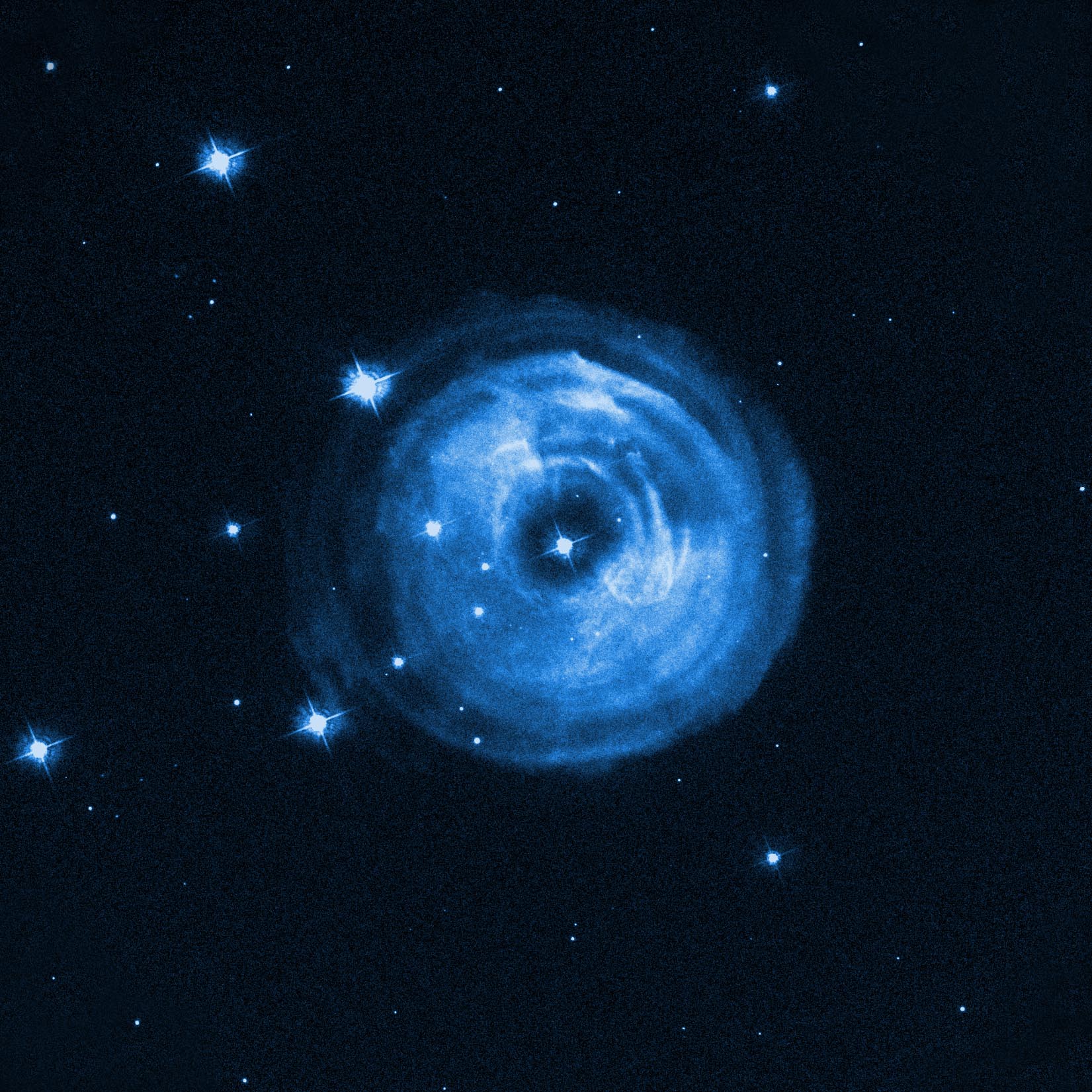
In January 2002, a dull star in an obscure constellation suddenly became 600,000 times more luminous than our sun, temporarily making it the brightest star in our Milky Way galaxy. The mysterious star has long since faded back to obscurity, but observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope of a phenomenon called a "light echo" have uncovered remarkable new features. These details promise to provide astronomers with a CAT-scan-like probe of the three-dimensional structure of shells of dust surrounding an aging star.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA and H.E. Bond (STScI)