3 min read
By Maria-José Viñas,
NASA's Earth Science News Team
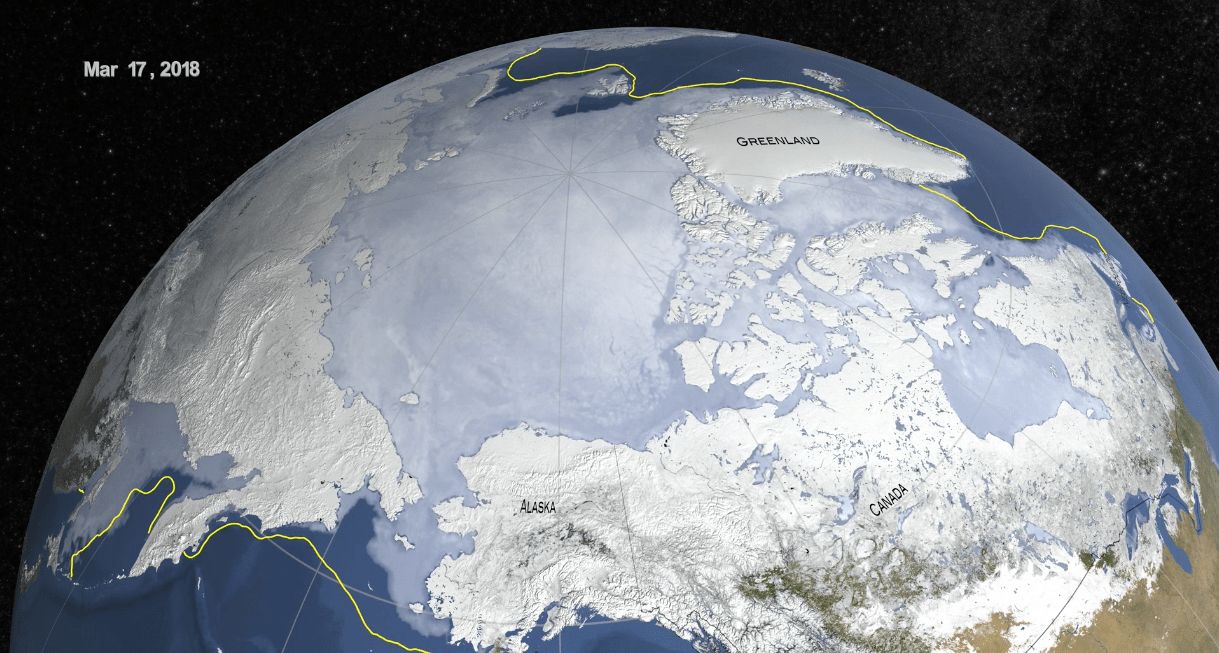
Sea ice in the Arctic grew to its annual maximum extent last week, and joined 2015, 2016 and 2017 as the four lowest maximum extents on record, according to scientists at the NASA-supported National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and NASA.
On March 17, the Arctic sea ice cover peaked at 5.59 million square miles (14.48 million square kilometers), making it the second lowest maximum on record, at about 23,200 square miles (60,000 square kilometers) larger than the record low maximum reached on March 7, 2017.
More significantly from a scientific perspective, the last four years reached nearly equally low maximum extents and continued the decades-long trend of diminishing sea ice in the Arctic. This year’s maximum extent was 448,000 square miles (1.16 million square kilometers) — an area larger than Texas and California combined – below the 1981 to 2010 average maximum extent.
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/ Katy Mersmann. This video is available for download at NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio.
Every year, the sea ice cover blanketing the Arctic Ocean and surrounding seas thickens and expands during the fall and winter, reaching its maximum yearly extent sometime between late February and early April. The ice then thins and shrinks during the spring and summer until it reaches its annual minimum extent in September. Arctic sea ice has been declining both during the growing and melting seasons in recent decades.
The decline of the Arctic sea ice cover has myriad effects, from changes in climate and weather patterns to impacts on the plants and animals dependent on the ice, and to the indigenous human communities that rely on them. The disappearing ice is also altering shipping routes, increasing coastal erosion and affecting ocean circulation.

“The Arctic sea ice cover continues to be in a decreasing trend and this is connected to the ongoing warming of the Arctic,” said Claire Parkinson, senior climate scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “It’s a two-way street: the warming means less ice is going to form and more ice is going to melt, but also, because there’s less ice, less of the sun’s incident solar radiation is reflected off, and this contributes to the warming.”
The Arctic has gone through repeated warm episodes this winter, with temperatures climbing more than 40 degrees above average in some regions. The North Pole even experienced temperatures above the freezing point for a few days in February.