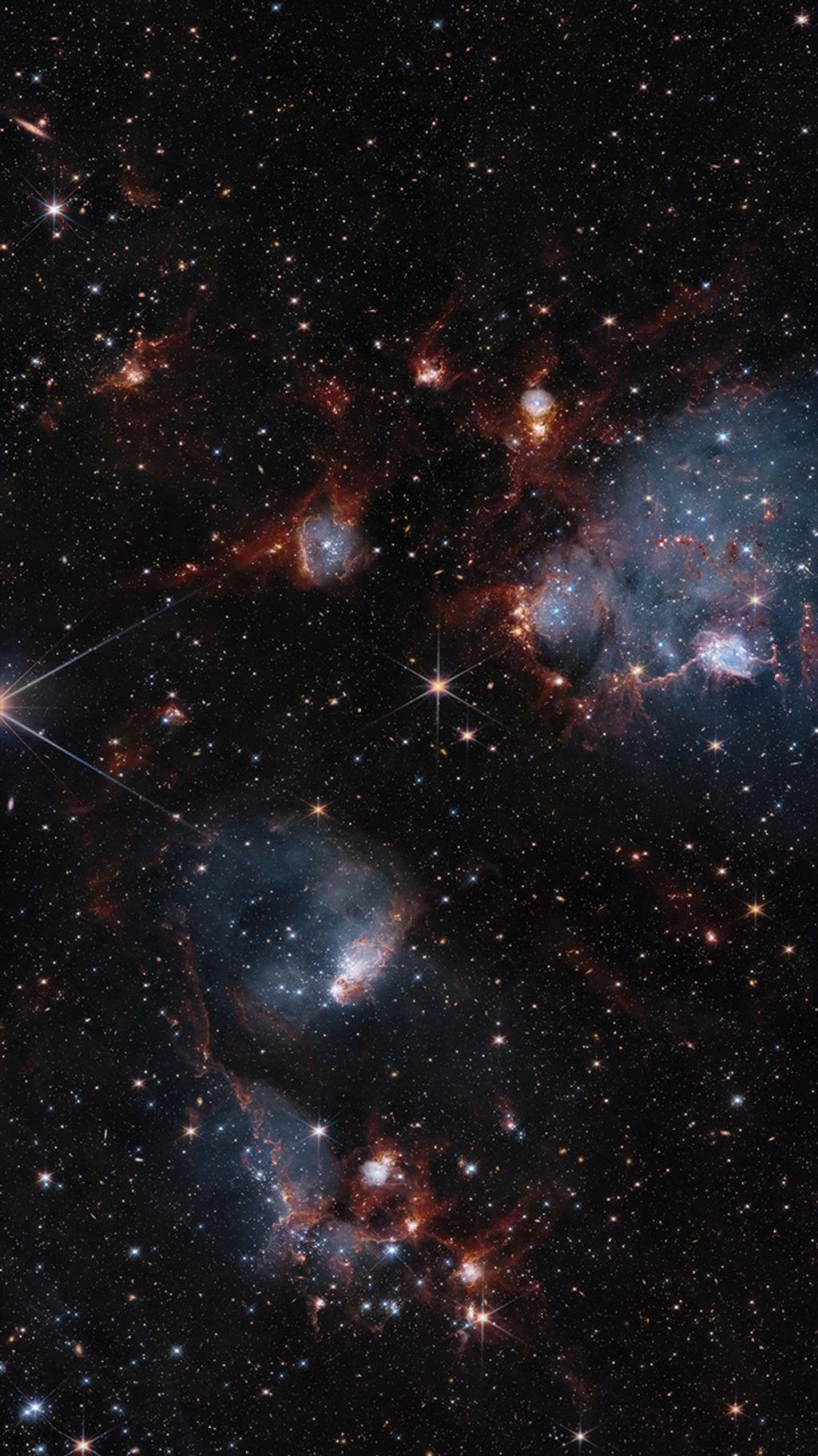
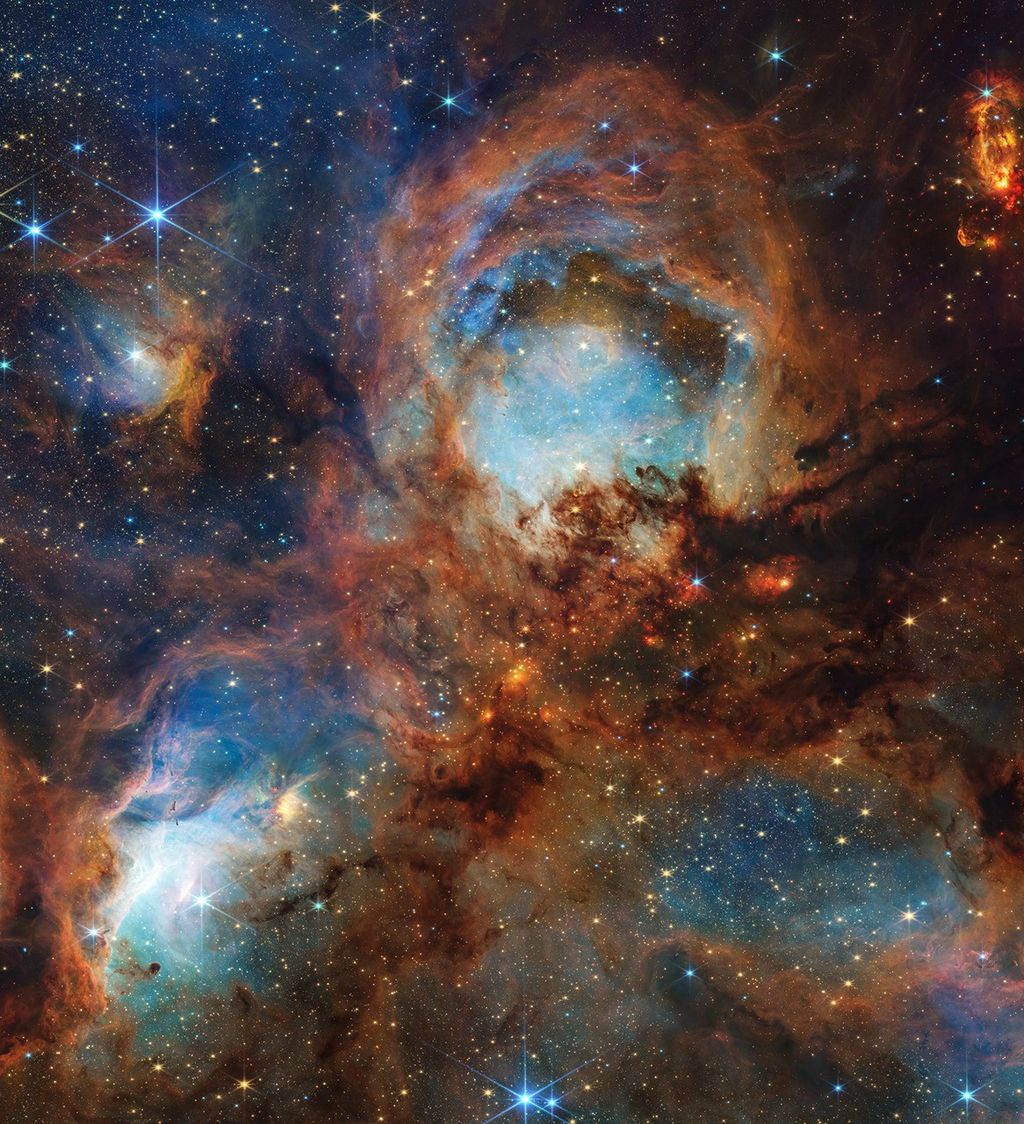
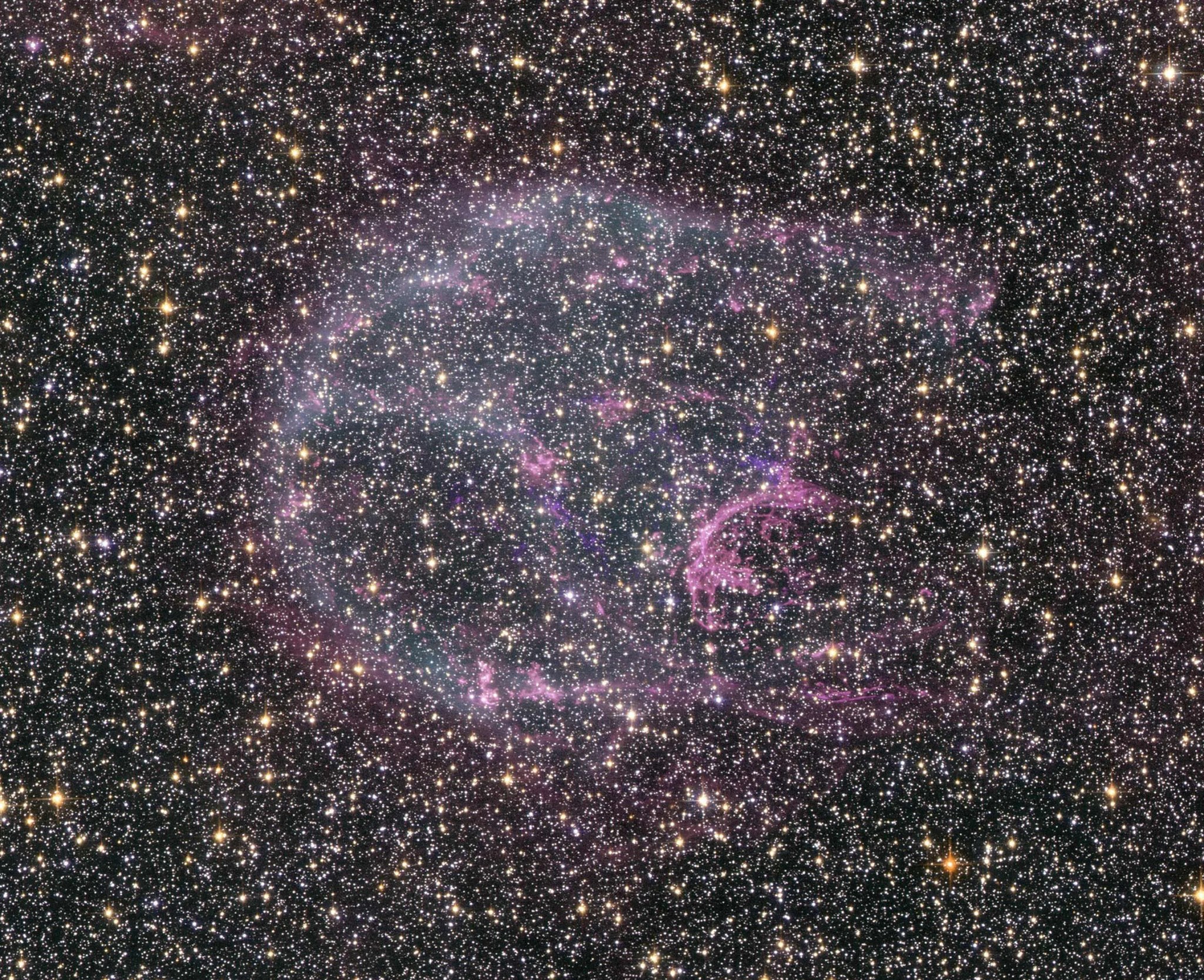
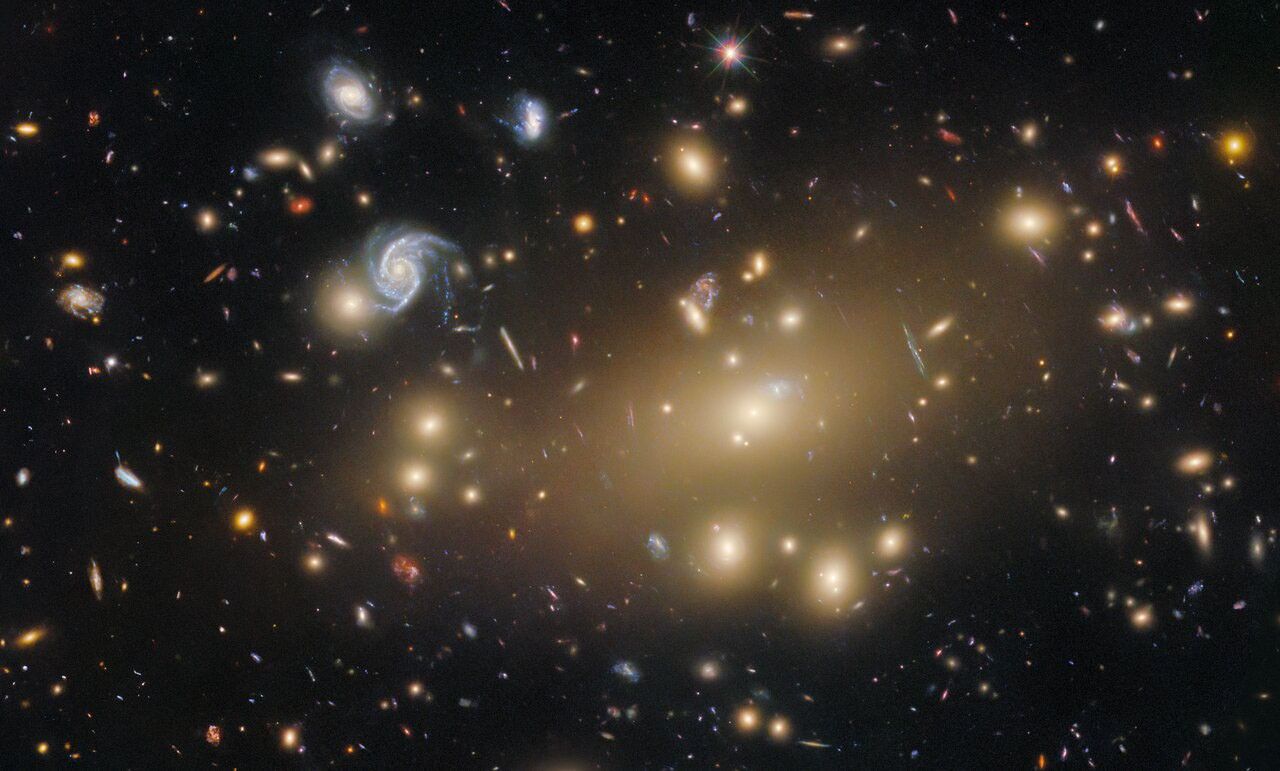
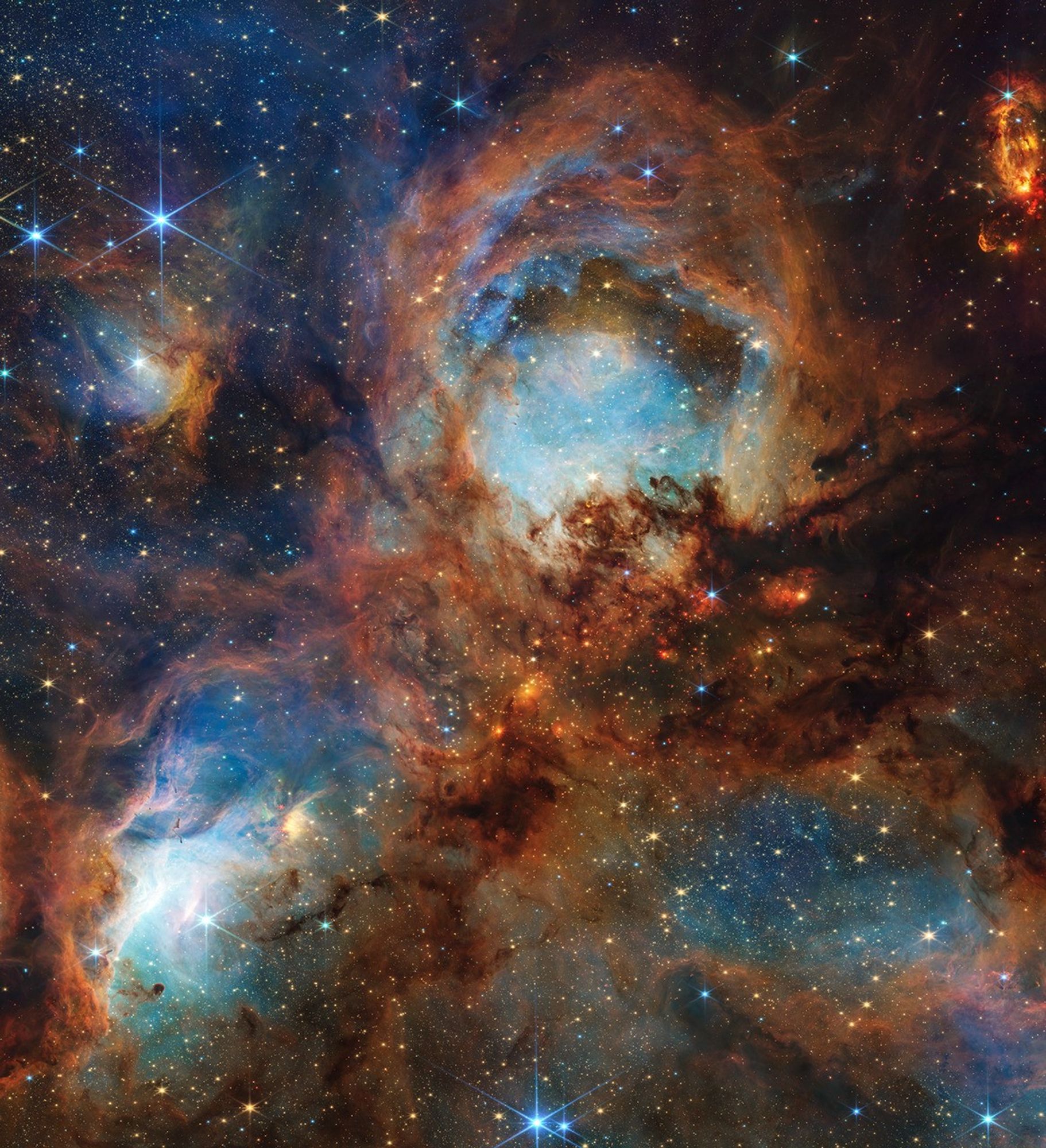
Intricate wisps of glowing gas float amid a myriad of stars in this image created by combining data from NASA's
and the
. The gas is a supernova remnant, cataloged as N132D, ejected from the explosion of a massive star that occurred some 3,000 years ago. This titanic explosion took place in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a nearby neighbor galaxy of our own Milky Way. It is estimated that the star that exploded as a supernova to produce the N132D remnant was 10 to 15 times more massive than our own sun.
This marks the first Hubble Heritage image that combines pictures taken by two separate space observatories.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)