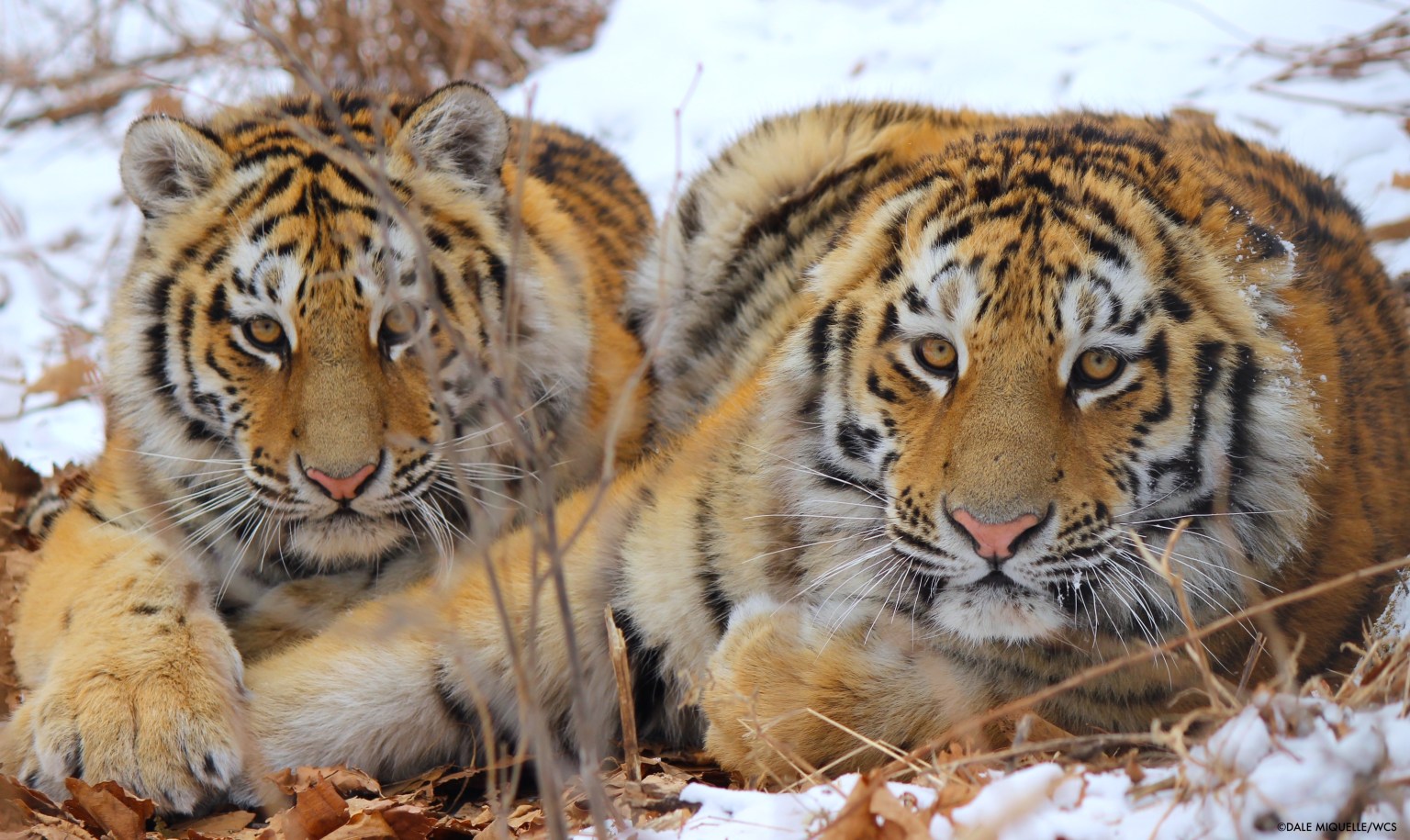
As human populations grow, habitat loss threatens many creatures. Mapping wildlife habitat using satellites is a rapidly expanding area of ecology, and NASA satellites play a crucial role in these efforts. Tigers, jaguars, and elephants are a few of the vulnerable animals whose habitats NASA is helping track from space.
“Satellites observe vast areas of Earth's surface on daily to weekly schedules,” said Keith Gaddis, ecological conservation program manager at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “That helps scientists monitor habitats that would be logistically challenging and time-consuming to survey from the ground — crucial for animals like tigers that roam large territories.”
Here’s how NASA and its partners help protect three of Earth’s most iconic species:
Trouble (and Hope) for Tigers
Tigers have lost at least 93% of their historical range, which once spanned Eurasia. Roughly 3,700 to 5,500 wild tigers remain, up from an estimated low of 3,200 in 2010.
In a recent study, researchers reviewed over 500 studies that contained data on tigers and their habitat across Asia. The team found that the area where the big cats are known to live declined 11%, from about 396,000 square miles in 2001 to about 352,000 square miles in 2020.
Led by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) and funded by NASA’s Ecological Conservation program, the team developed a tool that uses Google Earth Engine and NASA Earth observations to monitor changes in tiger habitat. The goal: aid conservation efforts in near-real time, using data from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) and Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) imagers, and Landsat satellites.
The researchers mapped large stretches of “empty forests” without recent tiger presence. Because these areas were suitable habitat and are still big enough to support tigers, they are potential landscapes for restoration, assuming there is enough food. If tigers could reach those areas, either through natural dispersal or active reintroduction, it could “increase the land base for tigers by 50%,” the scientists reported.
“There’s still a lot more room for tigers in the world than even tiger experts thought,” said lead author Eric Sanderson, formerly a senior conservation ecologist at WCS and now vice president of urban conservation at the New York Botanical Garden. “We were only able to figure that out because we brought together all of this data from NASA and integrated it with information from the field.”
Where the Jaguars Are
Jaguars once roamed from the U.S. Southwest to Argentina. But in the past century, they have lost about 50% of their range, according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Like tigers, jaguars must contend with poaching and the loss of food sources. Wild jaguars number between 64,000 and 173,000 individuals, and IUCN classifies them as near-threatened.
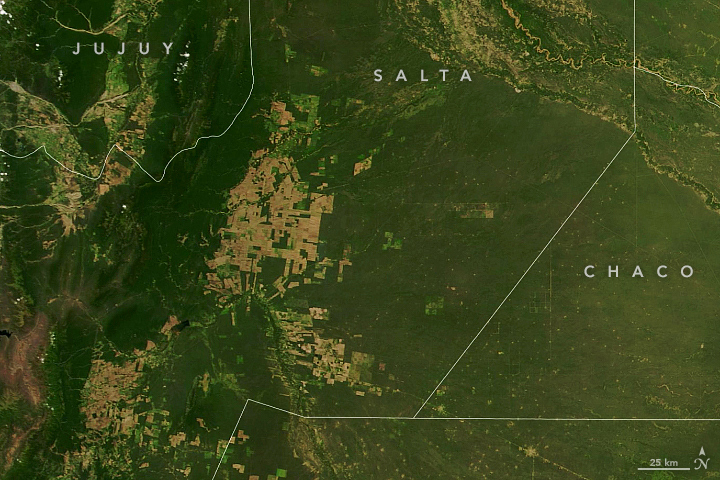
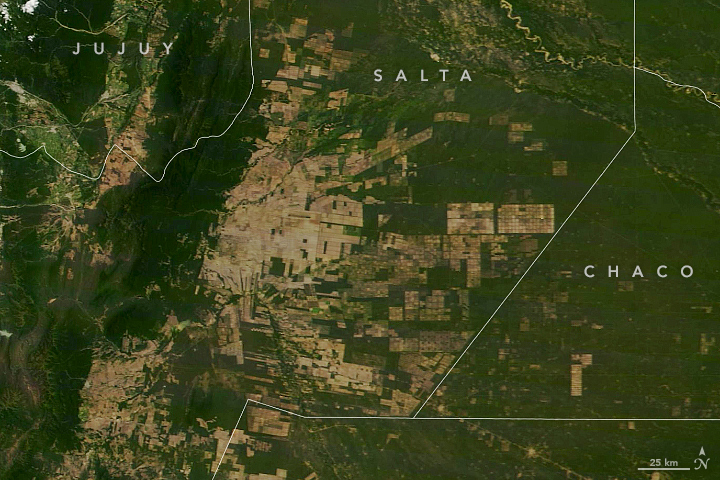
In Gran Chaco, South America’s second largest woodland, jaguars and other animals live in an especially threatened ecosystem. The dry lowland forest stretches from northern Argentina into Bolivia, Paraguay, and Brazil, and has experienced severe deforestation.
















-1.jpg?w=1024)