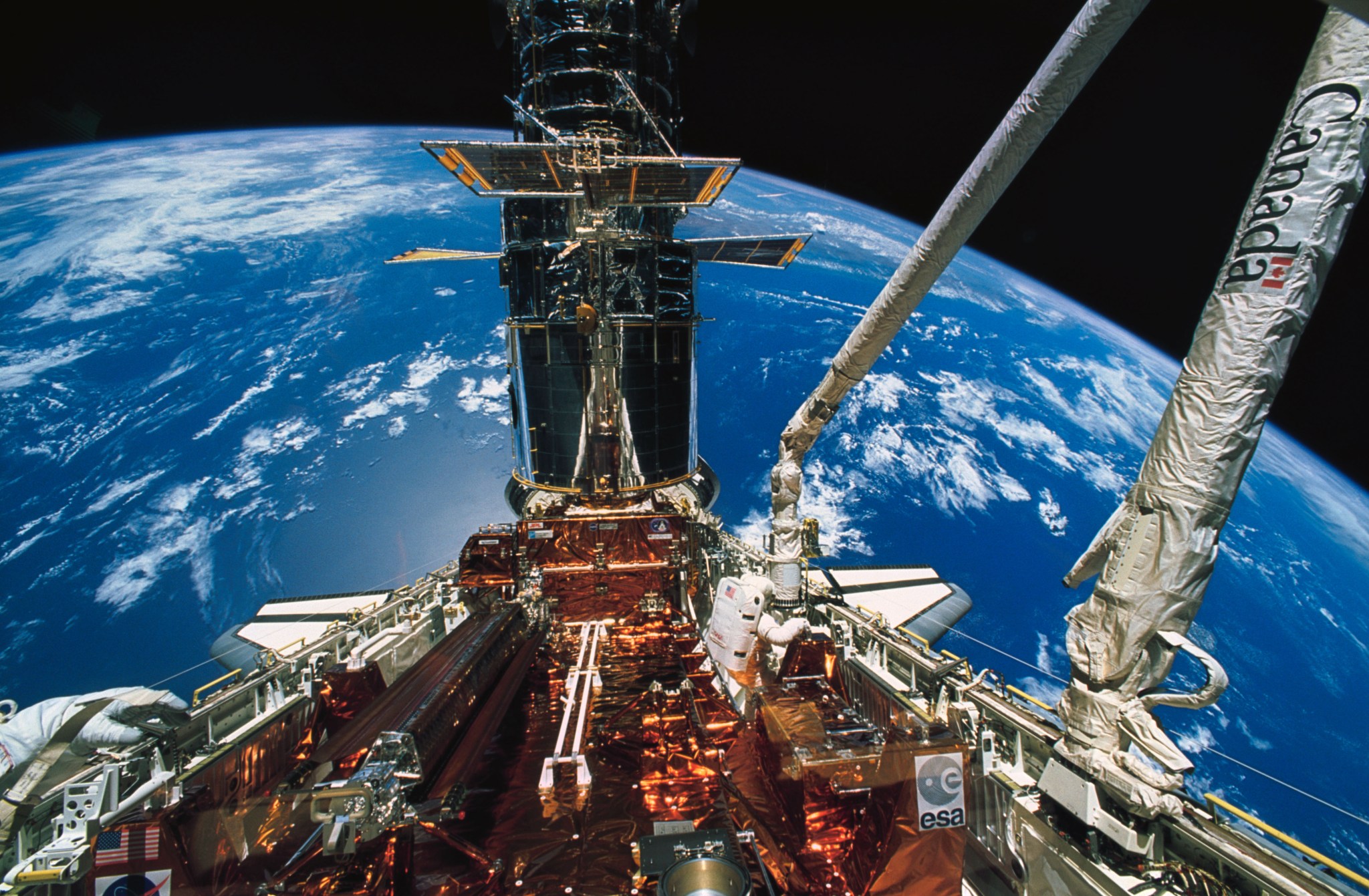
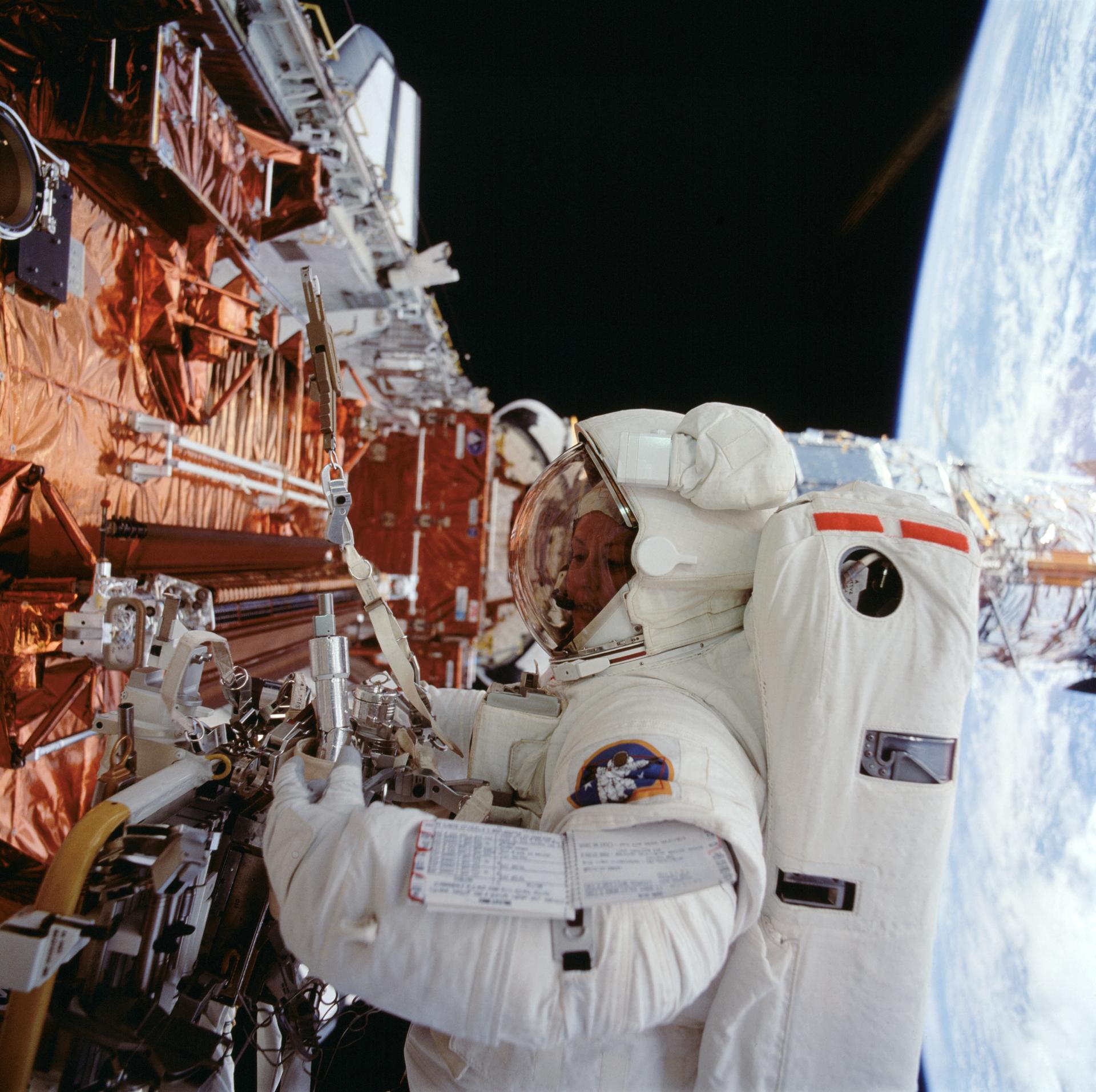
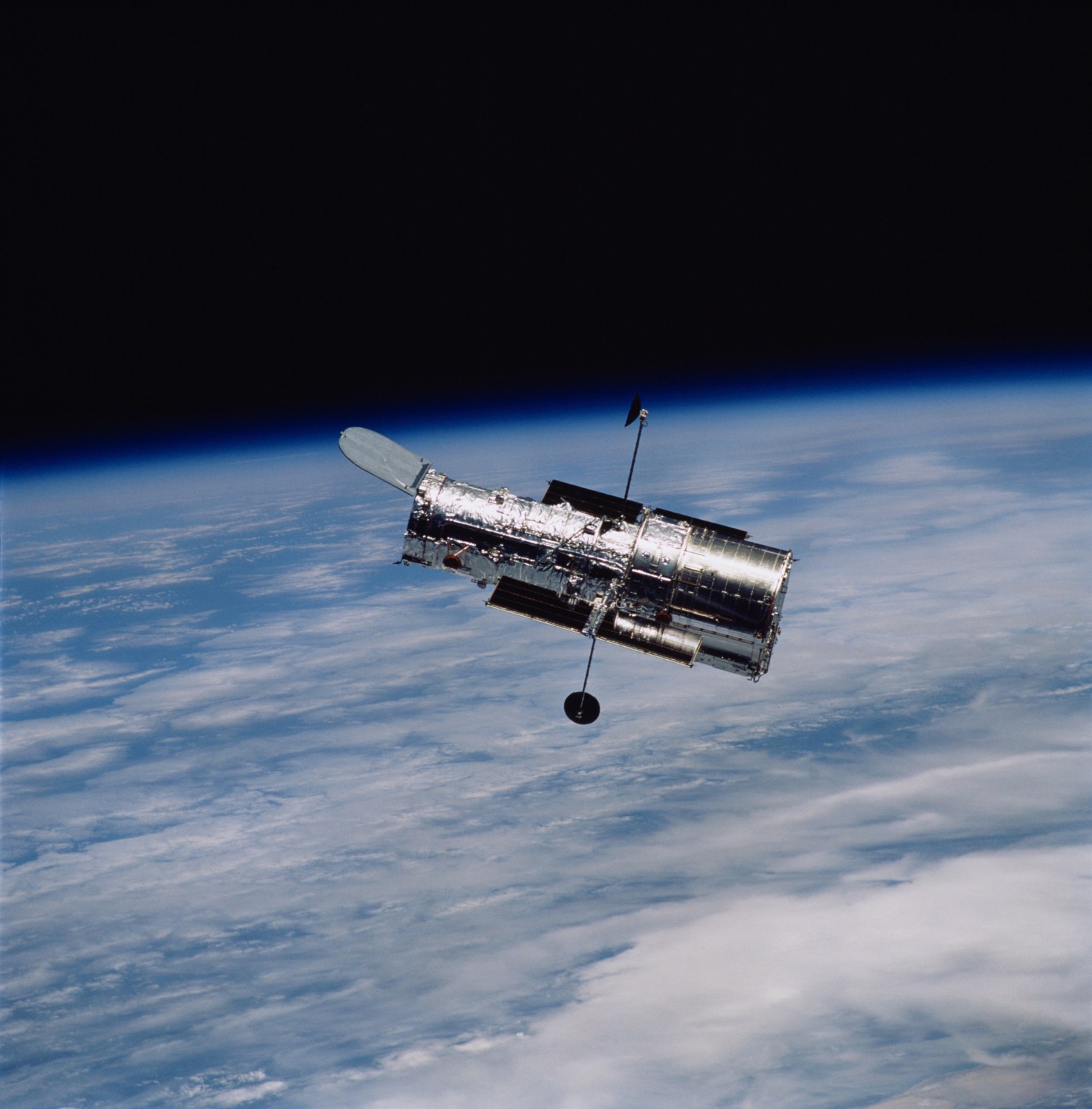
In the pre-dawn hours on Dec. 2, 1993, the space shuttle Endeavour launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida on a critical mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope.
Hubble was designed to be serviced in space with components that astronauts can slide in and out of place. But prior to launch, no one expected the first servicing mission to be of such urgency.
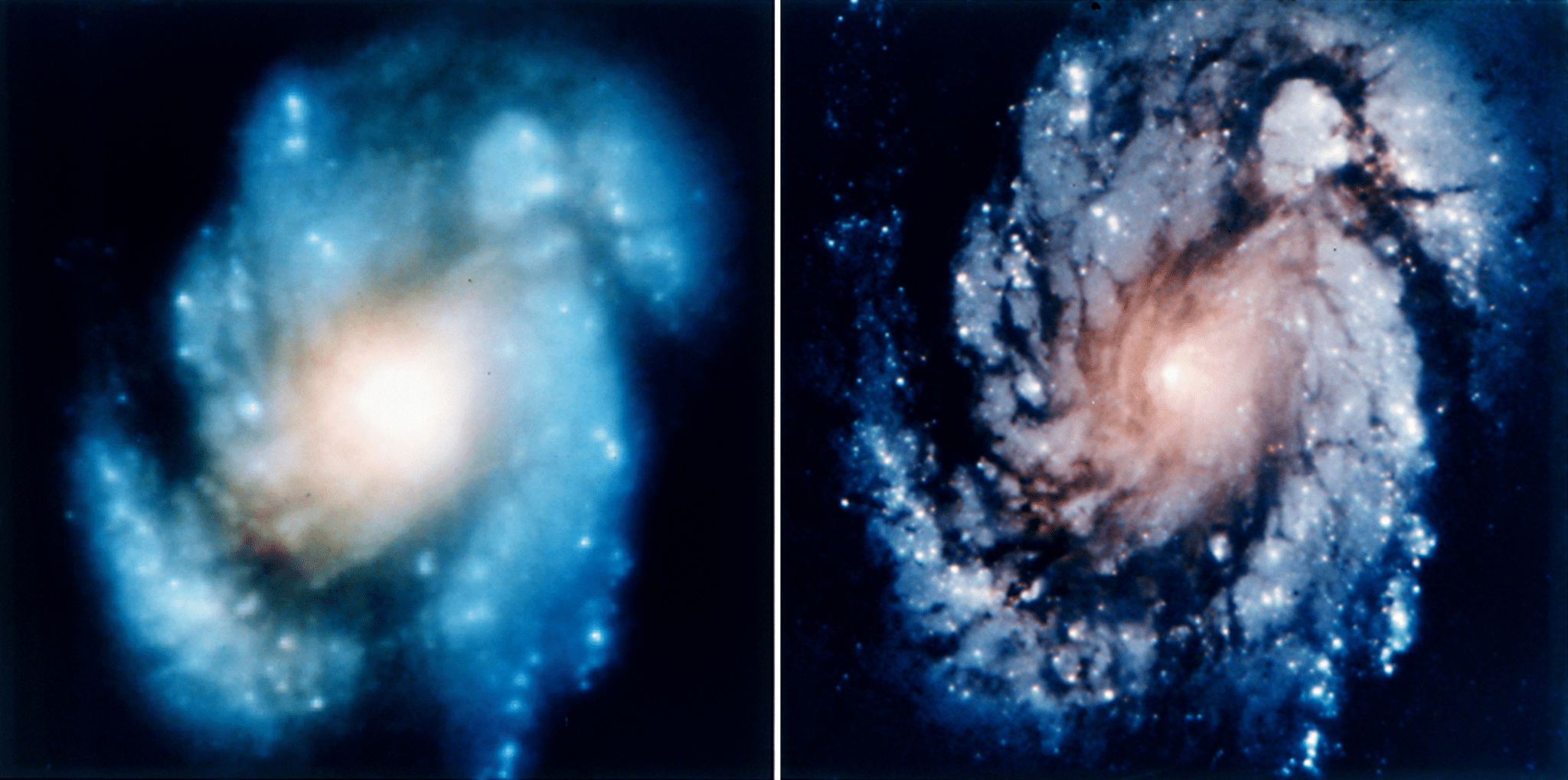
For three years, Hubble had been the punchline of late-night comics and editorial cartoons: the telescope that couldn’t see straight. Since its deployment in 1990, the telescope had been beaming blurry images back to Earth, the result of a flaw in the shape of its primary mirror. Though the mirror was off by only one-fiftieth the width of a human hair, the error had devastating consequences: the light from the mirror didn’t focus quite right. While the images were still better than those taken from Earth and science was still possible, their quality was not what the world expected.
The sense that you got was everybody was looking at the servicing and repair of the Hubble Space Telescope as the mission that could prove NASA’s worth … There was this overarching focus and pressure on the success of this mission.

Richard Covey
Servicing Mission 1 Astronaut
Servicing Mission 1 was the solution. Aboard the shuttle were the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) and Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR), along with other critical components to upgrade the telescope. WFPC2, responsible for the telescope’s visually impactful images, had built-in corrective optics to compensate for the mirror flaw and would replace the Wide Field/Planetary Camera that Hubble launched with. COSTAR was a refrigerator-sized component containing a constellation of mirrors, some only the size of a U.S. nickel, intended to correct and redirect light to the telescope’s other cameras and spectrographs.
The shuttle’s crew of seven astronauts was aware that not only Hubble’s fate was on their shoulders, but the public perception of NASA and its space program as well.
“If the Hubble repair is a failure, we can write off space science for the foreseeable future,” John Bahcall, the late astrophysicist who advocated for the telescope and a member of its science working group, told the New York Times in 1993.
On Dec. 2, 2023, NASA commemorates the 30th anniversary of Servicing Mission 1 and its success in transforming Hubble into one of NASA’s greatest triumphs: a shining example of human ingenuity in the face of adversity.
During one of the most complex spacewalking missions ever attempted, astronauts conducted five extravehicular activities, totaling over 35 hours. They removed the High Speed Photometer instrument to add COSTAR and swapped out the original Wide Field/Planetary Camera for the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. They also installed other critical components to upgrade the telescope.

At 1 a.m. on December 18, 1993, about a week after the mission had ended, astronomers gathered around computers at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore to witness the first new image from the telescope: a star, shining clear and pristine in the image without the hazy effects of Hubble’s flawed mirror. The new images were so dramatically different that even though the telescope needed around 13 weeks for adjustment to reach its full capabilities, NASA released them early. “It’s fixed beyond our wildest expectations,” said Ed Weiler, Hubble chief scientist during SM1, at a January 1994 press conference.
The look on people’s faces as this picture came up – this was an old [cathode ray] tube-type TV. It took a while for it to build up, but it got clearer and clearer and clearer. Everybody starts shouting.

Ed Weiler
Hubble chief scientist during SM1
Senator Barbara Mikulski of Maryland, who had advocated diligently for Hubble, was the first to show off the new images to the public at the Jan. 13 press conference. “I’m happy to announce today that after its launch in 1990 and some of its earlier disappointments, the trouble with Hubble is over,” she said.
Though Servicing Mission 1 is best remembered for its resolution of Hubble’s blurry vision, it accomplished a host of additional tasks that helped transform the telescope into the astronomical powerhouse it remains today.
By the time Servicing Mission 1 launched, the telescope’s gyroscopes – delicate pieces of equipment required to steer and point Hubble – were already breaking down. Three of the six gyroscopes, or gyros, aboard Hubble had failed. The other three – typically kept as backups – were in operation, the minimum number needed to keep Hubble collecting science data. Astronauts replaced four gyroscopes, a fix that would help keep the telescope running smoothly for several years.
Early in Hubble’s time in orbit, NASA discovered that the telescope’s solar arrays would expand and contract excessively in the alternating heat and cold of space as the telescope traveled in and out of sunlight, causing them to vibrate. This forced engineers to use Hubble’s computing capacity to compensate for the “jitter” and reduced observation time. Astronauts replaced Hubble’s solar arrays with new versions that brought the natural jitter down to acceptable levels.
Astronauts also performed an augmentation whose vital importance would become clear a year later: upgrading Hubble’s flight computer with a co-processor and associated memory. Just weeks before the disintegrating comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 collided with Jupiter in 1994, Hubble went into a protective “safe mode” due to a memory unit problem in the main computer. Engineers were able to use that co-processor’s memory to fix the problem, capturing stunning images of the gas giant being pummeled by comet fragments.
Servicing Mission 1’s impact echoed far beyond Hubble. The mission was a showcase for tasks that could be done in space, proving humanity’s ability to perform highly complex work in orbit. The lessons learned from training for Hubble and from the servicing work itself would be built upon for other astronaut missions, including the four subsequent servicing visits to Hubble between 1997-2009. These additional missions to Hubble would enable the installation of new, cutting-edge instruments, repair of existing science instruments, and the replacement of key hardware, keeping Hubble at the forefront of astrophysics exploration.
Further, the lessons learned from Servicing Mission 1 were a guiding force for work on the International Space Station, and for missions yet to occur. “A lot of the knowledge that was developed there transferred directly to construction of the International Space Station and it’ll transfer to the things we do with [the future orbiting lunar space station] Gateway someday,” said Kenneth Bowersox, associate administrator for NASA’s Space Operations Mission Directorate, who was also an astronaut on Servicing Mission 1. “And it’ll apply to things we do on the Moon and in deep space, going to Mars and beyond. It all links.”
To celebrate Servicing Mission 1, NASA is releasing a series of videos over the next two weeks featuring key players – astronauts, scientists, engineers, and more – as they reflect on the struggles and triumphs of that time, as well as the emotional and personal impact that Hubble and SM1 had on their lives. Follow @NASAHubble on X, Instagram, and Facebook, or go to nasa.gov/hubble to watch as the series kicks off this weekend.