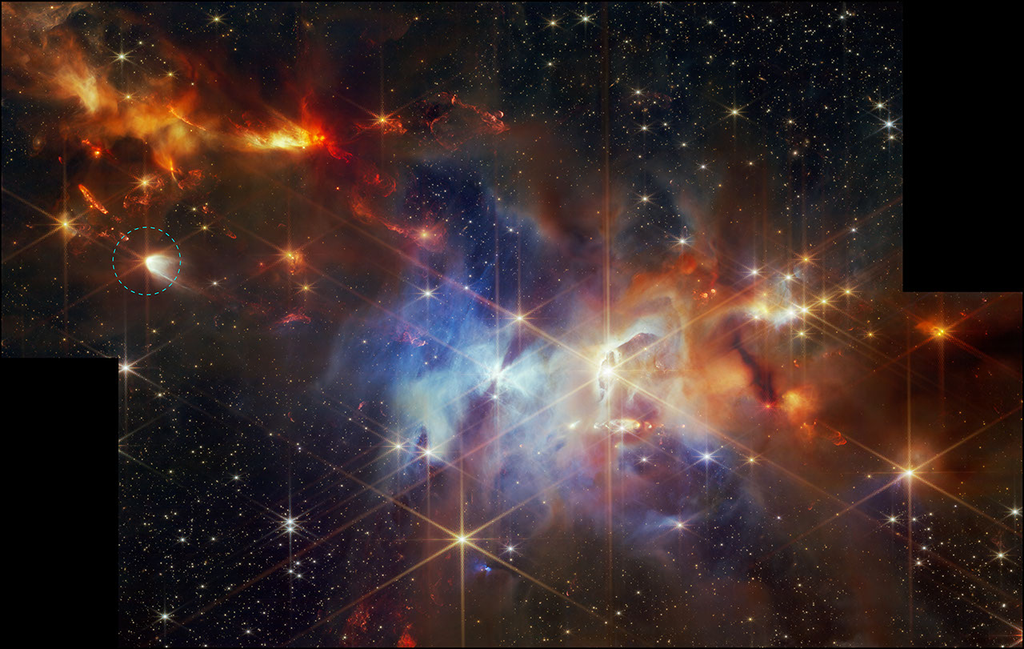
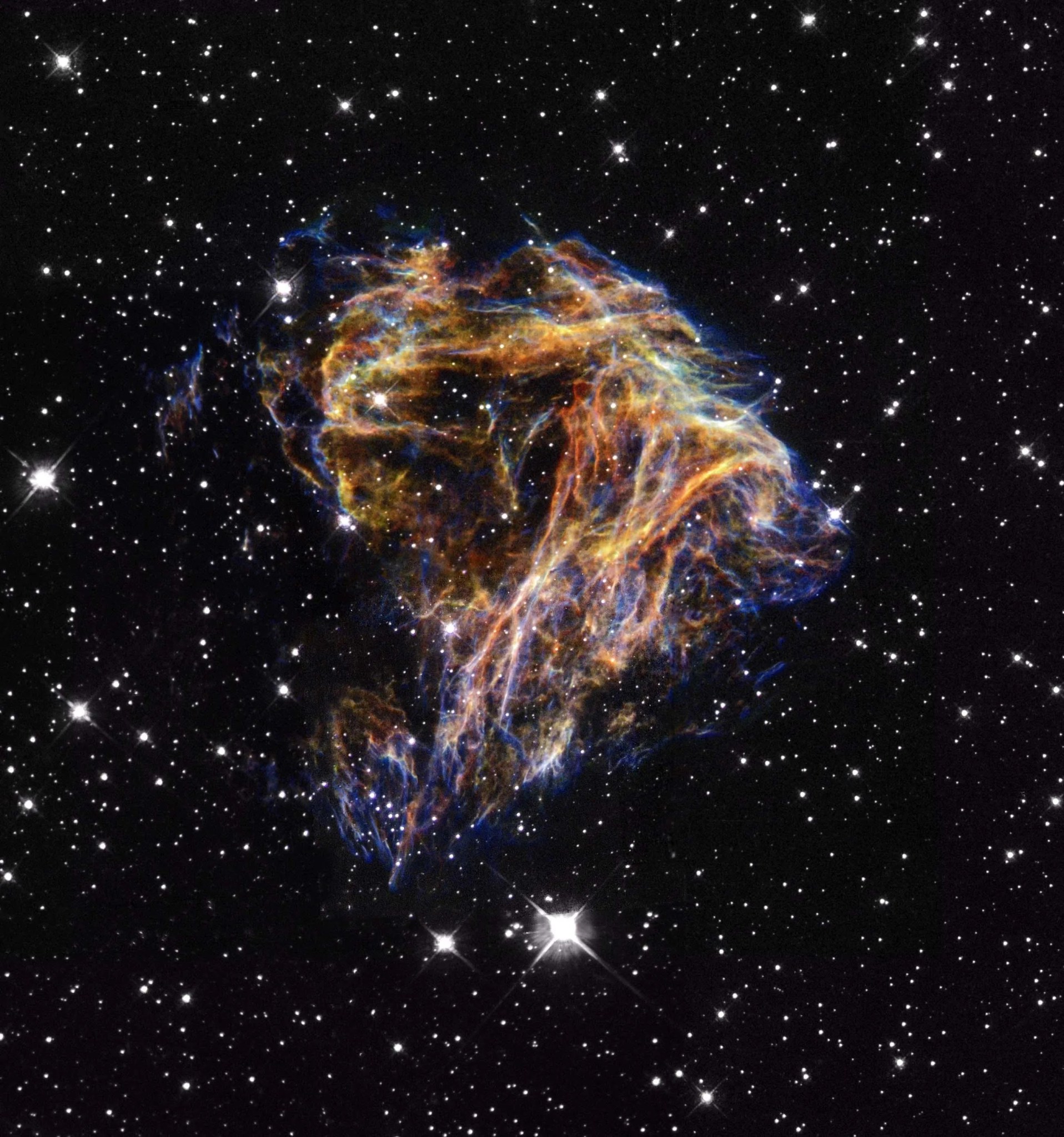
Resembling the puffs of smoke and sparks from a summer fireworks display, these delicate filaments are actually a supernova remnant within the Large Magellanic Cloud, a nearby small companion galaxy to the Milky Way visible from the southern hemisphere. Denoted N 49, or DEM L 190, this remnant is from a massive star that died in a supernova blast whose light would have reached Earth thousands of years ago. This filamentary material will eventually be recycled into building new generations of stars. Our own Sun and planets are constructed from similar debris of supernovae that exploded in the Milky Way galaxy billions of years ago.
Image Credit: NASA
1 min read
Like a Whiff of Smoke
Share
Details
Last Updated
Apr 17, 2023