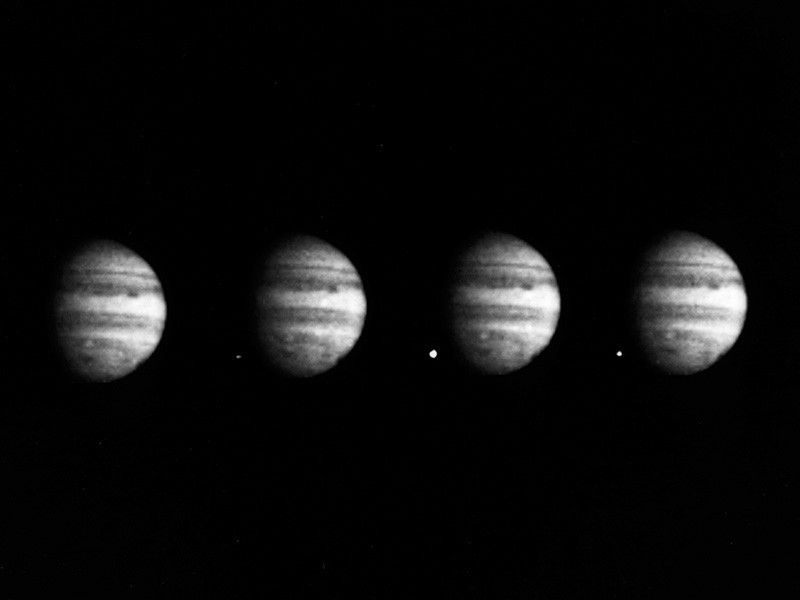
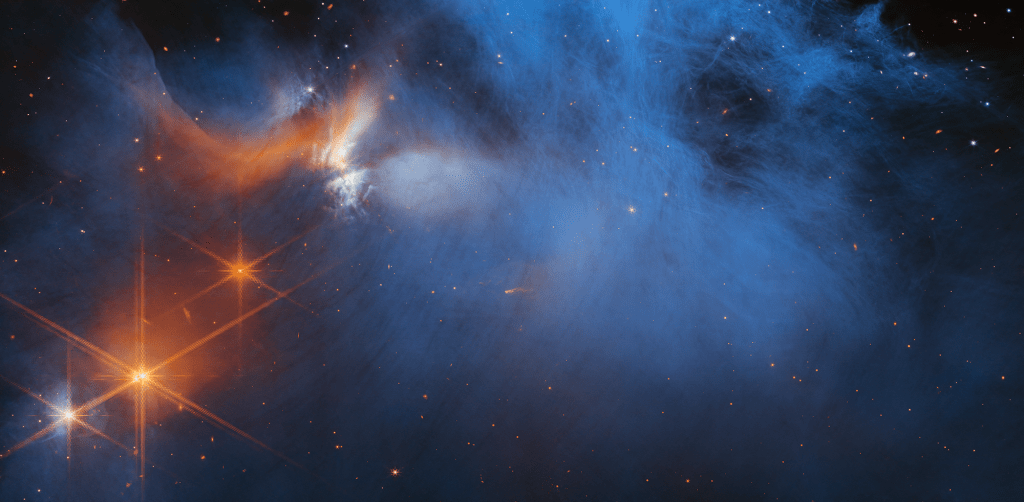
Overview
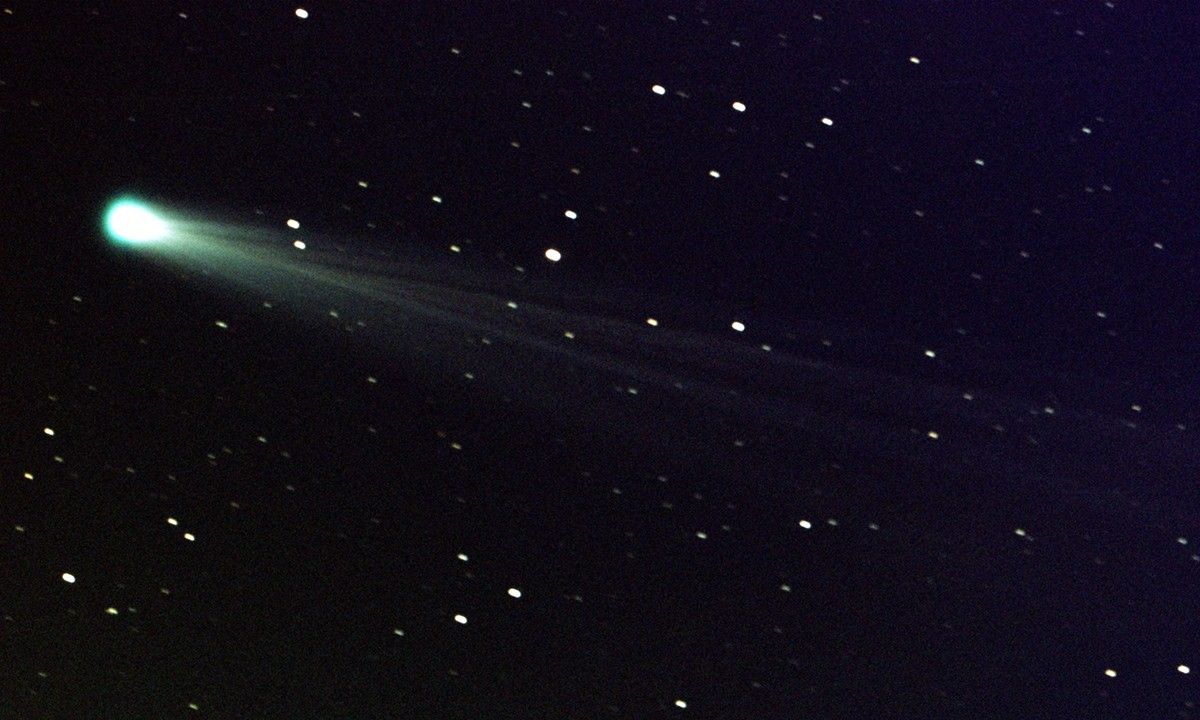
Comets are frozen leftovers from the formation of the solar system composed of dust, rock, and ices. They range from a few miles to tens of miles wide, but as they orbit closer to the Sun, they heat up and spew gases and dust into a glowing head that can be larger than a planet. This material forms a tail that stretches millions of miles.
Comets are cosmic snowballs of frozen gases, rock, and dust that orbit the Sun. When frozen, they are the size of a small town. When a comet's orbit brings it close to the Sun, it heats up and spews dust and gases into a giant glowing head larger than most planets. The dust and gases form a tail that stretches away from the Sun for millions of miles. There are likely billions of comets orbiting our Sun in the Kuiper Belt and even more distant Oort Cloud.
NASA Researchers Discover More Dark Comets
These celestial objects look like asteroids but act like comets now come in two flavors. The first dark comet —…
Read the Story
Featured Comets

Comet 103P/Hartley (Hartley 2)

109P/Swift-Tuttle
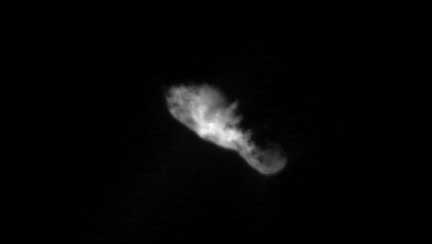
Comet 19P/Borrelly

1P/Halley
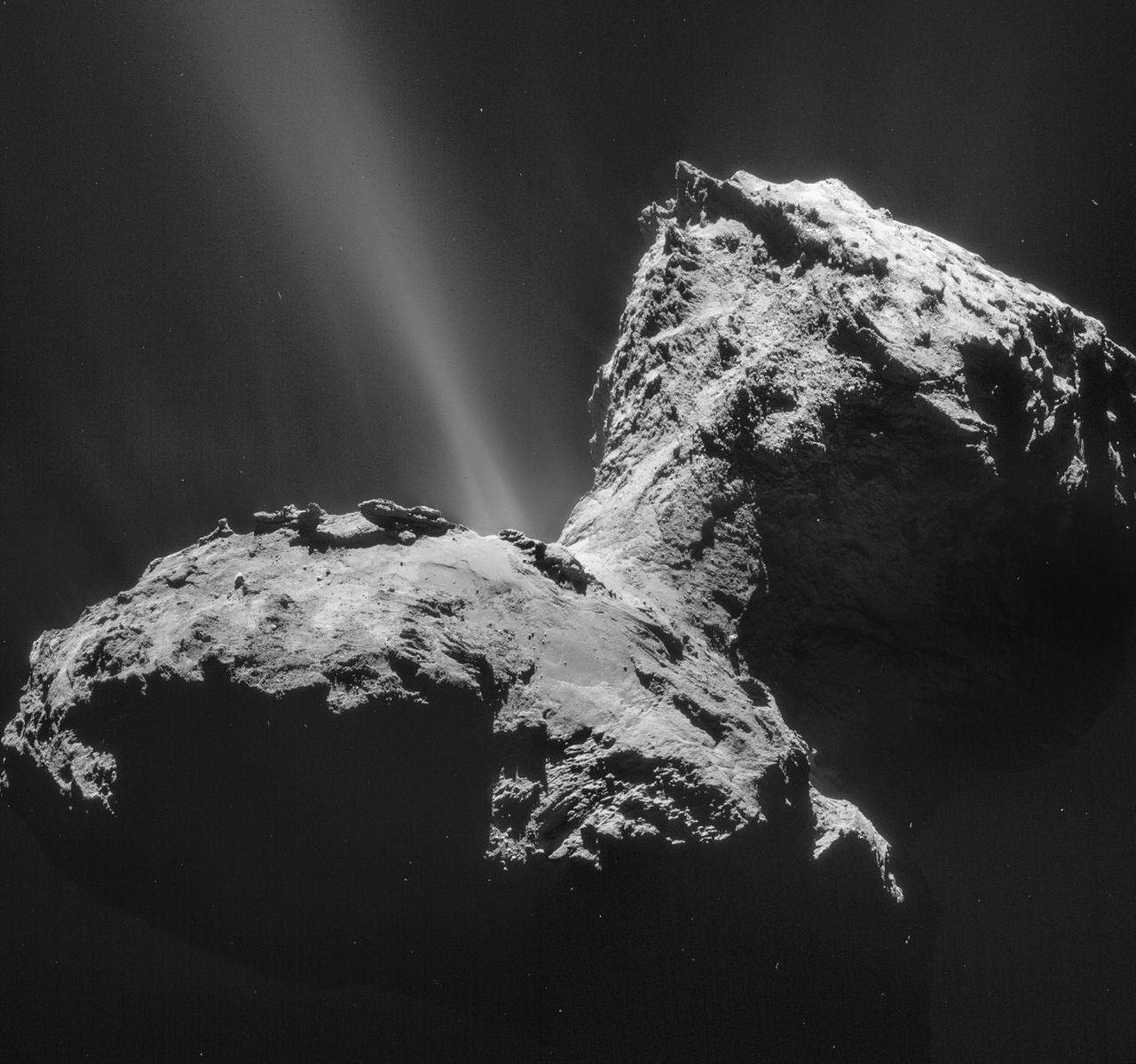

67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko
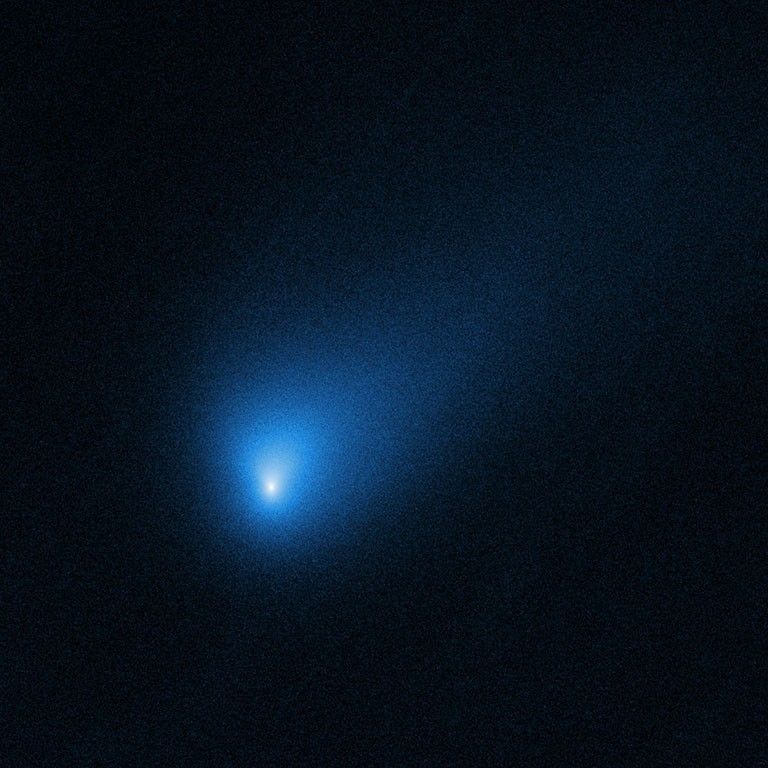

Comet 2I/Borisov
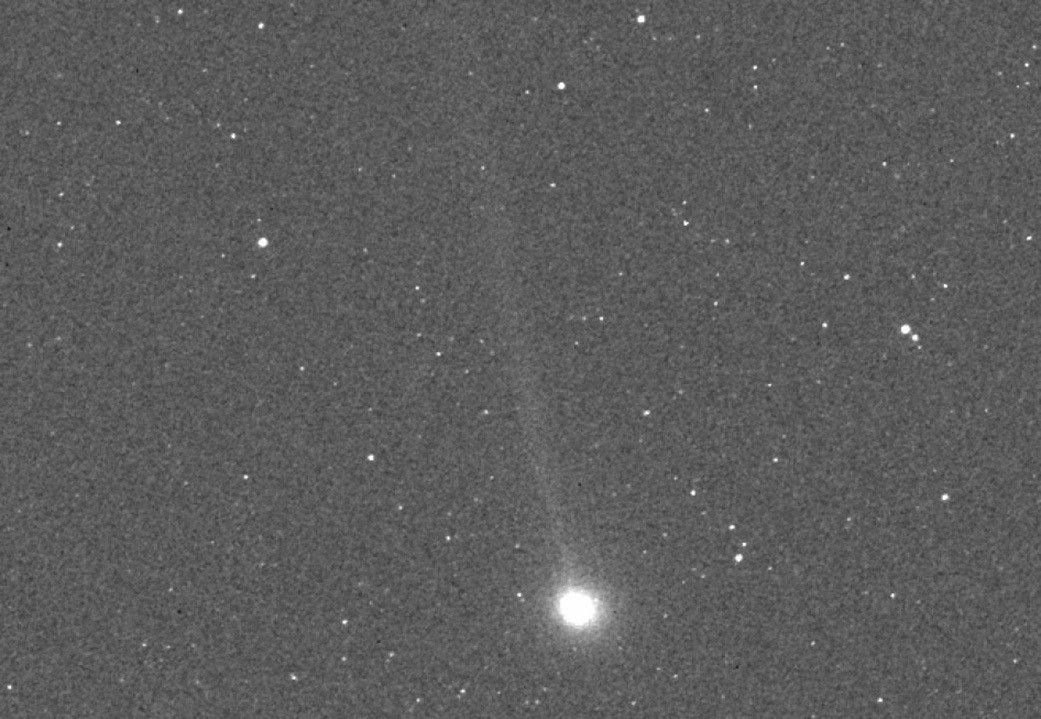

2P/Encke
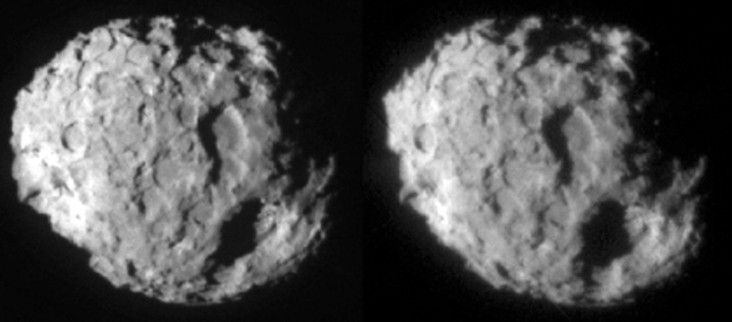
81P/Wild (Wild 2)
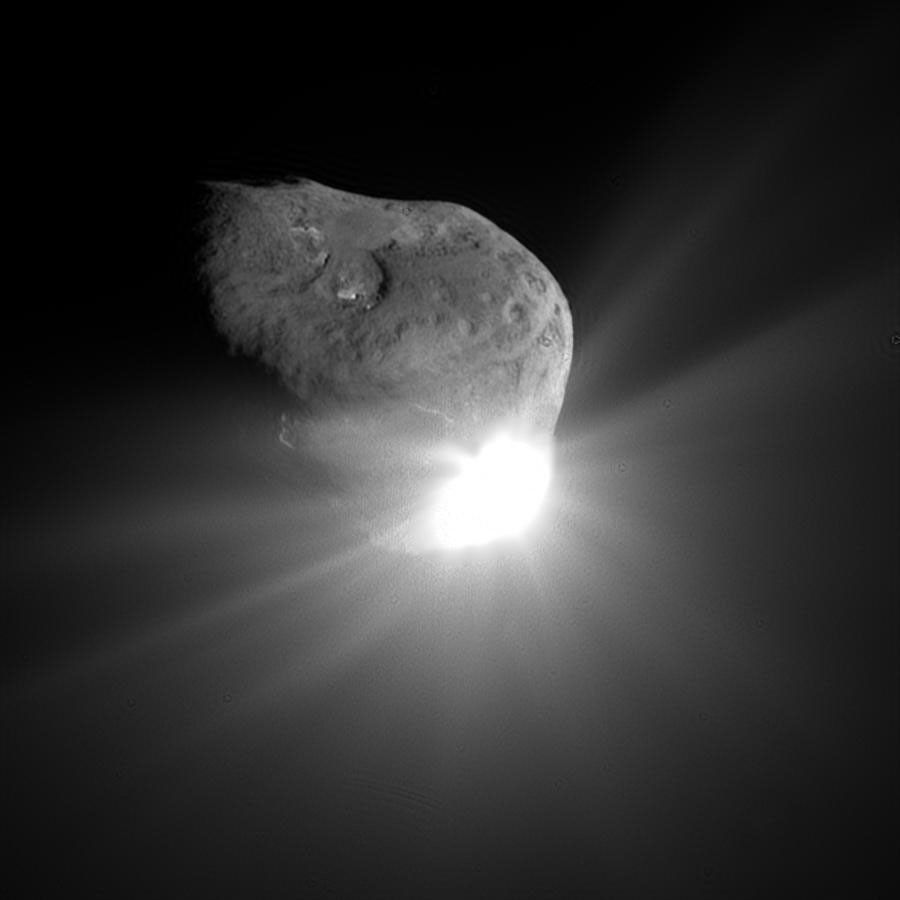

9P/Tempel 1
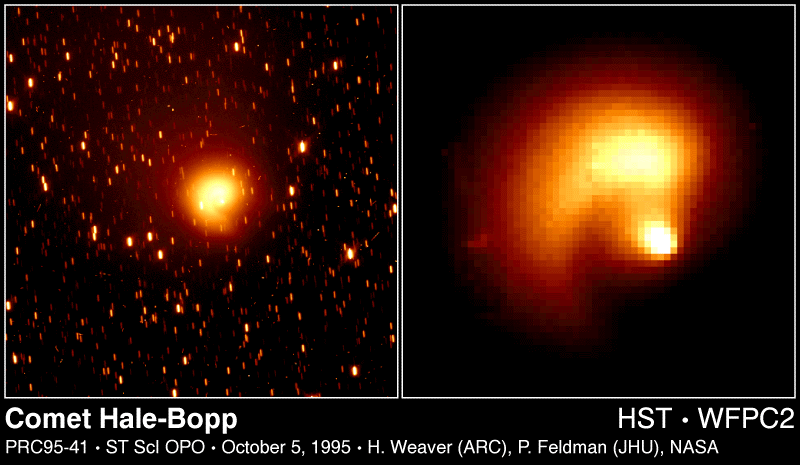
C/1995 O1 (Hale-Bopp)

C/2013 A1 Siding Spring

C/2012 S1 (ISON)
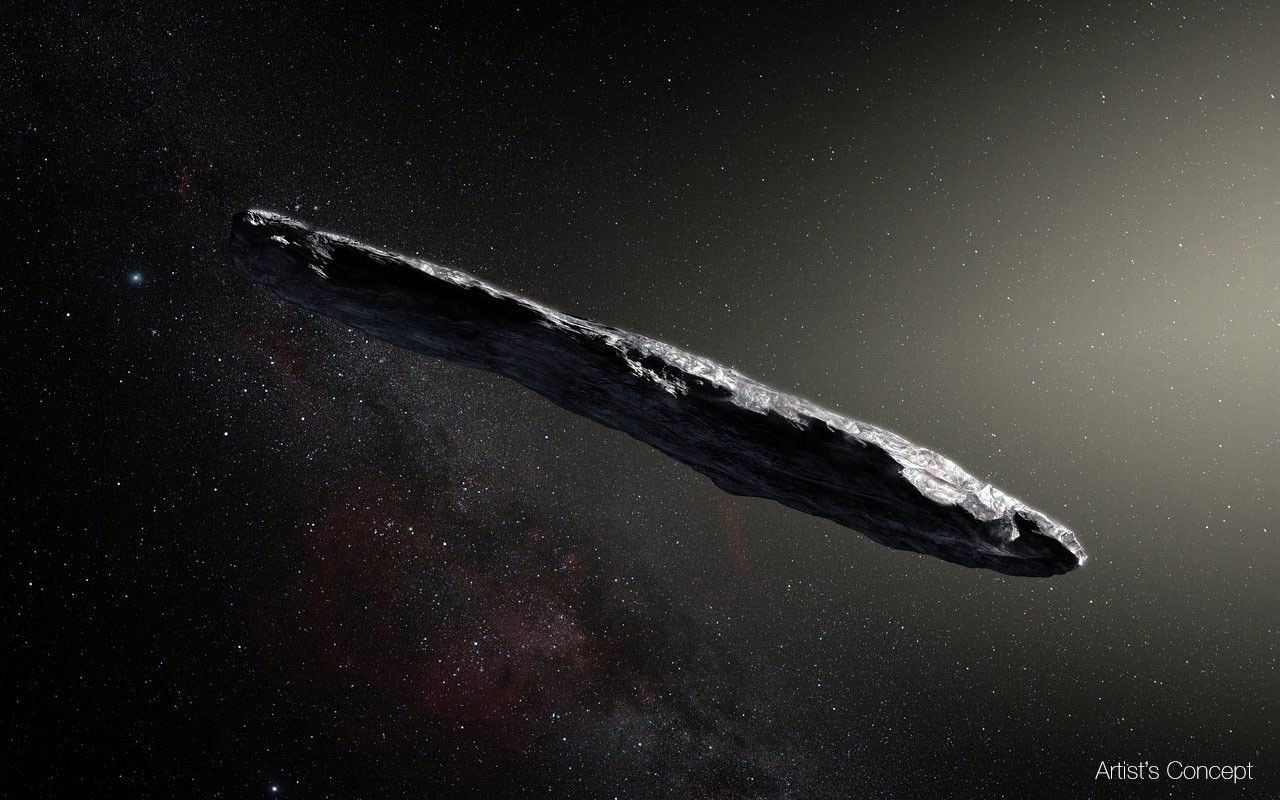

'Oumuamua