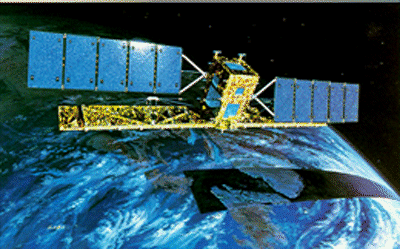
RADARSAT-1
Radar Satellite-1
Type
Launch
Target
Objective
Canada's RADARSAT-1 is a radar satellite featuring variable resolution, and different view angles at a number of preset positions. This sophisticated remote sensing satellite was a Canadian-led project involving the United States. It carries a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), a powerful microwave instrument that can transmit and receive signals to "see" through clouds and darkness, obtaining detailed images of the Earth. This provides significant advantages in viewing under conditions that preclude observation by aircraft or optical satellites. RADARSAT-1 collects data on resource management, ice, ocean and environmental monitoring and Arctic and off-shore surveillance. RADARSAT-1 also supports fishing, shipping, oil exploration, offshore drilling and ocean research. The RADARSAT-1 provides complete global coverage with the flexibility to support specific requirements.
The Radar Satellite (RADARSAT-1) was a joint Canada (Canadian Space Agency/Canada Center for Remote Sensing) and United States (NASA) project. RADARSAT-1 is owned and operated by CSA; NASA provided the launch. RADARSAT was designed to provide detailed information on sea ice and terrestrial ice sheets for climate research, to produce radar imagery for geographical applications in oceanography, agriculture, forestry, hydrology, and geology, and to provide real-time products for arctic ocean navigation including ice surveillance. RADARSAT-1 was also designed to provide data products for commercial applications such as fishing, shipping, oil exploration, offshore oil drilling, and resource management. RADARSAT-1 carries an advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) operating at 5.3 GHz (C-band). The RADARSAT-1 spacecraft consisted of two major components: the spacecraft bus and the payload module. The spacecraft bus, built by Ball Aerospace, consists of the structure power units, solar arrays, attitude control, propulsion deck, and telemetry, tracking, and command systems. Over time, the primary and secondary on-board tape recorders have failed, but RADARSAT-1 continues to operate with provision of only direct downlink to various receiving stations. Over its long career, RADARSAT-1 has been used to collect substantial and significant science data sets of Antarctica and Arctic sea ice.
Mission Statistics:
- Country of Origin Canada
- Customer/User Canadian Space Agency (CSA)
- Manufacturer(s)
- SPAR Aerospace, Ball Space Systems
- Size 1.2 meter cube, antenna 1.5 x 15 meters
- Orbit Sun-synchronous 793x821 km; incl.= 98.6 degrees; period=101 min.
- Design Life 5 years
- Related Sites RADARSAT
- Launch Date/Time: 1995-11-04 at 14:22:00 UTC On-orbit Dry Mass: 2713 kg Nominal Power Output: 2500 W
Top of Page | Back to Missions