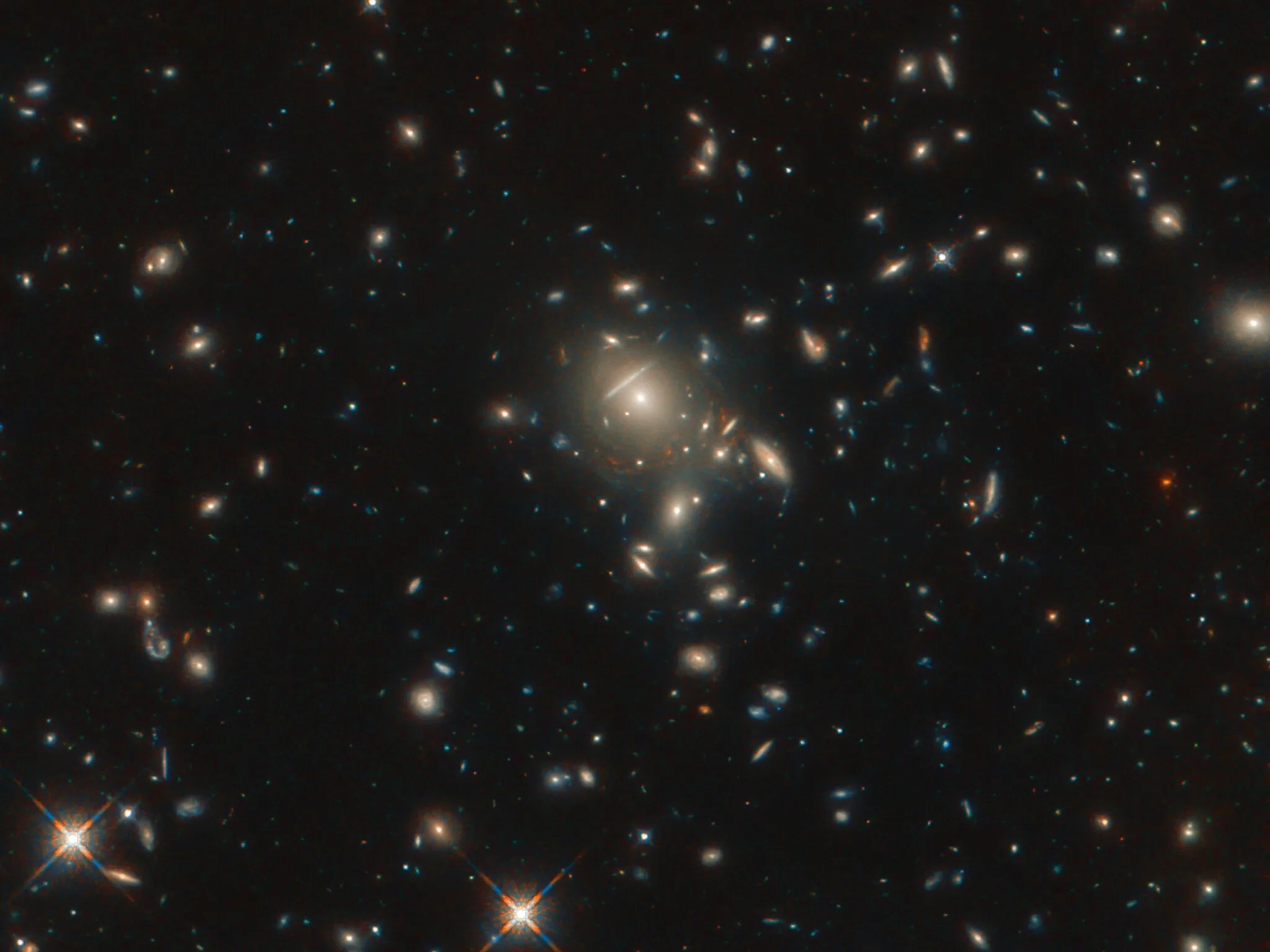
Seen here in incredible detail, thanks to the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, is the starburst galaxy formally known as PLCK G045.1+61.1. The galaxy, which appears as multiple reddish dots near the center of the image, is being gravitationally lensed by a cluster of closer galaxies, also seen in the image.
Gravitational lensing occurs when a large distribution of matter, such as a galaxy cluster, sits between Earth and a distant light source. As space is warped by massive objects, the light from the distant object bends as it travels to us, creating stretched, magnified and sometimes multiple images of the lensed object. This effect was first predicted by Einstein’s general theory of relativity.
From 2009 to 2013, the European Space Agency’s Planck space observatory captured multiple all-sky surveys. In the course of these surveys, with complementary observations by the Herschel Space Observatory, Planck discovered some of the brightest gravitationally lensed, high-redshift galaxies in the night sky.
It was during the study of these Planck-Herschel selected sources using Hubble that the optical starlight emitted from this ultra-bright galaxy was found.
Text credit: ESA (European Space Agency)