What’s Up: June 2023 Skywatching Tips from NASA
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
Mars and Venus, Summer Stars, and the June Solstice!
The planets of war and love draw nearer each night, as the bright stars of Northern Hemisphere summer rise. And note the June solstice on the 21st.
Monthly Highlights
- June 1-2 – Mars is in the Beehive Cluster (M44). Look for the Red Planet in the west after dark, where binoculars or a small telescope will reveal a backdrop of glittering stars in this open star cluster.
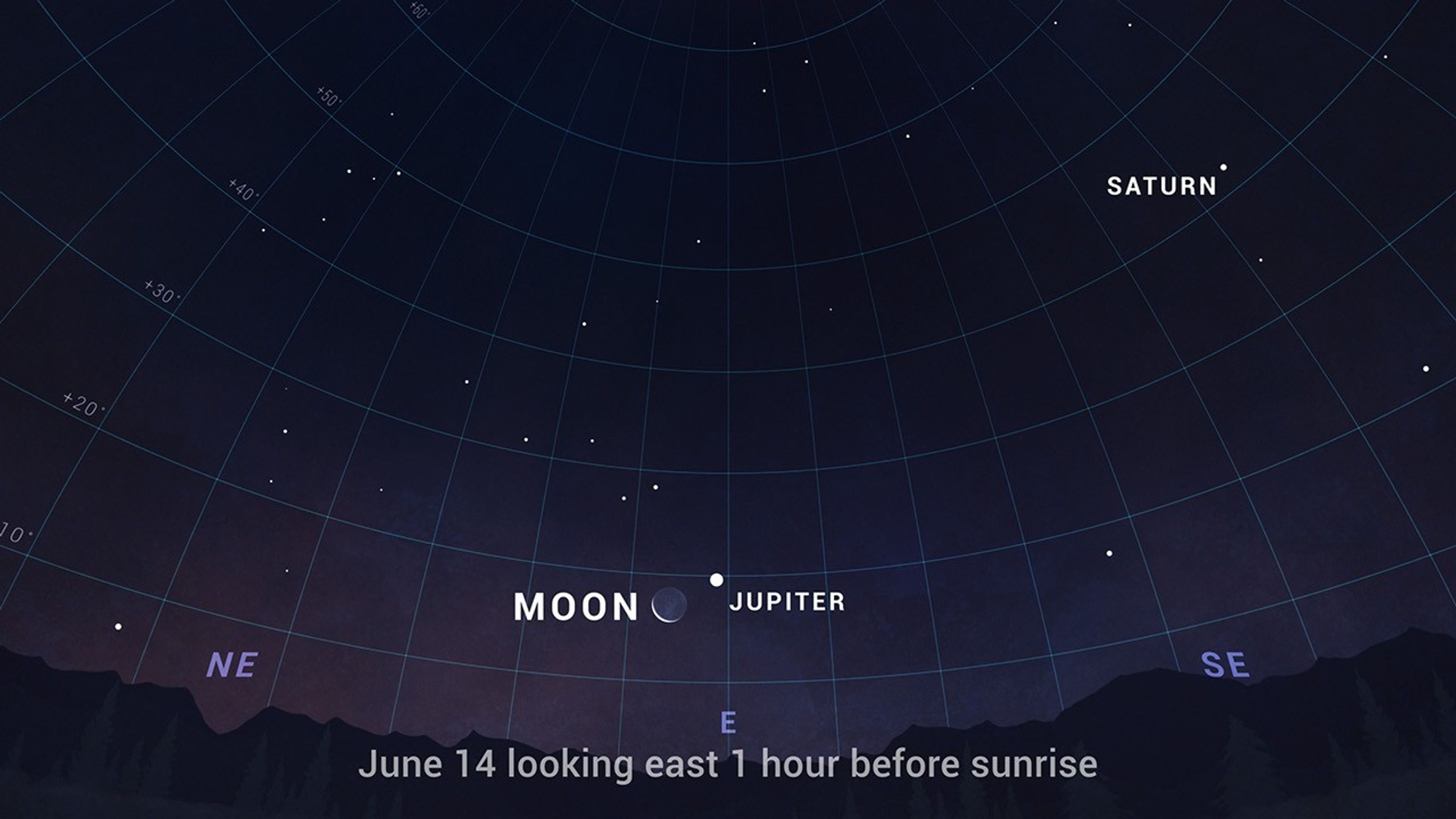
- June 3 – Full moon
- June 18 – New moon
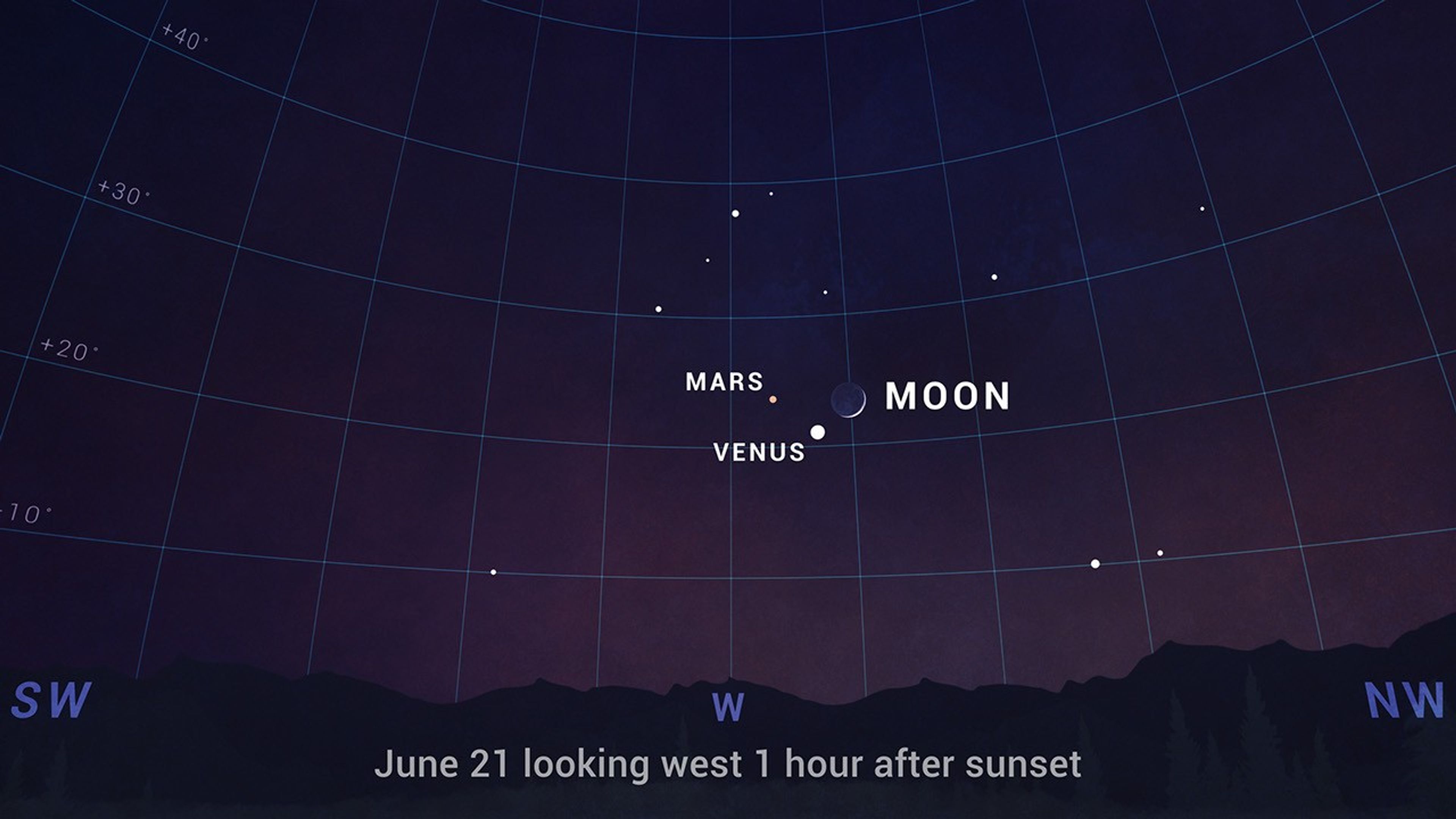
- June 21 – The crescent Moon makes a lovely grouping with Venus and Mars tonight. Find them in the west following sunset.
- June 21 – June Solstice. For the north, it's the longest day of the year, as the Sun traces its highest, longest path across the sky. The situation is reversed in the Southern Hemisphere, where it's the shortest day of the year, during the cool months of winter.
- All month – Mars and Venus draw nearer each evening in the western sky following sunset. The pair will appear a bit lower in the sky each night.
- All month – Saturn leads Jupiter into the new day. The Ringed Planet rises around midnight, with Jupiter trailing behind a couple of hours later.
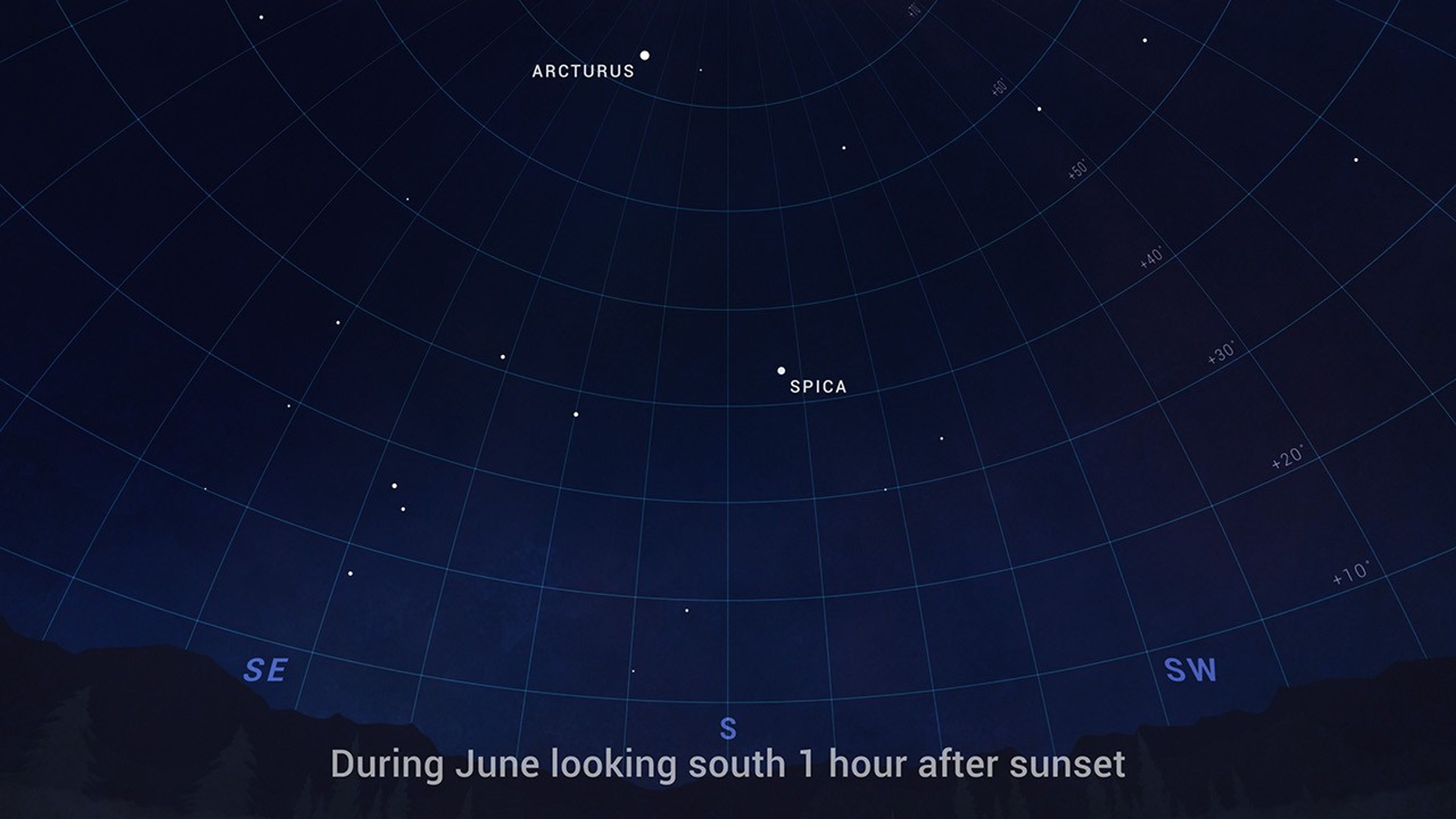
- All month – The two bright stars high overhead in the first few hours after dark are Spica and Arcturus (for Northern Hemisphere skywatchers).
- Southern Hemisphere observers will find bright stars Alpha Centauri and Hadar, along with the stars of constellation Crux, in their south-facing view.
- All month – Notice the stars of the Summer Triangle – Vega, Deneb, and Altair – rising in the east in the couple of hours after dark. They rise earlier each month throughout the summer.
TRANSCRIPT
What's Up for June? Planets buzz the Beehive, your bright evening stars, and how the Summer Solstice revealed the size of planet Earth.
On June 1st and 2nd, Mars will be in the Beehive. The Red Planet passes through the Beehive Cluster, also known as Praesepe or M44. It's a well-known open cluster of stars located around 600 light years away in the constellation Cancer, the crab. The pairing will make for great viewing through binoculars or a small telescope, with a sparkle of faint stars surrounding the rust-colored disk of Mars.
You can watch Mars and Venus draw closer together throughout the month in the western sky following sunset. Nearby is brilliant, blue-white star Regulus – the heart of Leo, the lion. And on the 20th through the 22nd the crescent Moon passes through, making an especially lovely grouping at dusk on June 21st.
Turning to the morning sky, Saturn and Jupiter rise before dawn, with the Ringed Planet rising around midnight and leading brilliant Jupiter into the new day. Early risers will find them on the eastern side of the sky before sun-up all month long. And you'll find Jupiter rising with the crescent Moon on June 14th.
Facing southward early on June evenings, you'll notice two particularly bright stars high in the sky. They are Spica and Arcturus.
Blue-white Spica is the brightest star in the constellation Virgo, the maiden. It's located about 250 light years away, and is actually two stars orbiting each other every 4 days at a distance far closer than Mercury orbits our Sun.
Orange giant Arcturus is the brightest star in Bootes, the herdsman. It's the fourth brightest star in the sky. It's much closer than Spica, at a distance of about 37 light years. It's also quite an old star, compared to our Sun, at an age of 7-8 billion years.
Also on June evenings, you'll notice the stars of the Summer Triangle – Vega, Deneb, and Altair – rising in the couple of hours after dark, and heralding the long, warm nights of Northern summer. The Triangle rises earlier each month as summer progresses.
June 21 is the Summer Solstice for the Northern Hemisphere, and Winter Solstice in the Southern Hemisphere. For the north, it's the longest day of the year, as the Sun traces its highest, longest path across the sky. More hours of sunlight, in addition to the more direct angle of the Sun overhead, translate into warmer summertime temperatures for our planet's summer hemisphere. The situation is reversed for those living south of the equator, where it's the shortest day of the year, during the cool months of winter.
The June summer solstice has another interesting claim to fame. It helped the Ancient Greeks, 2,200 years ago, to understand the size of our planet with remarkable accuracy. A scholar named Eratosthenes noted the difference in the length of the shadows cast by poles placed in the ground in two cities, 800 kilometers apart, at noon on the day of the solstice. One cast no shadow at all and the other cast a significant shadow. By comparing the shadows with the separation of the two cities, Eratosthenes deduced that Earth was about 40,000 kilometers in circumference, which is the actual value.
He was also the first to calculate the tilt of Earth's axis – which, after all, is what's responsible for the solstices and for the seasons themselves.
Here are the phases of the Moon for June.
Stay up to date with all of NASA's missions to explore the solar system and beyond at nasa.gov. I'm Preston Dyches from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and that's What's Up for this month.