2 min read


NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is back in business, ready to uncover new worlds, peer ever deeper into space, and even map the invisible backbone of the universe.
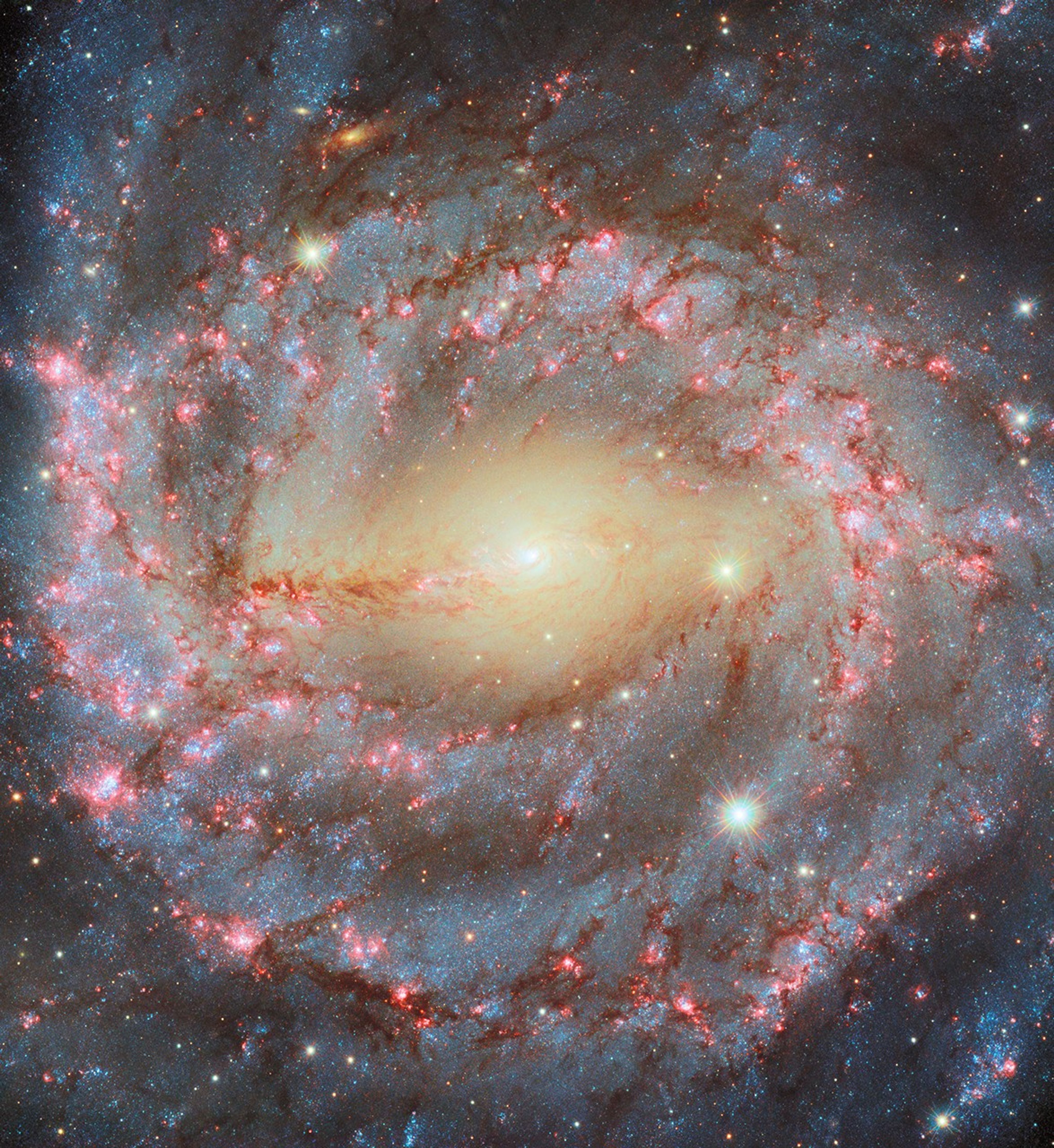
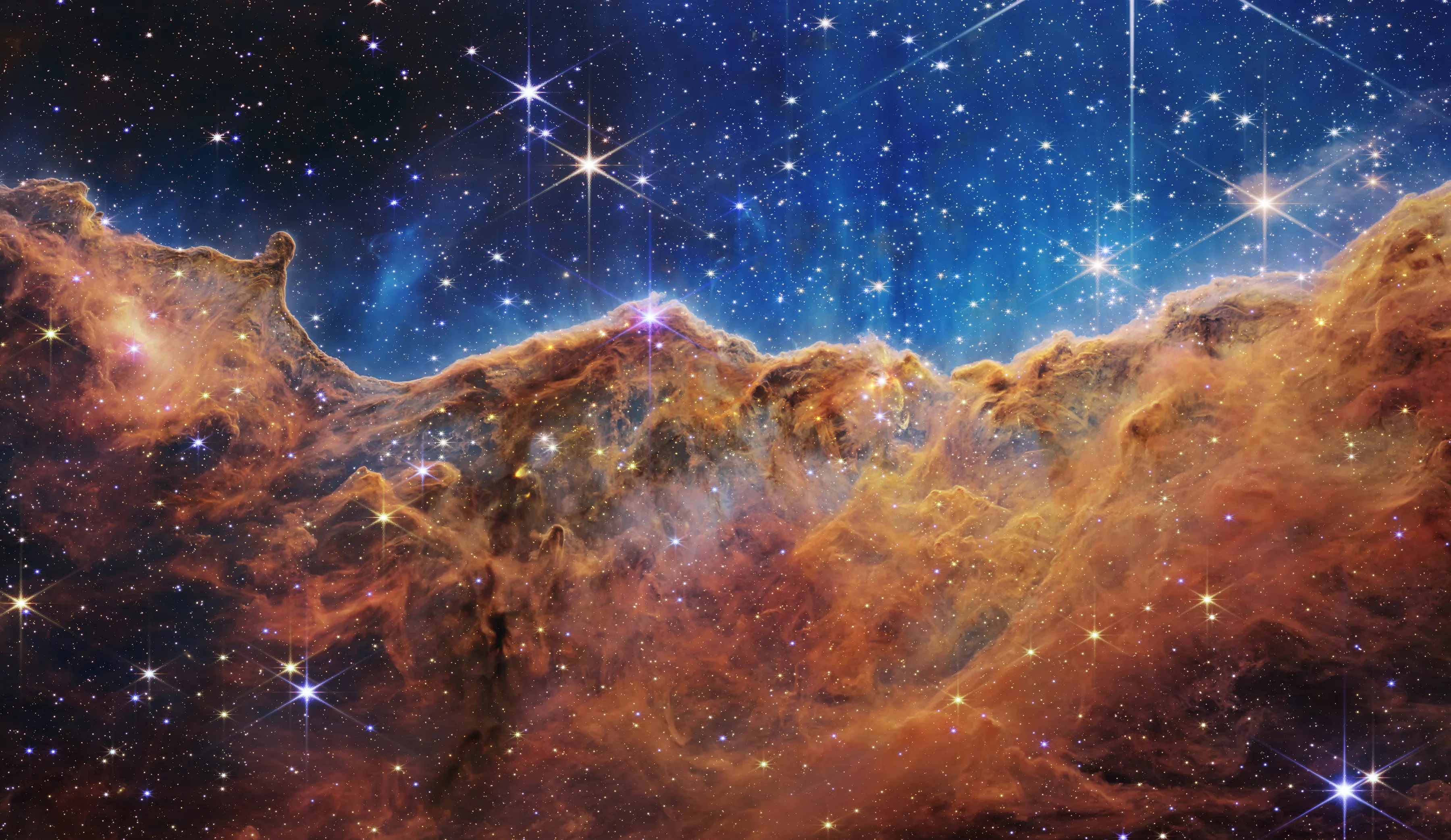
The first snapshots from the refurbished Hubble showcase the 19-year-old telescope's new vision. Topping the list of exciting new views are colorful multi-wavelength pictures of far- flung galaxies, a densely packed star cluster, an eerie "pillar of creation," and a "butterfly"nebula.
With the release of these images, astronomers have declared Hubble a fully rejuvenated observatory. Sen. Barbara A. Mikulski, D-Md., unveiled the images at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C., on Sept. 9, 2009.
With its new imaging camera, Hubble can view galaxies, star clusters, and other objects across a wide swath of the electromagnetic spectrum, from ultraviolet to near-infrared light. A new spectrograph slices across billions of light-years to map the filamentary structure of the universe and trace the distribution of elements that are fundamental to life.
The telescope's new instruments also are more sensitive to light and can observe in ways that are significantly more efficient and require less observing time than previous generations of Hubble instruments.
NASA astronauts installed the new instruments during the space shuttle servicing mission in May 2009. Besides adding the instruments, the astronauts also completed a dizzying list of other chores that included performing unprecedented repairs on two other science instruments.
Now that Hubble has reopened for business, it will tackle a whole range of observations. Looking closer to Earth, such observations will include taking a census of the population of Kuiper Belt objects residing at the fringe of our solar system, witnessing the birth of planets around other stars, and probing the composition and structure of the atmospheres of other worlds.
Peering much farther away, astronomers have ambitious plans to use Hubble to make the deepest-ever portrait of the universe in near-infrared light. The resulting picture may reveal never-before-seen infant galaxies that existed when the universe was less than 500 million years old. Hubble also is now significantly more well-equipped to probe and further characterize the behavior of dark energy, a mysterious and little-understood repulsive force that is pushing the universe apart at an ever-faster rate.
Related Links:
Space Telescope Science Institute
Baltimore, MD







