What Is the Greenhouse Effect?
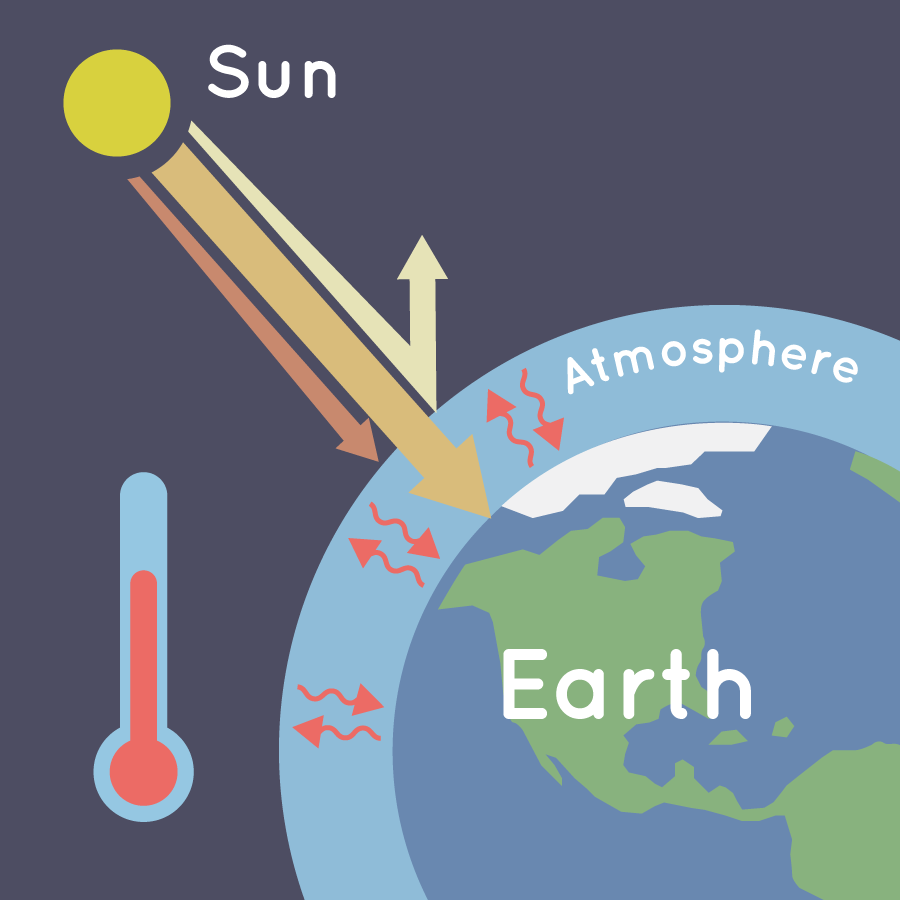
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when certain gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the heat from the sun near the surface. This process keeps Earth’s surface warmer than it would be without it. It is similar to how a glass greenhouse keeps plants warm.
Watch this video to learn about the greenhouse effect!
How does the greenhouse effect work?
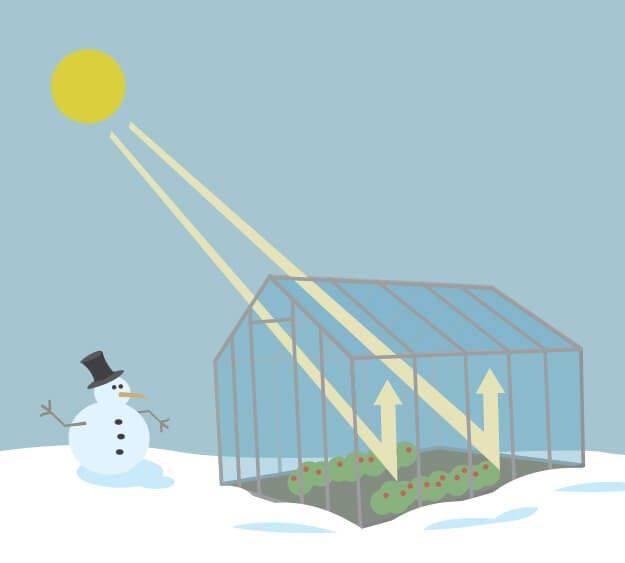
As you might expect from the name, the greenhouse effect works … like a greenhouse! A greenhouse is a building with glass walls and a glass roof. Greenhouses are used to grow plants, such as tomatoes and tropical flowers. They are often used in places that are colder than a plant's natural environment.
A greenhouse stays warm inside, even during the winter. In the daytime, sunlight passes through the glass into the greenhouse. It warms the soil, plants, and air inside. At night, the soil and plants slowly release this heat. But the glass traps it in, making the greenhouse warmer than it is outside.
The greenhouse effect on Earth works much the same way. Certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat like the glass of a greenhouse. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
During the day, sunlight travels through the atmosphere and warms Earth’s surface. Some of that sunlight bounces, or reflects, off the surface back into space. The rest of it gets absorbed and heats up the surface. At night, Earth's surface cools, releasing this heat back into the air. But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. That's what keeps our Earth warm enough to support life as we know it.
What increases the greenhouse effect on Earth?
The greenhouse effect increases on Earth when greenhouse gases are added to the atmosphere. They can be added to the air by a variety of sources.
Scientists have found that over the last 100 years extra greenhouse gases have mainly come from a few sources. These are things like burning coal and oil for energy or burning gasoline to run cars and planes. Other sources, such as erupting volcanoes, have also added some greenhouse gases to the air. But those natural additions have been too small to account for the amount of greenhouse gases we measure in the air today.
What reduces the greenhouse effect on Earth?
To reduce the greenhouse effect, greenhouse gases need to be taken out of the atmosphere. Earth has a few ways it does this with plants, soil, and oceans.
All plants — from tall trees to blades of grass, and even the tiny plant-like phytoplankton in the ocean — take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen. They do this in a process known as photosynthesis. This is when plants take carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight and change it into food (sugar) and oxygen.
The soil and ocean also absorb carbon dioxide from the air. It changes into other things over time through chemical reactions. It can also make the soil and ocean more acidic, which can impact plants and animals. For example, ocean acidification can be harmful to many ocean creatures, such as shellfish and coral, as it weakens their shells and skeletons.
How does NASA measure the greenhouse effect?
The Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) instruments measure changes in the greenhouse effect. They collect data to show how much heat is getting trapped on Earth compared to how much is escaping to space. This data has shown that more heat is getting trapped than what is leaving, which is warming the planet.
NASA also tracks changes in greenhouse gases over time with satellites. The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, and OCO-3 keep track of carbon dioxide in the air. The Earth Source Mineral Dust Source Investigation, or EMIT, satellite can track methane. Other satellites, like the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem, or PACE, measure changes in the ocean.