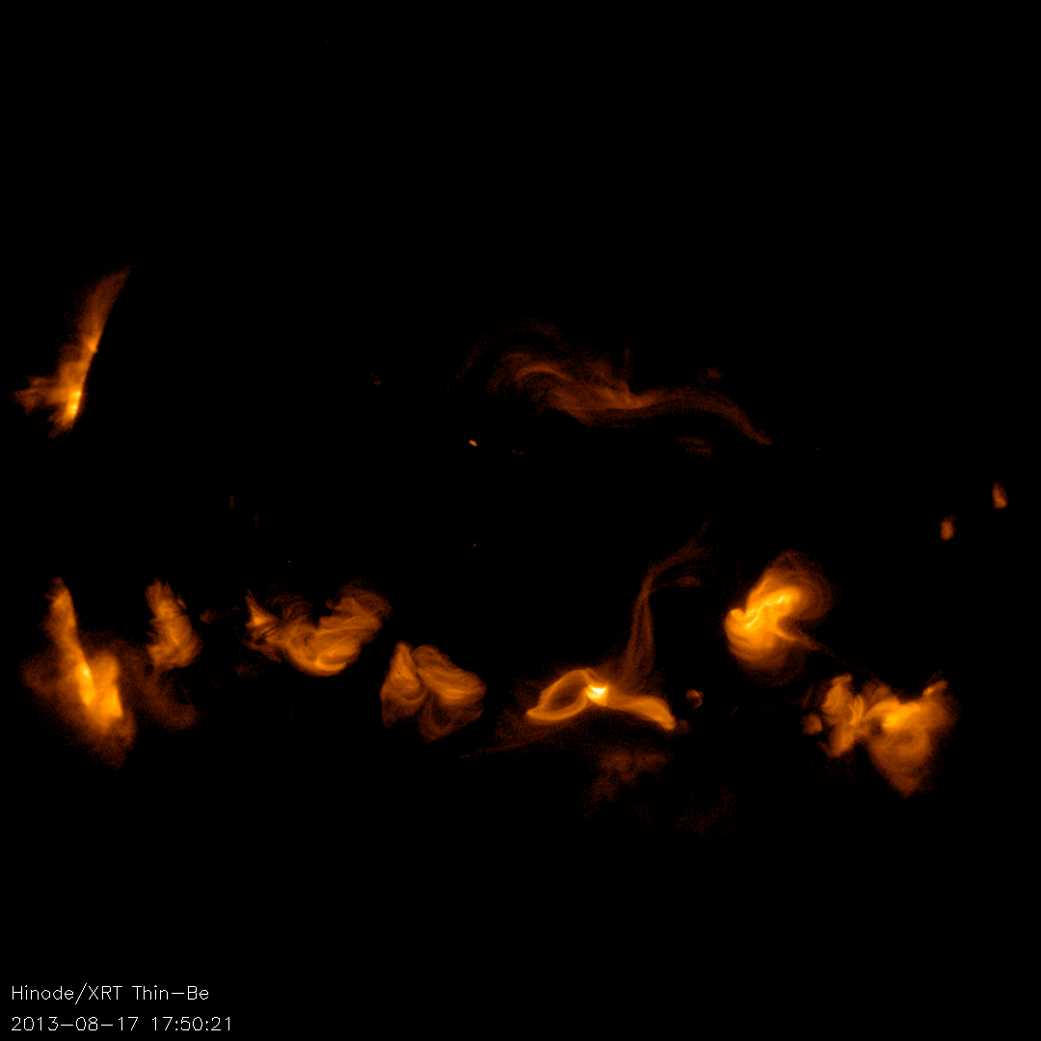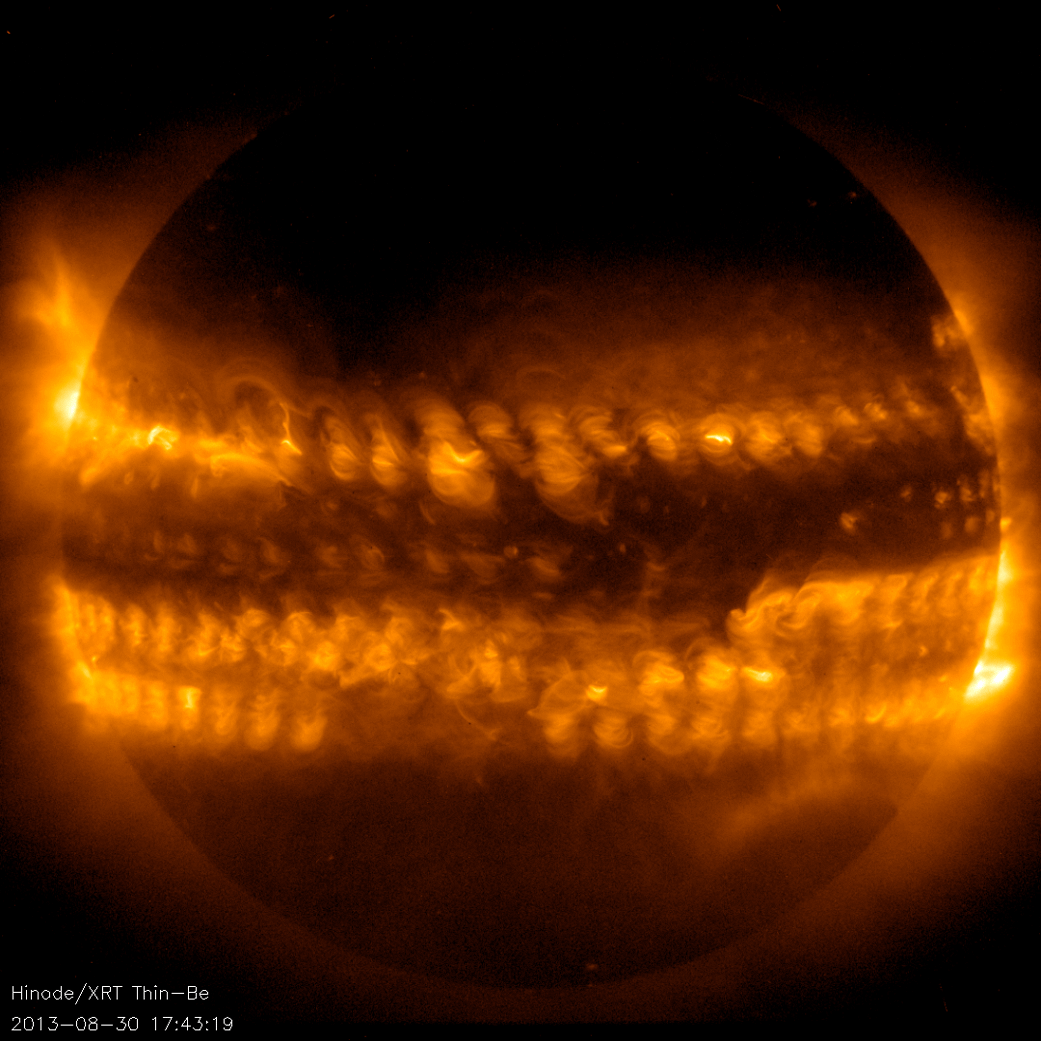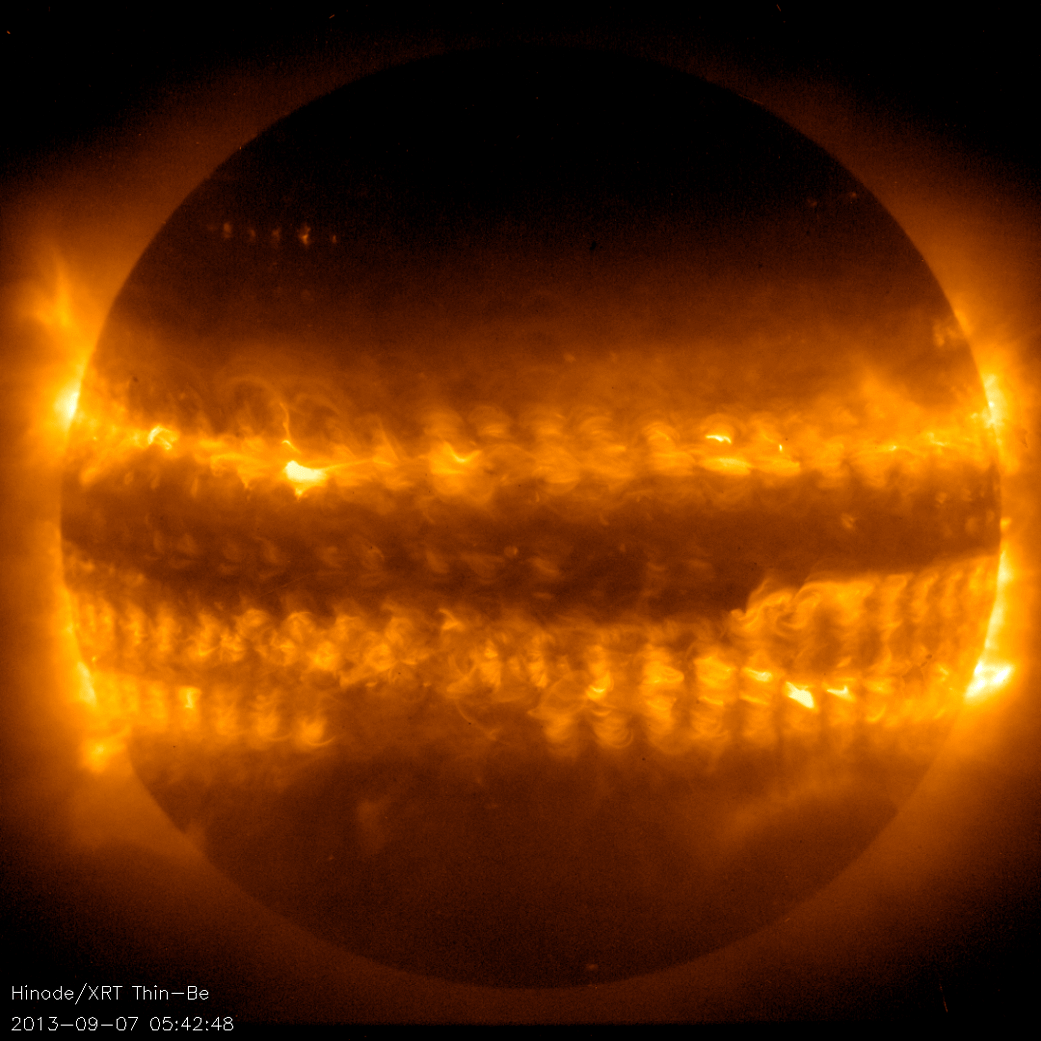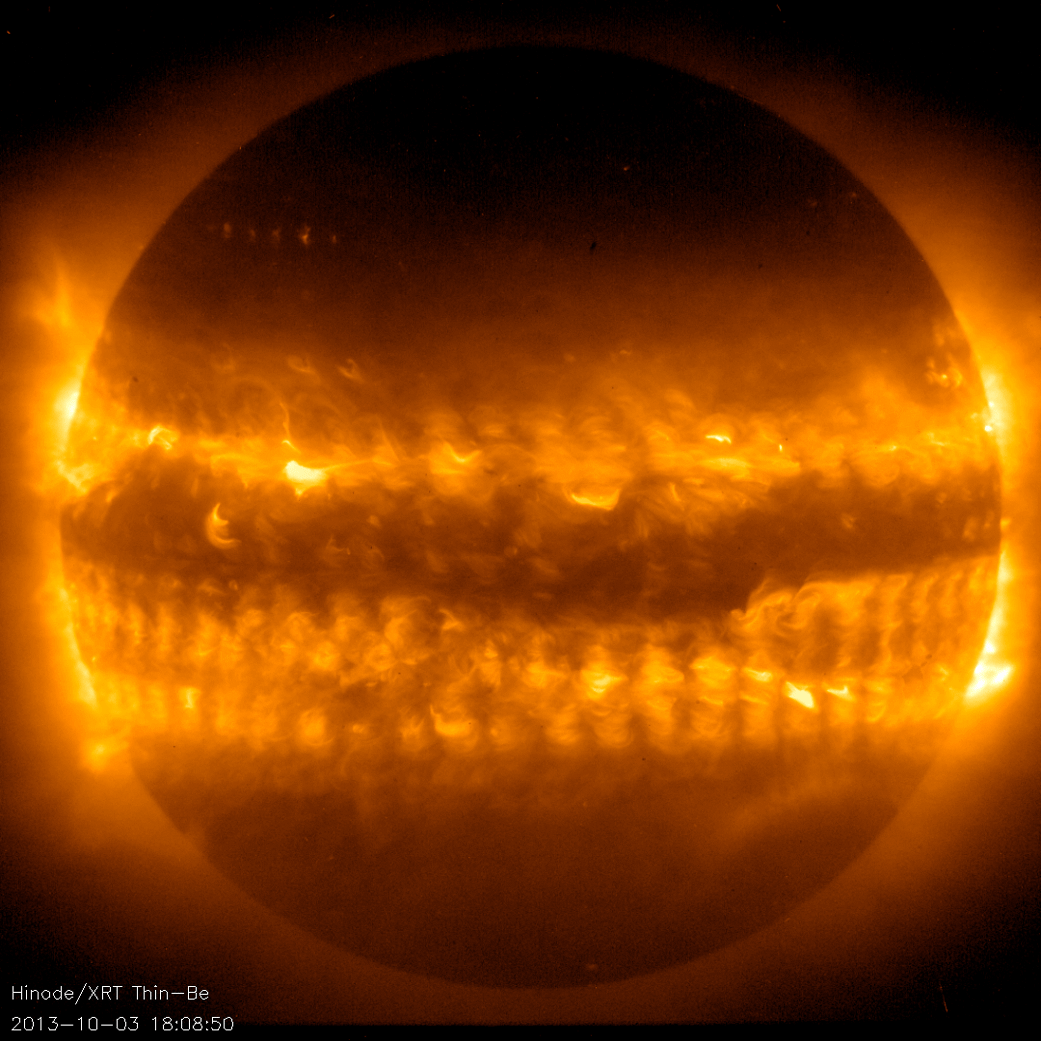
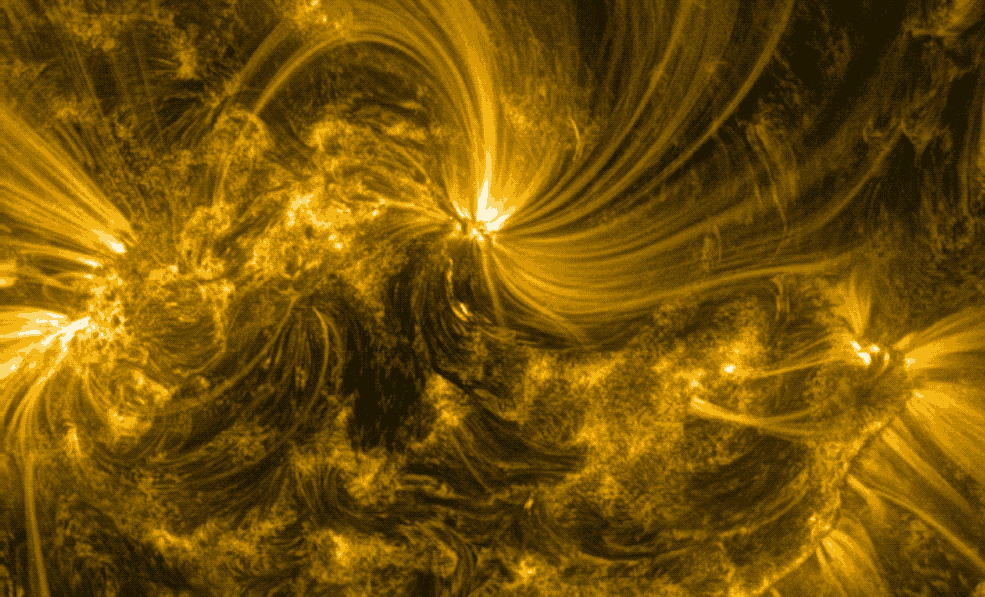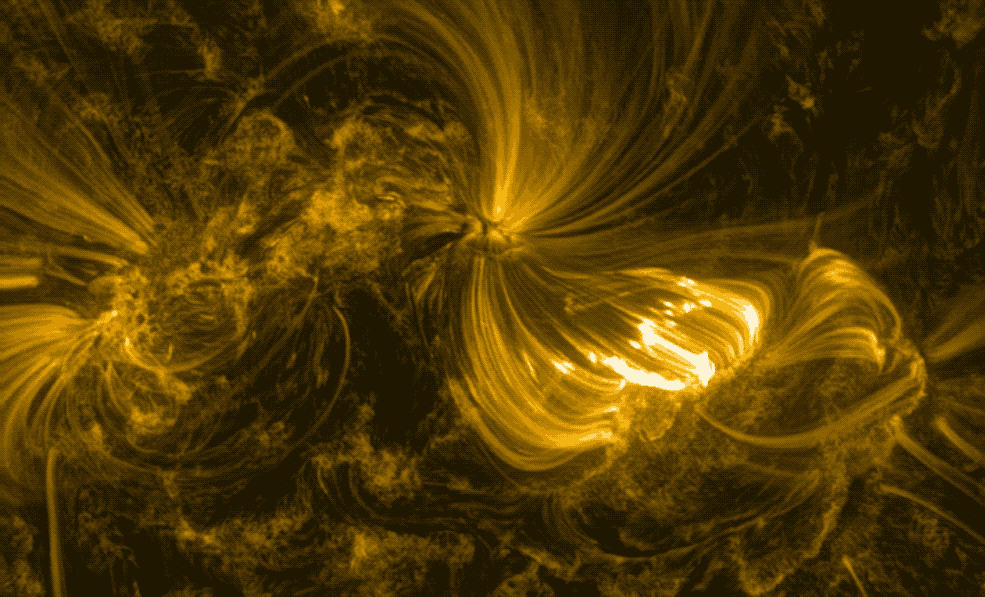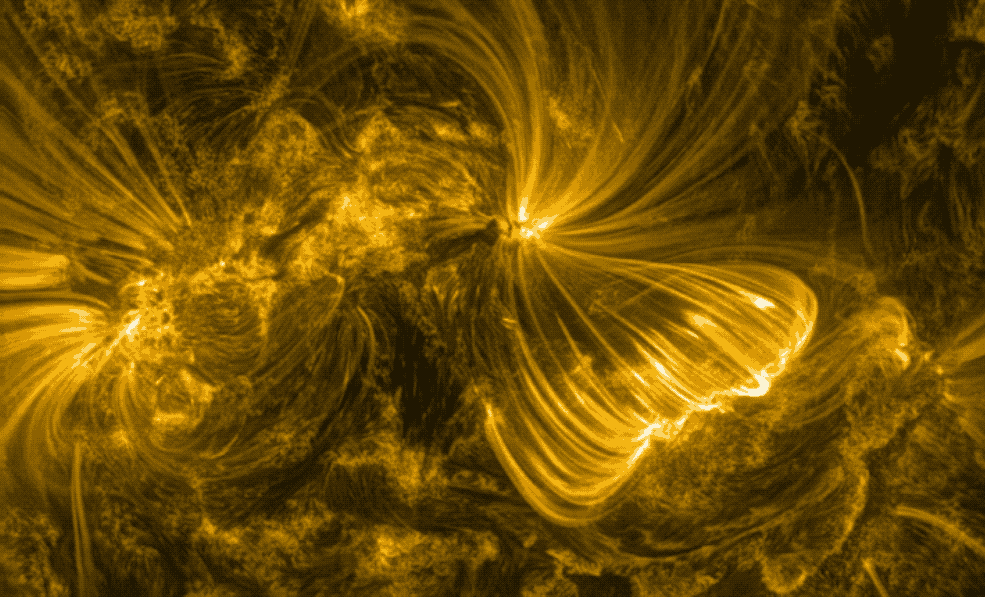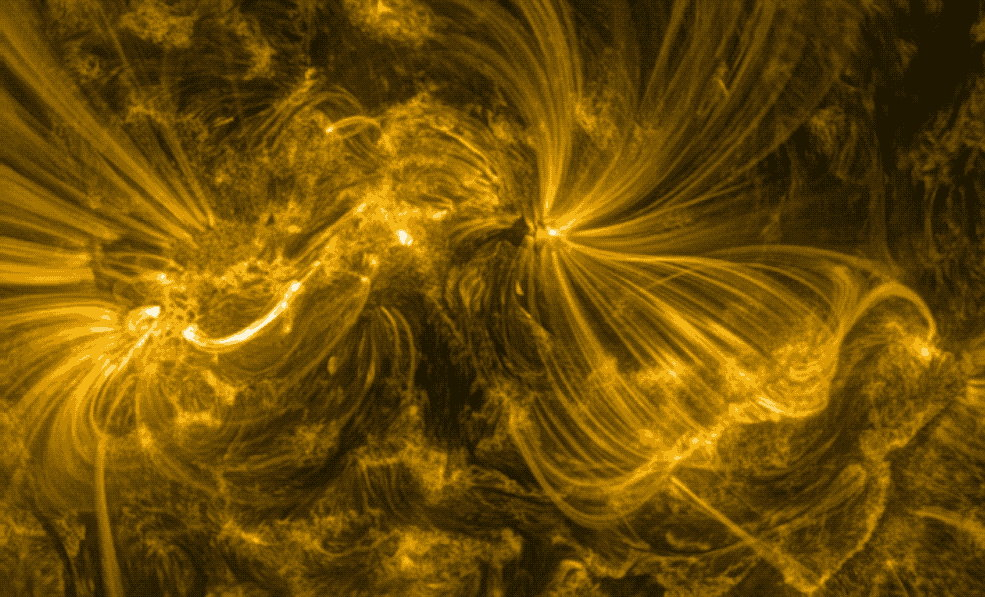
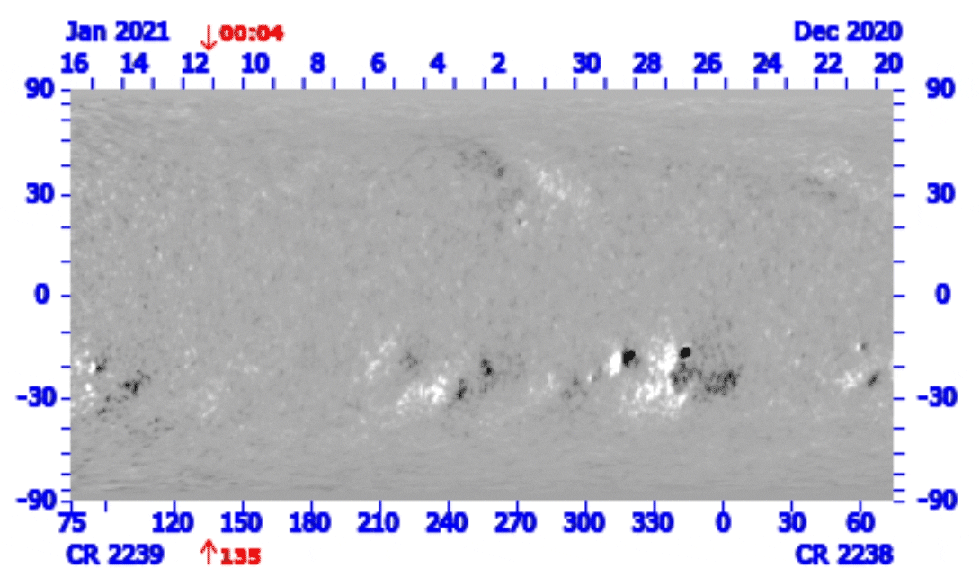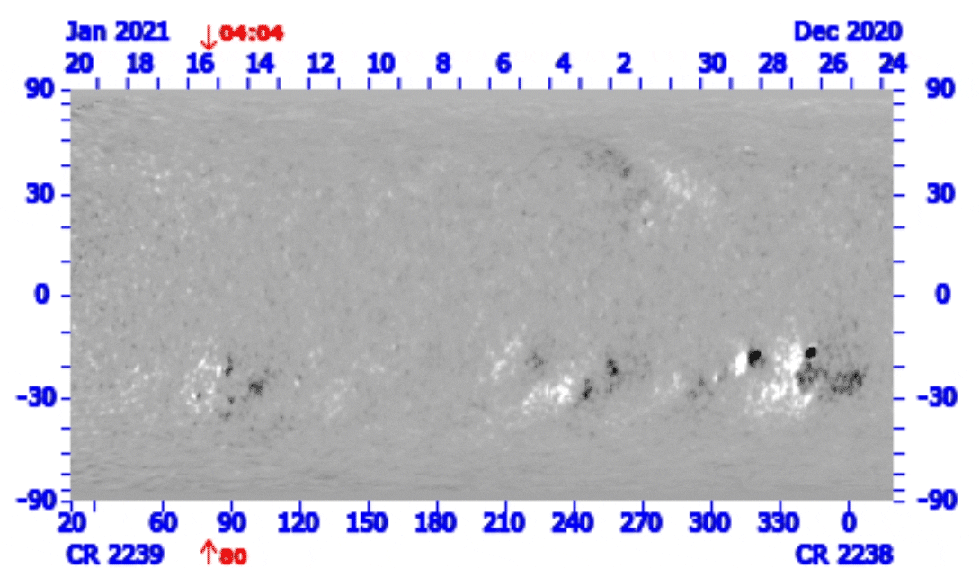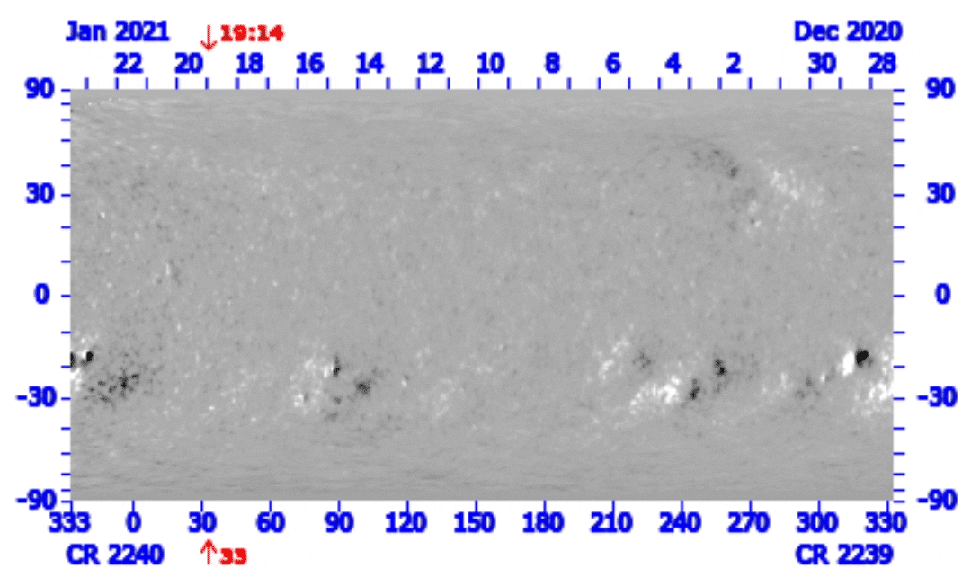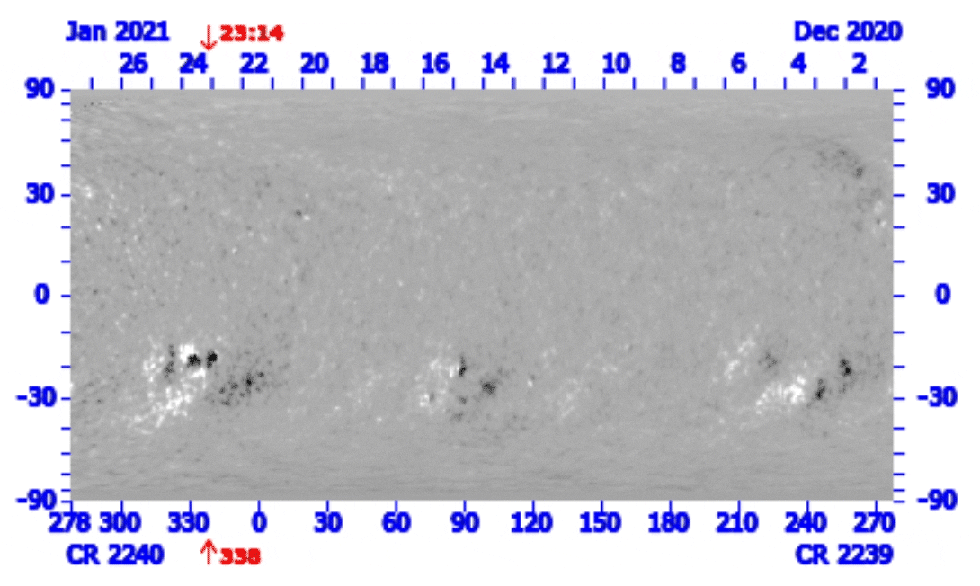
Hinode’s Solar Optical Telescope is the first space-borne instrument to measure the strength and direction of the Sun’s magnetic field on the Sun’s surface, the photosphere. Combined with two other Hinode instruments, the EUV imaging spectrometer, or EIS, and the X-ray/EUV telescope, or XRT, the mission is designed to understand the causes of eruptions in the solar atmosphere and relate those eruptions to the intense heating of the corona and the mechanisms that drive the constant outflow of solar radiation, the solar wind.
Hinode (Solar-B) Stories
Hinode Images
18 Images
1 Video