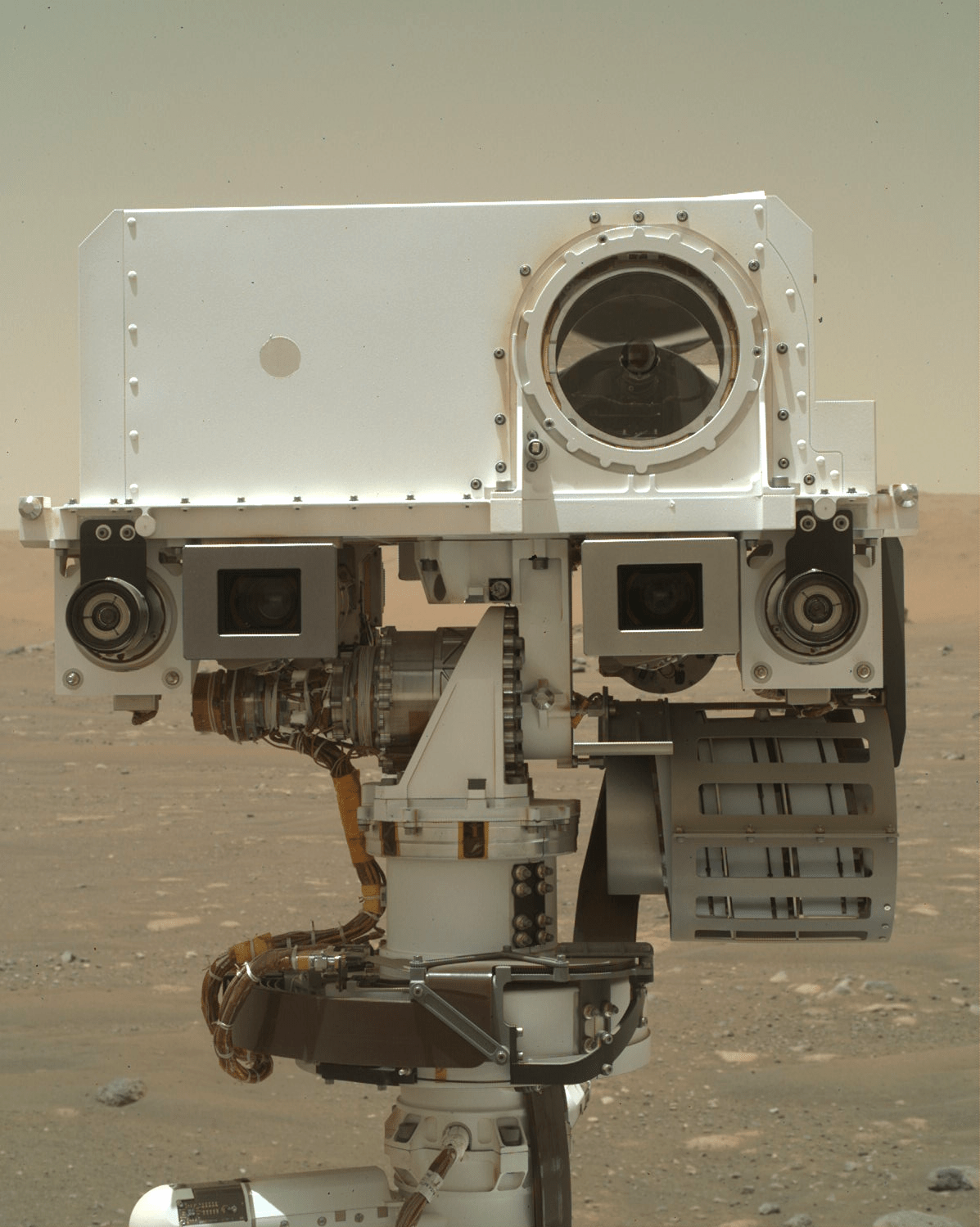
MSL drove 12.5
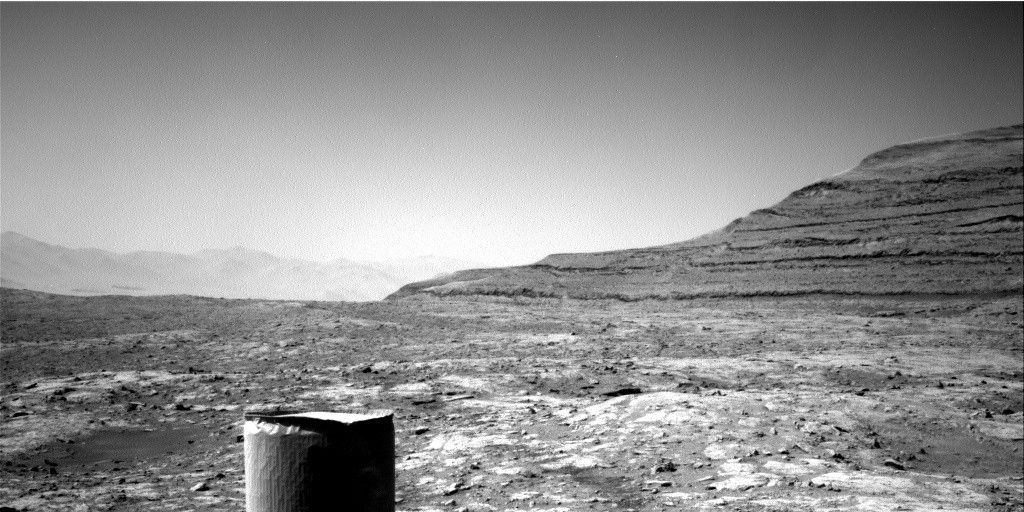
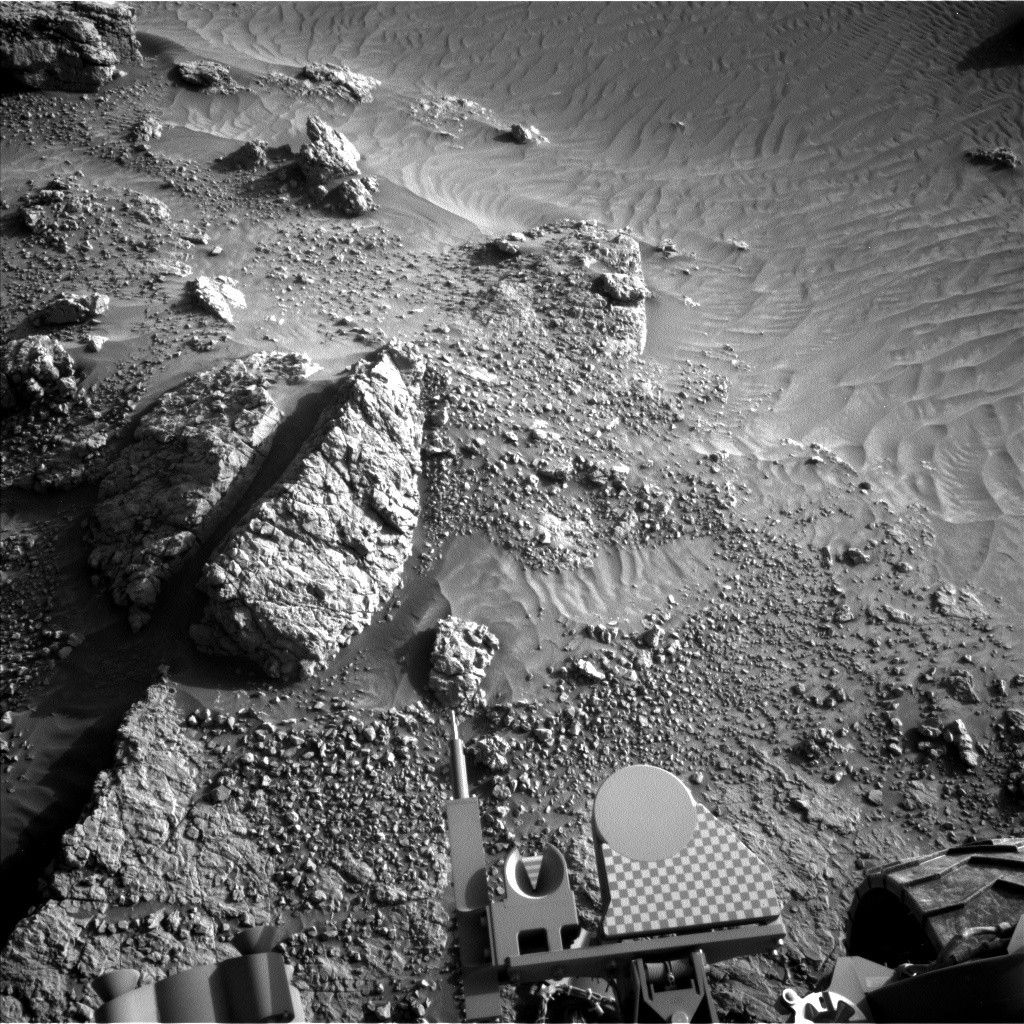
MSL drove 12.5 meters on Sol 1478, to an area with lots of nodules in the bedrock .
The tactical planning team decided to exercise the "touch and go"
option, so the arm will be deployed for contact science before driving
away on Sol 1480. The plan is packed with a variety of activities,
starting with a short APXS integration and MAHLI imaging of a
nodule-rich target named "Oodi." The arm will then be moved out of the
way for ChemCam and Right Mastcam observations of Oodi and nearby
bedrock targets "Calenga" and "Caconda." The Right Mastcam will also
acquire images of targets dubbed "Chitembo," "Chingufo," and "Chipindo"
to investigate sedimentary structures in more detail, and of the rock
that AEGIS selected for autonomous ChemCam chemical measurements. Then
Mastcam will measure dust in the atmosphere before the next drive and
the usual post-drive imaging. Overnight, CheMin will analyze the Quela
drill sample again, to improve the quality of mineralogical
measurements. On Sol 1481, Navcam will search for clouds, AEGIS will
autonomously select a target for ChemCam observations, and the results
of the CheMin analysis will be read out of the instrument to the rover computer. Finally,
SAM will perform a maintenance activity before the rover gets some
sleep and recharges her batteries in preparation for the next 2-sol
plan.
by Ken Herkenhoff
Dates of planned rover activities described in these reports are subject to change due to a variety of factors related to the Martian environment, communication relays and rover status.
Written by Ken Herkenhoff, Planetary Geologist at USGS Astrogeology Science Center