
What is the Carbon Cycle?
Carbon is found all around Earth, including inside us. It moves around Earth as part of the carbon cycle. One way carbon travels is in the form of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide traps some of the heat from the sun, warming the planet. However, the more carbon dioxide there is, the hotter the planet becomes, which can affect weather patterns, sea levels, and more.
What is the carbon cycle?
Take a deep breath in. And breathe out. You just exhaled carbon dioxide, or CO2!
All living things on Earth contain carbon — even you! Lots of it! Like every other living thing on this planet, we are a part of Earth's carbon cycle.
The carbon cycle describes how carbon moves through the planet, including the process for adding and removing carbon from the atmosphere. Here is the carbon cycle in a nutshell:
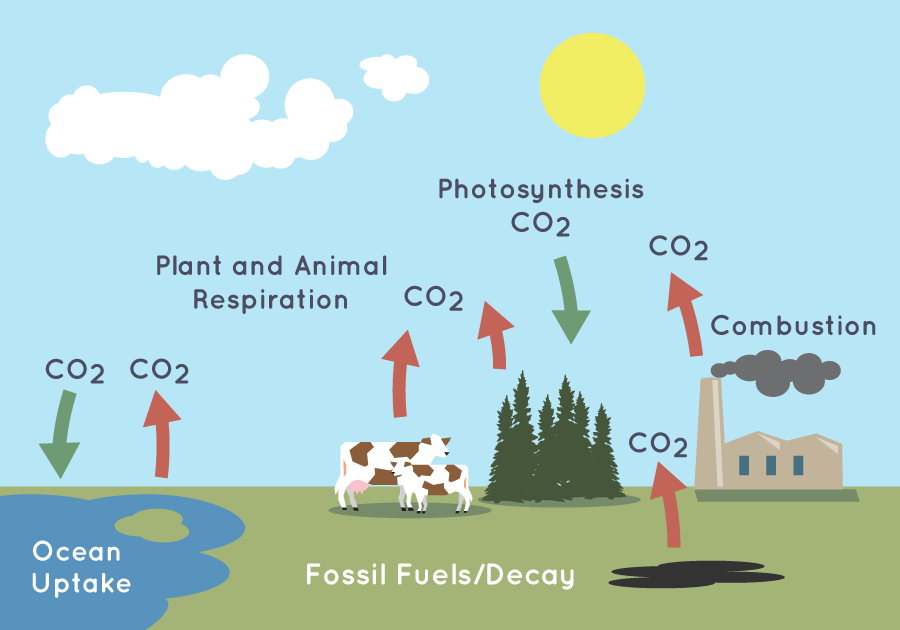
Carbon is added to the atmosphere by living organisms, like when we breathe out. It is also released when plants and animals decay. Volcanic eruptions add CO2 to the air. And the burning of fuels like gas, oil, and coal for energy and transportation also adds CO2 into the air.
Carbon is removed from the atmosphere by plants, soil, and the ocean. Plants, both on land and in the water, absorb CO2 during photosynthesis – a process where they use CO2, water, and sunlight to make food and release oxygen. The ocean and soil also absorb CO2 directly from the air. It then undergoes a chemical reaction that turns it into new forms, allowing it to be stored. On the land, some of this carbon slowly sinks deeper into the Earth over long periods of time. Eventually, this sinking forms fossil fuels like oil and coal that can be used as energy.
This cycle circulates carbon around the planet. Some parts of the cycle happen very quickly – like when a person breathes, which takes less than a second. Other parts take much longer. For example, forming oil from ancient plant and animal remains can take millions of years.
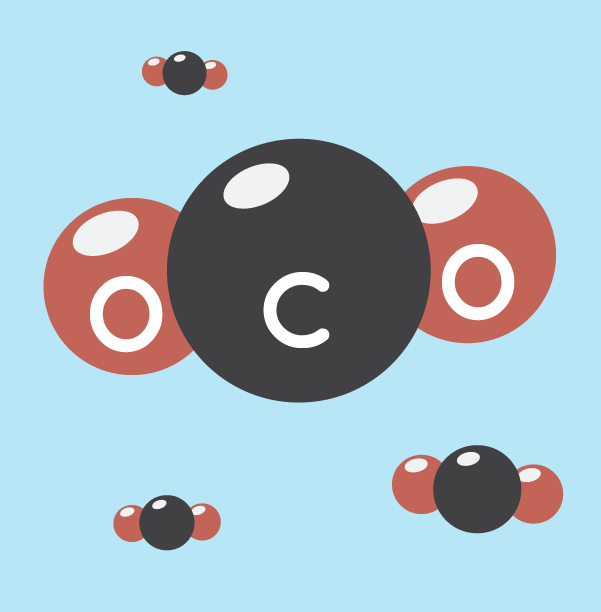
What is carbon dioxide?
Carbon dioxide is an important gas for life on the planet. (Remember our deep breath in and out?) It is one of the primary greenhouse gases on Earth.
Greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun in Earth’s atmosphere. This process is known as the greenhouse effect. Without it, that heat would escape Earth's atmosphere and go into space. It would make Earth too cold to support life as we know it. But the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere affects Earth’s temperature. If the amount of greenhouse gases increases, then more heat is trapped and the planet becomes warmer. This can lead to changes in climate, weather patterns, and sea levels.
How is carbon dioxide changing?
In Earth’s long history, the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere has changed many times. There have been periods with more CO2, and other periods with less. One thing has remained consistent: when the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere has gone up, the temperature of Earth has also gone up.
But there's more to it. As Earth’s temperature rises, CO2 levels in the atmosphere increase further. This is mostly because of the role the ocean plays in the carbon cycle. The ocean absorbs and stores a lot of CO2, but when ocean temperatures increase, they release some of their stored CO2 back into the atmosphere. This is similar to how a glass of soda loses its bubbles more quickly on a warm day — warm water can’t hold as much gas.
Over the last 150 years though, there was something new added to this cycle: CO2 from things we do to produce energy and to help us go places. These include things like burning coal, oil, and gas to power factories, generate electricity, and fuel cars and trucks. Cutting down forests to build towns and cities also means there are fewer trees to help absorb CO2 from the air.
Combined, these changes have led to an increase in CO2 in the atmosphere. This increase is more than the plants, soil, and ocean can absorb quickly, and as a result, the planet has been warming. When the planet’s temperature changes, it impacts many different things, such as the weather, climate, snow and ice, and sea level.
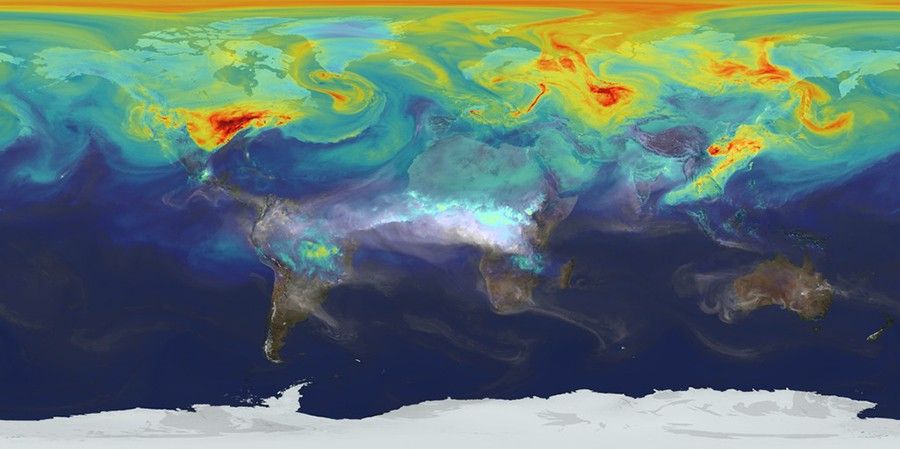
How is NASA learning about carbon dioxide?
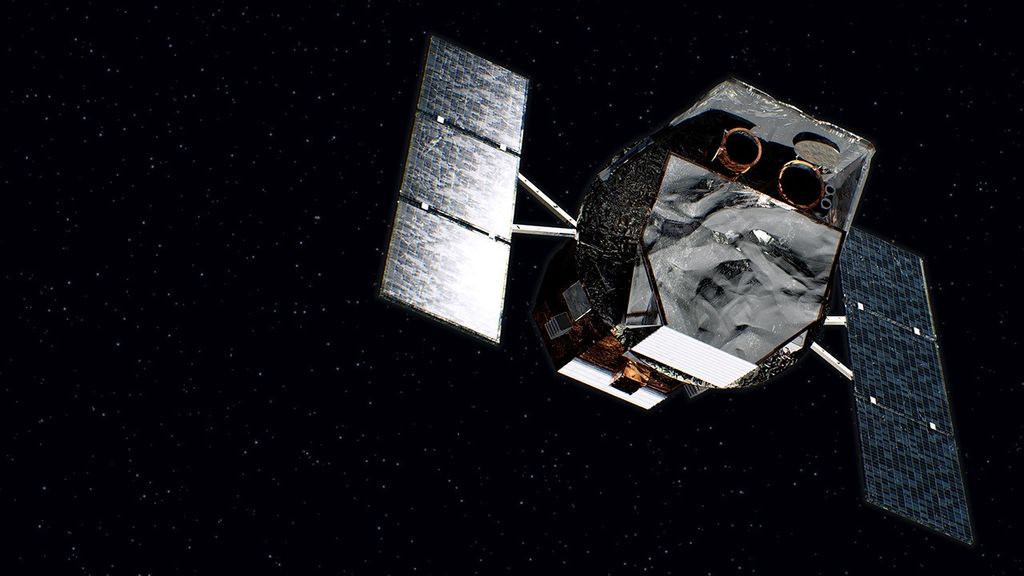
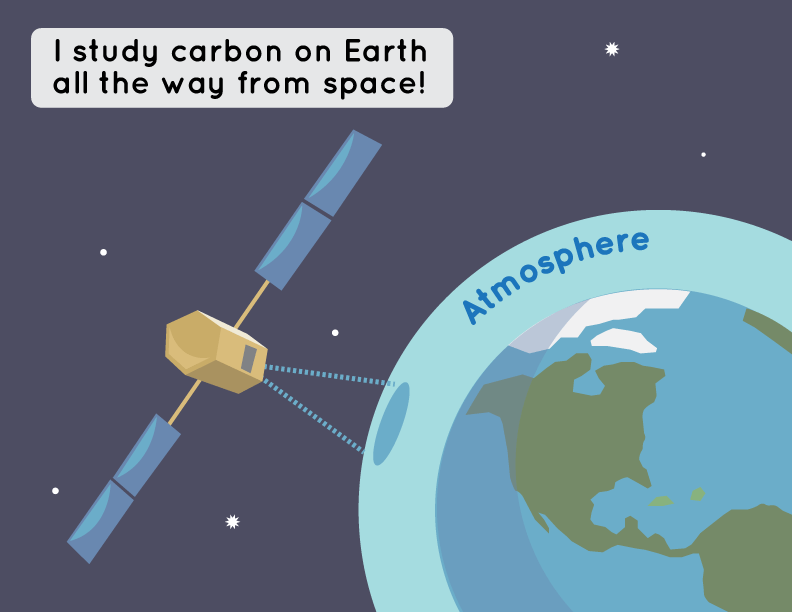
NASA and its partners have multiple research satellites in orbit that are studying how carbon moves around the planet.
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2, or OCO-2, satellite and OCO-3 instrument (which is on the International Space Station!) measure CO2 all the way from space! Scientists use these measurements to better understand Earth's carbon cycle and how it is changing over time.