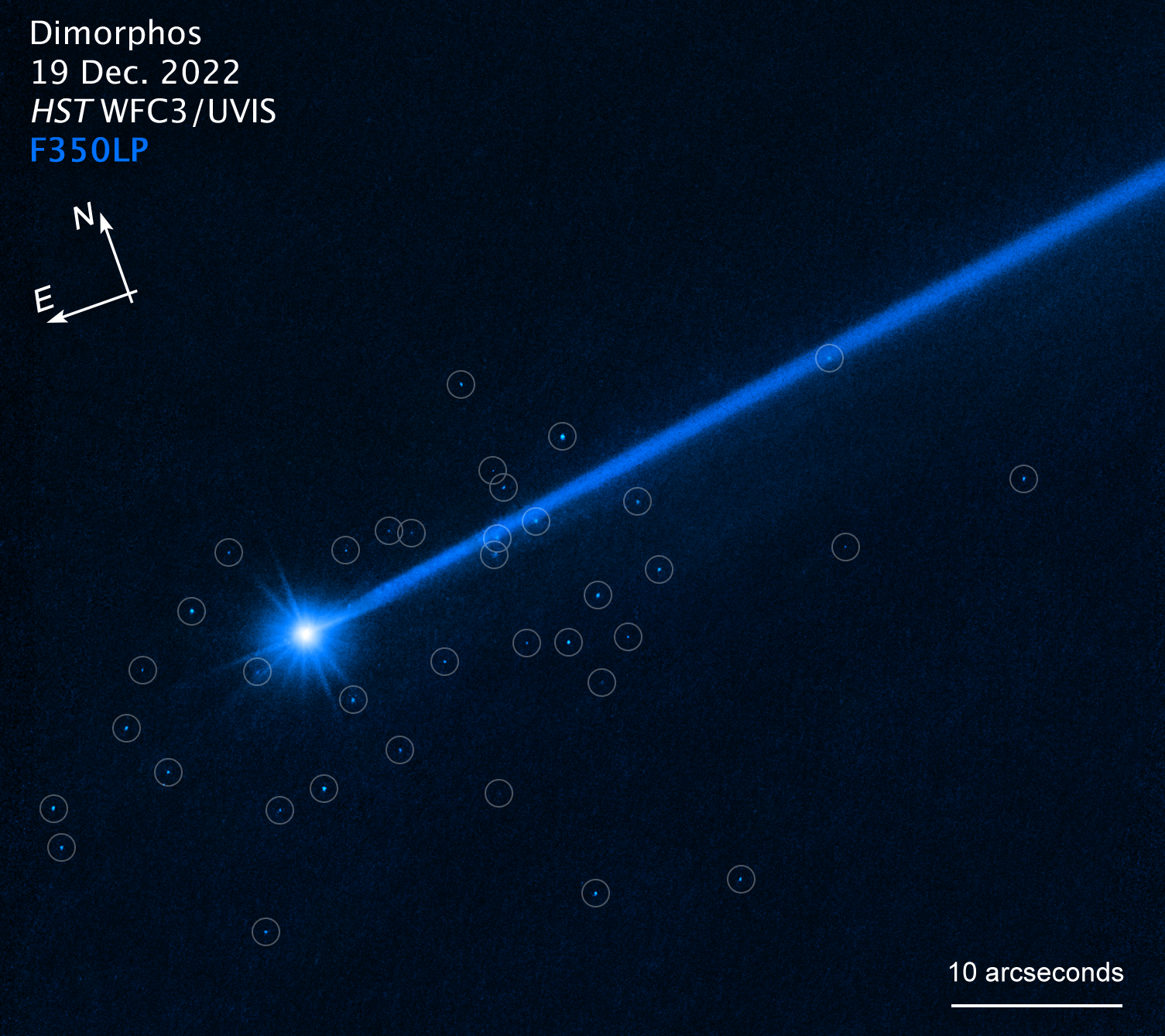
Hubble Photographs Boulders Flung Off Asteroid Dimorphos (Compass Image)
Image of the asteroid Dimorphos, with compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative to direction arrows on a map of the ground (as seen from above). The bright white object at lower left is Dimorphos. It has a bluish dust tail extending diagonally to the upper right. A cluster of blue dots (marked by white circles) surrounds the asteroid. These are boulders that were knocked off the asteroid when, on September 26, 2022, NASA deliberately slammed the half-ton DART impactor spacecraft into the asteroid as a test of what it would take to deflect some future asteroid from hitting Earth. Hubble photographed the slow-moving boulders using the Wide Field Camera 3 in December 2022. The color results from assigning a blue hue to the monochromatic (grayscale) image.
