Over the years disposable and rechargeable batteries for electronics have made life easier for millions of consumers, running everything from smoke detectors to digital cameras to computer laptops.
Hubble’s Rechargeable Batteries
The famed Hubble Space Telescope relies on specially formulated rechargeable batteries that provide power to the telescope’s science instruments and critical components during each night orbit.
During Hubble’s sunlight (or daytime) orbit, its solar arrays provide power to the electrical components and charge the batteries so they have enough power to support Hubble during its night orbit. Since Hubble spends about one third of its 97 minute orbit around the Earth “in the dark” it must rely on the energy that is stored in its onboard batteries to supply power to the entire telescope.
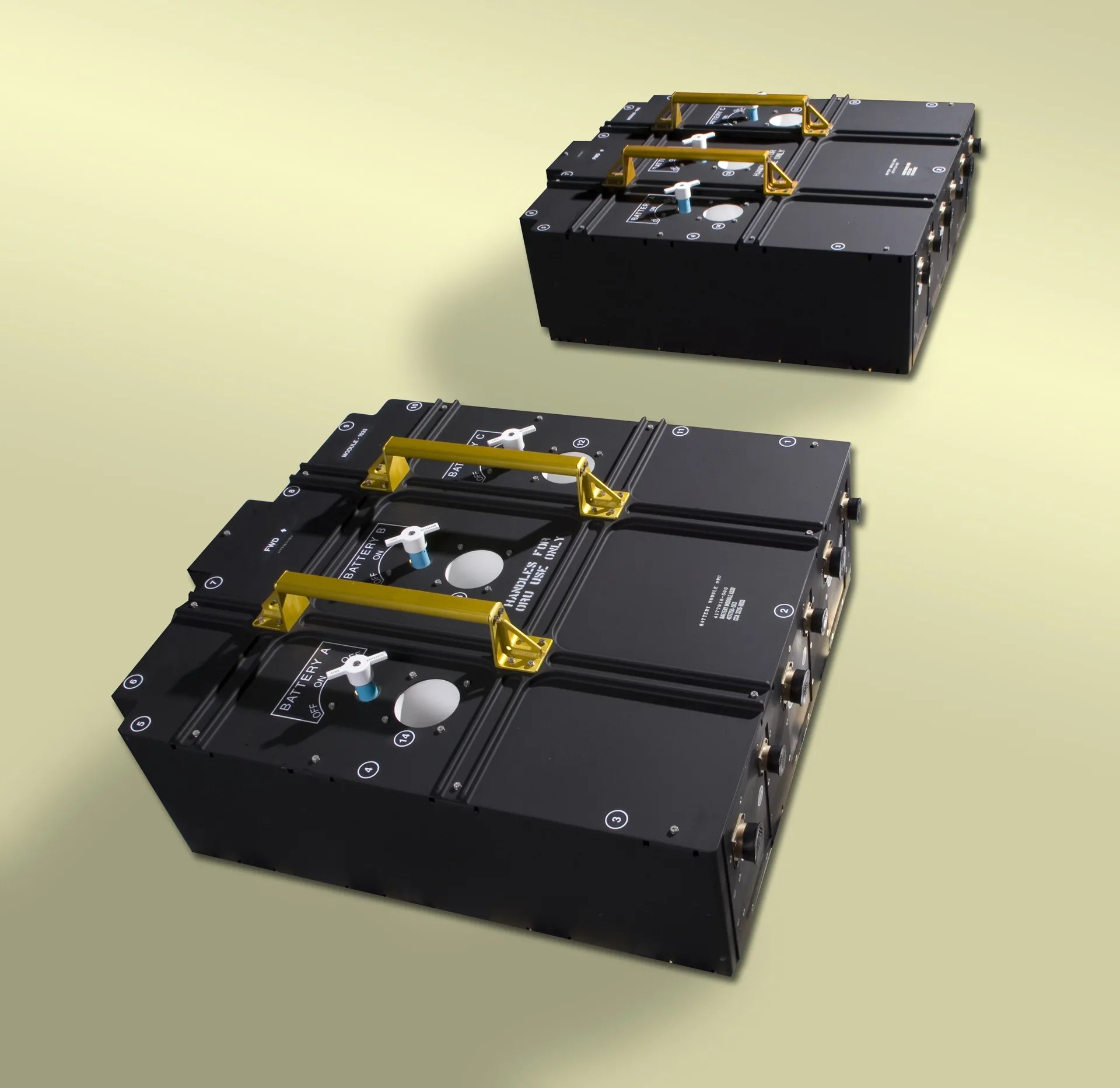
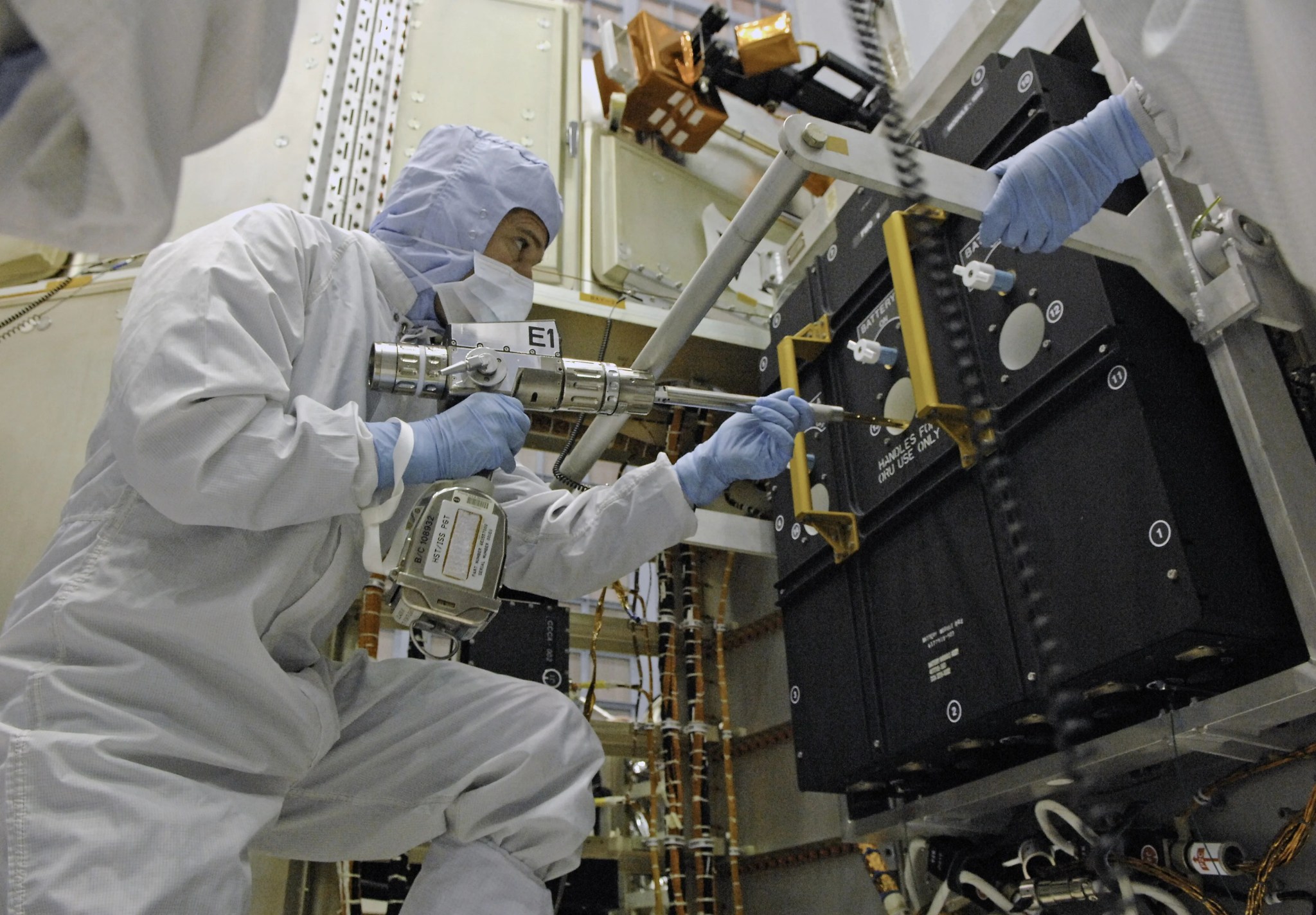
This image shows a close up of the two nickel hydrogen battery modules, containing three batteries each, destined for Hubble.
Credit:
NASA
For Hubble - Bigger Batteries are Better
The six, 125-lb nickel hydrogen batteries on Hubble have provided electrical power to the telescope during its night orbit since the telescope launched in 1990. That means they have been operating for more than 18 years and counting. How is this possible?
Engineers on the ground carefully manage the charging of Hubble’s batteries, enabling the spacecraft to function efficiently during the entire orbit. “Hubble’s batteries have far exceeded our expectations,” said Mike Weiss, Hubble’s Deputy Program Manager at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. “They have made possible all of the improvements we have made to Hubble over the course of four servicing missions. On SM4, after 18 years of remarkable performance, the time has finally come to renew Hubble’s lease on life with new batteries.”
Unlike a small digital camera battery that weighs only a few ounces, Hubble’s batteries are much larger and heavier. Collectively they weigh 460 pounds and measure 36 inches long, 32 inches wide, and 11 inches high.
A battery’s ability to store energy and supply this energy over time is measured in terms of battery storage capacity. Engineers measure such capacity in terms of ampere-hours or amp-hours. Each Hubble battery begins its life in space with about 75 amp-hours of capacity. By comparison, the typical modern digital camera battery has about 1 amp-hour of capacity. And while digital camera batteries deliver their power around 6 volts, Hubble’s power is delivered at 24 volts. This means Hubble batteries store about 2,000 times the amount of energy that is stored in a digital camera battery.
What Lies Ahead
Mission specialist Michael Good practices installing a battery module into the Hubble High Fidelity Mechanical Simulator, located in the cleanroom at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. Astronauts will install new batteries into the Hubble Space Telescope during SM4 in early 2009.
Credit:
NASA
The batteries on Hubble are original equipment. Not bad for components that were originally tagged with a five-year mission life. Their extended useful life is due largely to a team of electrical power system engineers at Goddard who constantly monitor the amount of current flowing into the batteries, along with their temperature during charging cycles. Small tweaks to the charging cycles are made when needed to ensure optimal performance.
However, due to normal aging and cycling, the telescope’s batteries are showing an expected slow loss in capacity, or their ability to hold a charge. So during the next Hubble servicing mission in 2009, astronauts will replace the existing batteries with new and improved ones that will enable Hubble to continue its amazing scientific journey for years to come.
Related link:
> Read the other stories in the "Next Stop: Hubble" series
Susan Hendrix
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center