Hubble WASP 121b Artist’s Concept
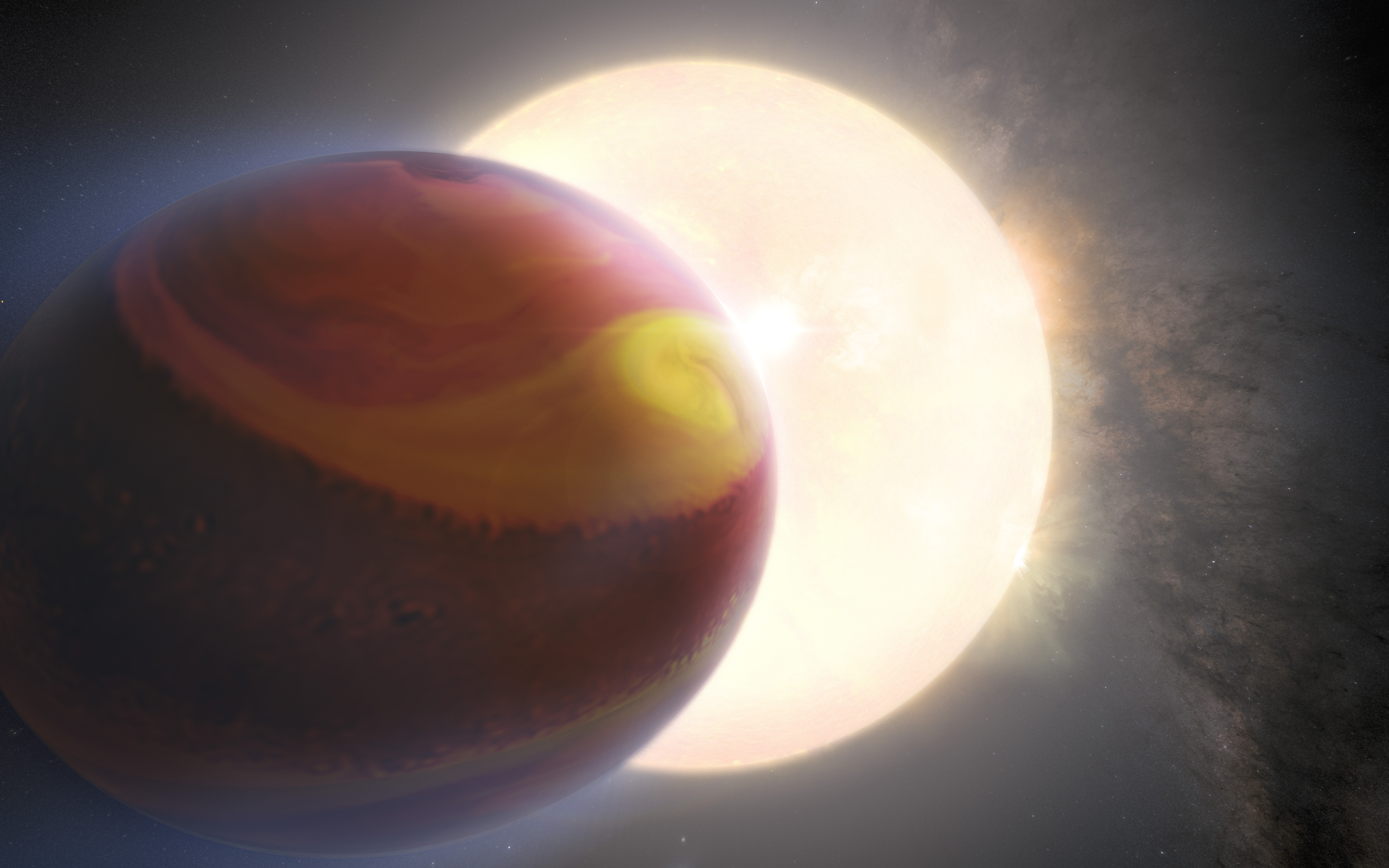
This is an artist's concept of the exoplanet WASP-121 b, also known as Tylos. The exoplanet's appearance is based on Hubble simulation data of the object. Using Hubble observations, another team of scientists had previously reported the detection of heavy metals such as magnesium and iron escaping from the upper atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter exoplanet; marking it as the first of such detection. The exoplanet is orbiting dangerously close to its host star, roughly 2.6% of the distance of Earth to the Sun, placing it on the verge of being ripped apart by the star's tidal forces. The powerful gravitational forces have altered the planet's shape. An international team of astronomers assembled and reprocessed Hubble observations of the exoplanet in the years 2016, 2018, and 2019. This provided them with a unique data-set that allowed them to not only analyze the atmosphere of WASP-121 b, but also to compare the state of the exoplanet's atmosphere across several years. They found clear evidence that the observations of WASP-121 b were varying in time. The team then used sophisticated modelling techniques to demonstrate that these temporal variations could be explained by weather patterns in the exoplanet's atmosphere.
- X

























