Editor’s Note, Feb. 25, 2025: The LEXI telescope was turned on successfully shortly after launch on Jan. 16. The instrument has operated for several hours every day conducting checkouts and initial commissioning, operating for a total of more than 50 hours so far in preparations for collecting images from the lunar surface.
During transit to the Moon, LEXI’s optics and detector are covered with a closed door to protect the instrument from dust and debris during lunar landing. This also enables LEXI to take dark images to measure detector backgrounds prior to operation on the lunar surface.
A NASA X-ray imager is heading to the Moon as part of NASA's Artemis campaign, where it will capture the first global images of the magnetic field that shields Earth from solar radiation.
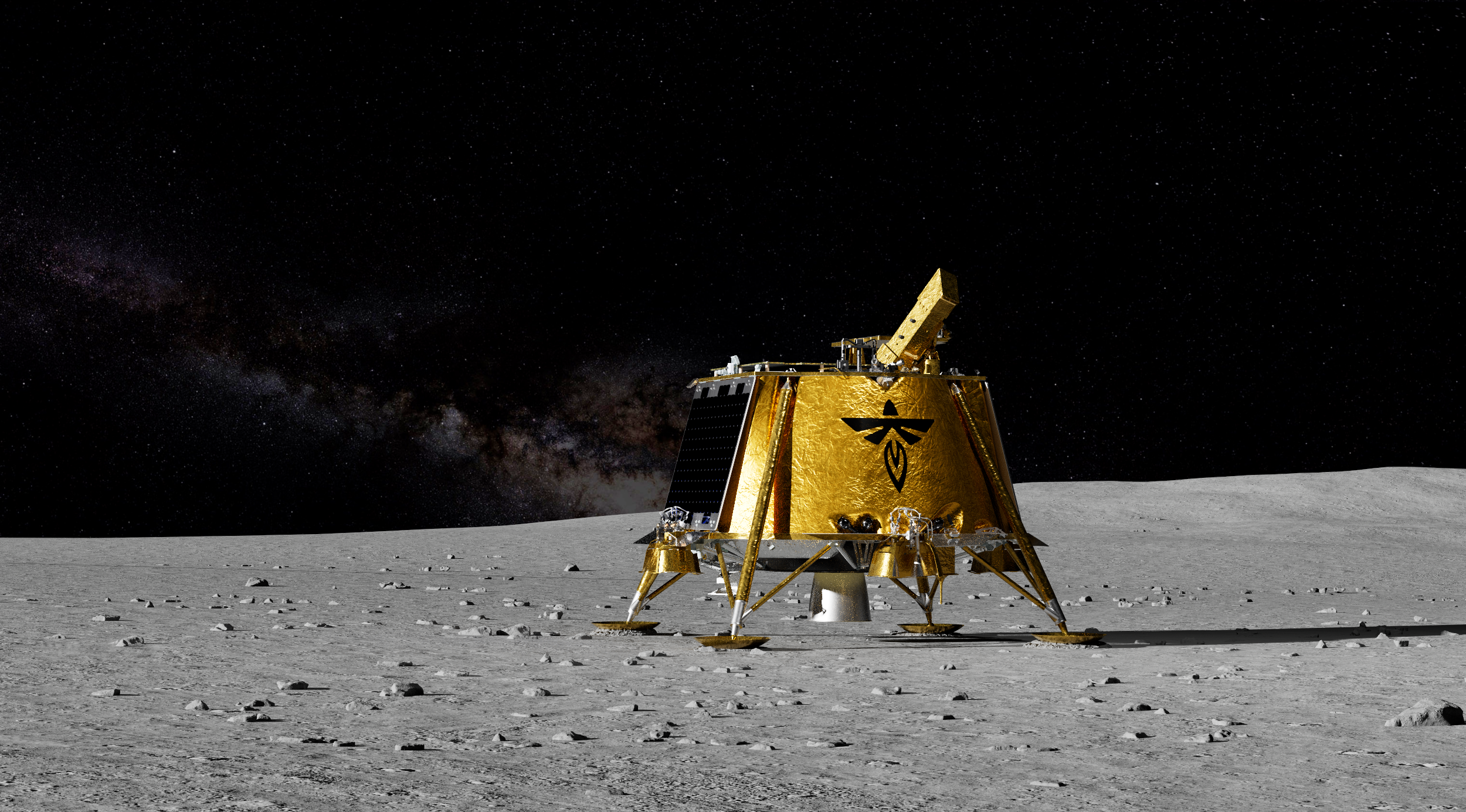
The Lunar Environment Heliospheric X-ray Imager, or LEXI, instrument is one of 10 payloads aboard the next lunar delivery through NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, set to launch from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida no earlier than mid-January, with Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Lander. The instrument will support NASA’s goal to understand how our home planet responds to space weather, the conditions in space driven by the Sun.
Credits: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Once the dust clears from its lunar landing, LEXI will power on, warm up, and direct its focus back toward Earth. For six days, it will collect images of the X-rays emanating from the edges of our planet’s vast magnetosphere. This comprehensive view could illustrate how this protective boundary responds to space weather and other cosmic forces, as well as how it can open to allow streams of charged solar particles in, creating aurora and potentially damaging infrastructure.
“We’re trying to get this big picture of Earth’s space environment,” said Brian Walsh, a space physicist at Boston University and LEXI’s principal investigator. “A lot of physics can be esoteric or difficult to follow without years of specific training, but this will be science that you can see.”
What LEXI will see is the low-energy X-rays that form when a stream of particles from the Sun, called the solar wind, slams into Earth’s magnetic field. This happens at the edge of the magnetosphere, called the magnetopause. Researchers have recently been able to detect these X-rays in a patchwork of observations from other satellites and instruments. From the vantage point of the Moon, however, the whole magnetopause will be in LEXI’s field of view.
The team back on Earth will be working around the clock to track how the magnetosphere expands, contracts, and changes shape in response to the strength of the solar wind.
“We expect to see the magnetosphere breathing out and breathing in, for the first time,” said Hyunju Connor, an astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and the NASA lead for LEXI. “When the solar wind is very strong, the magnetosphere will shrink and push backward toward Earth, and then expand when the solar wind weakens.”
The LEXI instrument will also be poised to capture magnetic reconnection, which is when the magnetosphere’s field lines merge with those in the solar wind and release energetic particles that rain down on Earth’s poles. This could help researchers answer lingering questions about these events, including whether they happen at multiple sites simultaneously, whether they occur steadily or in bursts, and more.
These solar particles streaming into Earth’s atmosphere can cause brilliant auroras, but they can also damage satellites orbiting the planet or interfere with power grids on the ground.
“We want to understand how nature behaves,” Connor said, “and by understanding this we can help protect our infrastructure in space.”
The CLPS delivery won’t be LEXI’s first trip to space. A team at Goddard, including Walsh, built the instrument (then called STORM) to test technology to detect low-energy X-rays over a wide field of view. In 2012, STORM launched into space on a sounding rocket, collected X-ray images, and then fell back to Earth.
It ended up in a display case at Goddard, where it sat for a decade. When NASA put out a call for CLPS projects that could be done quickly and with a limited budget, Walsh thought of the instrument and the potential for what it could see from the lunar surface.
“We’d break the glass — not literally — but remove it, restore it, and refurbish it, and that would allow us to look back and get this global picture that we’ve never had before,” he said. Some old optics and other components were replaced, but the instrument was overall in good shape and is now ready to fly again. “There’s a lot of really rich science we can get from this.”
Under the CLPS model, NASA is investing in commercial delivery services to the Moon to enable industry growth and support long-term lunar exploration. As a primary customer for CLPS deliveries, NASA aims to be one of many customers on future flights. NASA Goddard is a lead science collaborator on LEXI. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development of seven of the 10 CLPS payloads carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander, including LEXI.
Learn more about CLPS and Artemis at:
https://www.nasa.gov/clps
By Kate Ramsayer
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.