Description
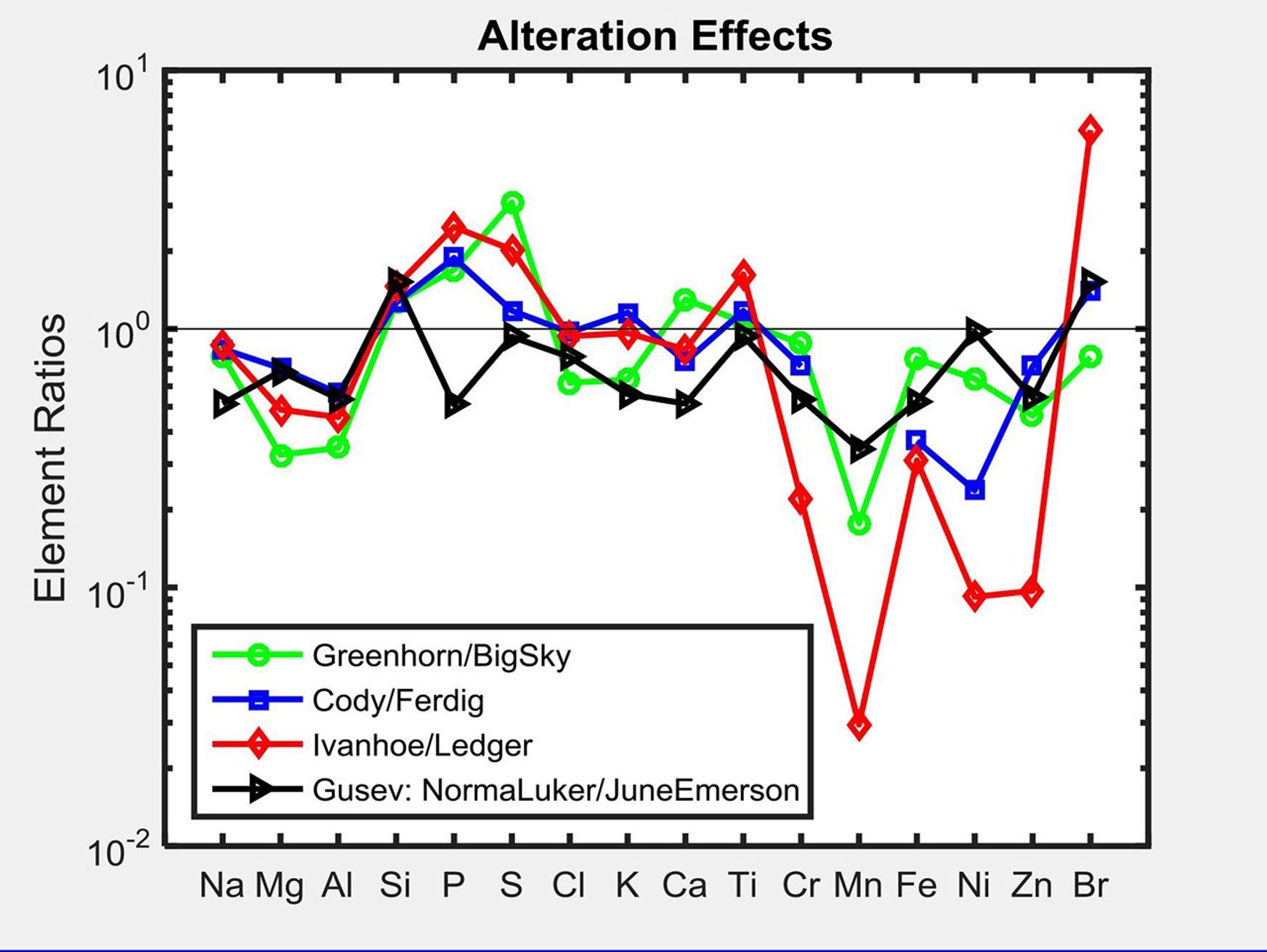
This graph shows the ratio of concentrations of several elements in four different pairs of targets examined by Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) instruments on NASA Mars rovers Curiosity and Spirit.
For each pair of targets, one shows evidence of mineral alteration and the other is an unaltered counterpart. The first three pairs (with ratios shown by green, blue and red lines) are targets in Gale Crater analyzed by Curiosity's APXS. The fourth pair (with ratio shown by the black line) is in Gusev Crater and was analyzed by Spirit's APXS.
Similar profiles are observed, suggesting the possibility of related formation processes. As with examples of silica enrichment found by Curiosity, the origin of high-silica nodular deposits found by Spirit also remains unresolved: Either acidic weathering or silica addition could be responsible. It is clear, however, that liquid water was involved in either alteration scenario.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed and built the project's Curiosity rover.
More information about Curiosity is online at http://www.nasa.gov/msl and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl/.