NASA’s LRO (Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter) has twice transmitted a laser pulse to a cookie-sized retroreflector aboard JAXA’s (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) SLIM lander on the Moon and received a return signal.
As LRO passed 44 miles above SLIM (Smart Lander for Investigating Moon) during two successive orbits on May 24, 2024, it pinged the lander with its laser altimeter instrument as it had done eight times before. But, on these two attempts, the signal bounced back to LRO’s detector.
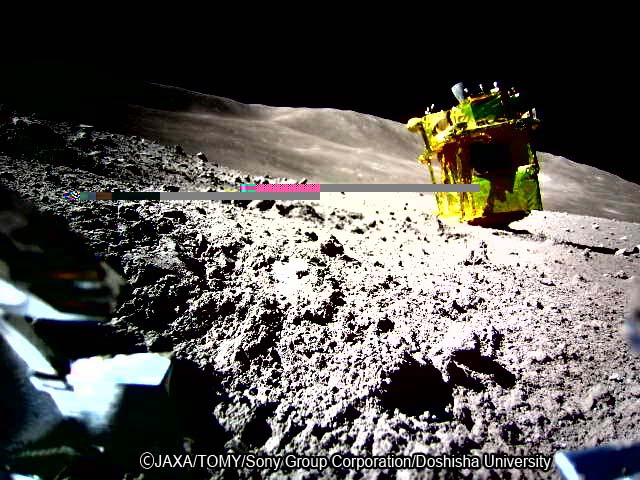
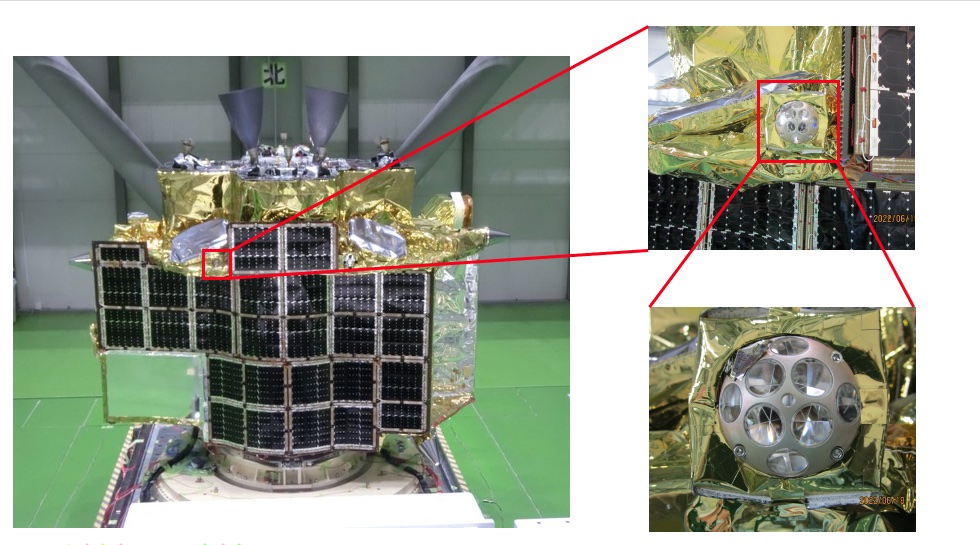
This was an important accomplishment for NASA because the device is not in an optimal position. Retroreflectors are typically secured to the top of landers, giving LRO a 120-degree range of angles to aim toward when sending laser pulses to the approximate location of a retroreflector. However, the SLIM lander had settled on the surface with its top facing sideways, limiting LRO’s range.
To boost the chances of reaching their target, the LRO team worked with JAXA to determine the exact location and orientation of SLIM. Then, NASA engineers predicted when LRO’s orbit trajectory would bring it to coordinates that would give it the best chance of reaching SLIM’s retroreflector with the laser beams.
“LRO’s altimeter wasn’t built for this type of application, so the chances of pinpointing a tiny retroreflector on the Moon’s surface are already low,” said Xiaoli Sun, who led the team that built SLIM’s retroreflector at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, as part of a partnership between NASA and JAXA.
“For the LRO team to have reached a retroreflector that faces sideways, instead of the sky, shows that these little devices are incredibly resilient,” Sun said.
SLIM touched down on the Moon’s surface on Jan. 20. The retroreflector that hitched a ride with the lander, called a Laser Retroreflector Array, is one of the six NASA has sent to the Moon aboard private and public landers, and the second to bounce signal back to LRO’s altimeter.
The first time a laser beam was transmitted from LRO to a NASA retroreflector and back was on Dec. 12, 2023, when LRO pinged ISRO’s (Indian Space Research Organisation) Vikram lander. LRO has since exchanged laser pings with Vikram three more times.
NASA’s retroreflector has eight quartz corner-cube prisms set into a dome-shaped aluminum frame that is 2 inches wide. With no power or maintenance required, retroreflectors can last on the Moon’s surface for decades and thus provide reliable beacons for future missions.
The retroreflectors could guide Artemis astronauts to the surface in the dark, for example, or mark the locations of spacecraft already on the surface to help astronauts and uncrewed spacecraft land near them.
LRO’s laser altimeter, the only laser instrument orbiting the Moon for now, was designed to map the Moon’s topography to prepare for missions to the surface — not to point to within 1/100th of a degree of a retroreflector, which is what LRO engineers are trying to do with every ping.
LRO is managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Launched on June 18, 2009, LRO has collected a treasure trove of data with its seven powerful instruments, making an invaluable contribution to our knowledge about the Moon. NASA is returning to the Moon with commercial and international partners to expand human presence in space and bring back new knowledge and opportunities.
By Lonnie Shekhtman
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media Contact:
Nancy Neal Jones
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.