Atlas
Contents
Discovery
Atlas was discovered in 1980 by R. Terrile and the Voyager 1 team from photographs taken during its encounter with Saturn.
Overview
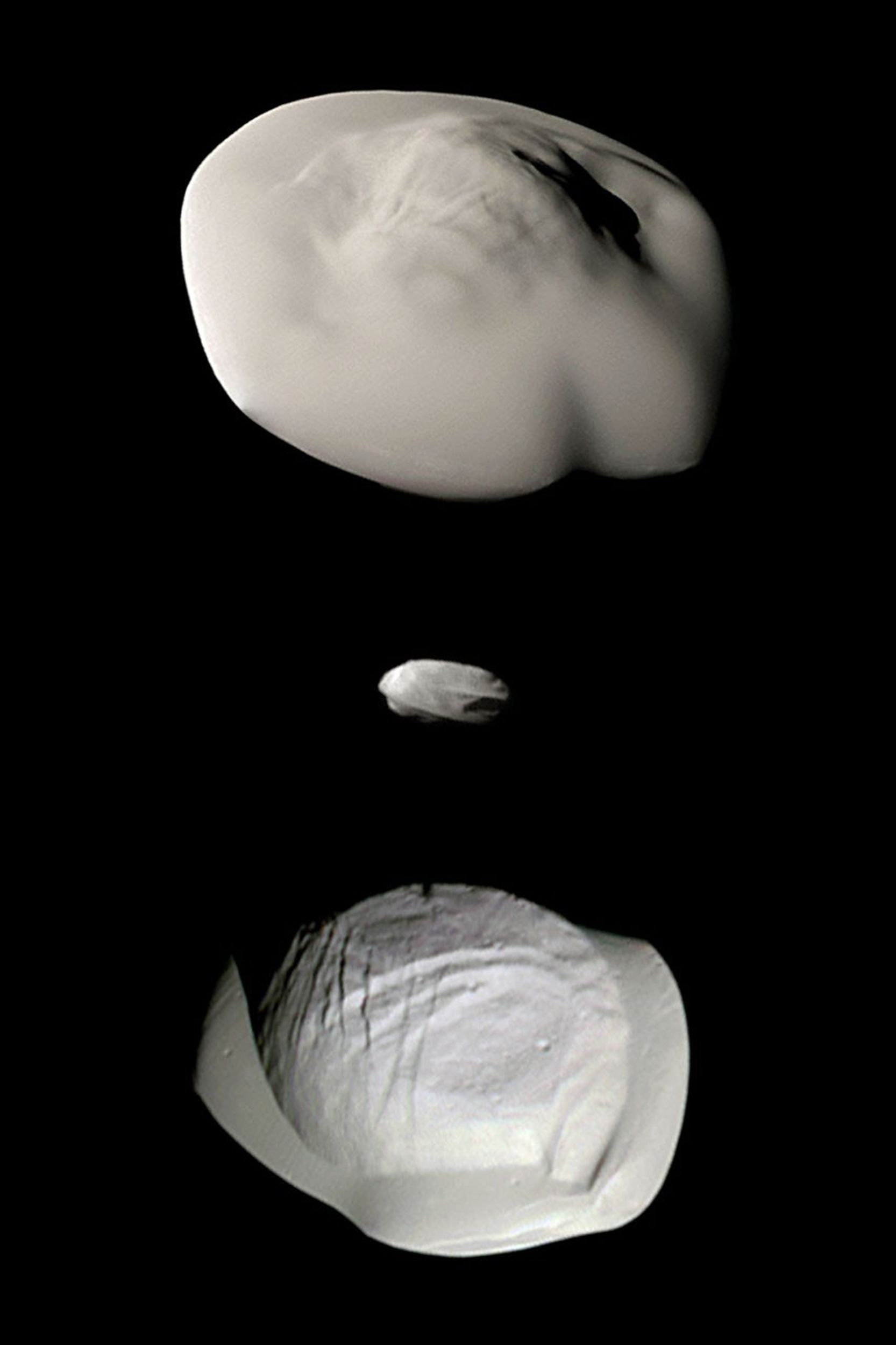
Atlas is an inner moon of Saturn, orbiting around the outer edge of Saturn's A Ring. Like Pan, Atlas has a distinctive flying saucer shape created by a prominent equatorial ridge not seen on the other small moons of Saturn. Cassini images revealed in 2004 that a temporary faint ring of material with the orbit of Atlas.
The small, pointy moon has a mean radius of 9.4 miles (15.1 km). It orbits 85,544 miles (137,670 km) away from, taking 14.4 hours to complete its trip around the planet.
How Atlas Got its Name
Moons of Saturn were originally named for Greco-Roman Titans and descendants of the Titans. But as many new moons were discovered, scientists began selecting names from more mythologies including Gallic, Inuit, and Norse stories.
Originally designated S/1980 S28, this moon is named after Atlas, a Titan, and a son of Iapetus. Atlas was ordered by Zeus to uphold the vault of the sky after the defeat of the Titans. Atlas was so strong that he supported the weight of the Universe on his shoulders.