After 15 years, the mission of NASA's Opportunity rover has come to an end, but its successes on Mars have earned it a spot in the robot hall of fame. Here's what you need to know about our intrepid Martian overachiever:
1. Opportunity was a twin.
The Mars Exploration Rovers mission featured two identical, golf-cart-sized, solar-powered rovers: Spirit and Opportunity. Spirit landed at Gusev Crater on Jan. 4, 2004. Opportunity landed on the opposite side of Mars at Meridiani Planum on Jan. 24, 2004 PST (Jan. 25 EST). Both rovers were managed for NASA by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California.
2. Opportunity and Spirit showed that Mars had the wet and warm conditions in its ancient past that were potentially hospitable to life.
Foremost among Spirit and Opportunity's many science discoveries: Mars was likely wetter and warmer in the past. These conditions could have served as a cradle for life on Mars at a time when life first emerged on Earth.
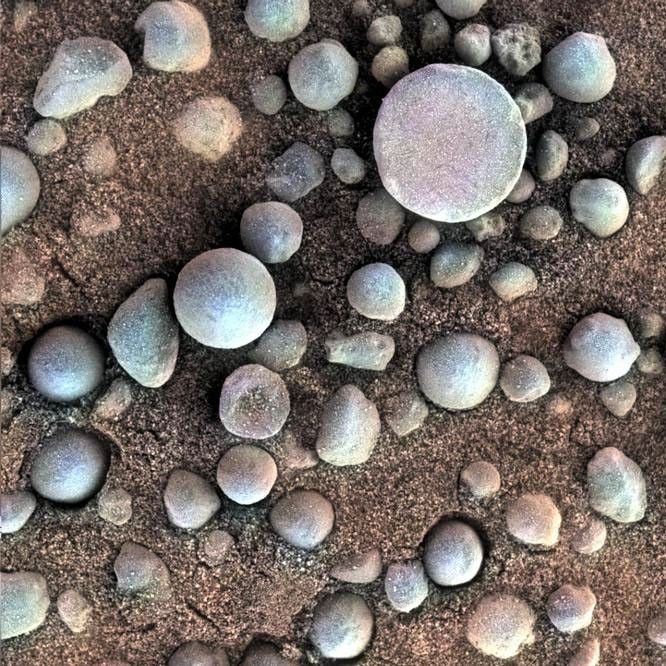
Opportunity contributed several key findings to this conclusion. It was the first rover to identify and characterize sedimentary rocks on a planet other than Earth. Opportunity's measurements showed these rocks formed in ancient ephemeral playas. Opportunity also discovered small spheres of hematite nicknamed "blueberries" that formed late from rising, acidic groundwater. Once Opportunity reached the rim of Endeavour crater, the rover found white veins of the mineral gypsum — a telltale sign of water that traveled through underground fractures. Opportunity also found more compelling signs of Mars' watery past in the rocks of Endeavour Crater: clay minerals that formed in neutral-pH (not too acidic, not too basic) water. Of all the places studied by Opportunity, the environment at Endeavour had the friendliest conditions for ancient microbial life.
3. Opportunity is an off-world record holder.
Opportunity worked longer on the surface of Mars than any other robot — more than 14 years. This far exceeded the original 90-day mission planned for Opportunity and Spirit.
During Opportunity's time on Mars, it also drove a total of 28.06 miles (45.16 kilometers), clinching the record for longest drive on another world in 2014.
4. Opportunity was the little rover that could.
Opportunity didn't survive for over 14 years because its mission was easy. It encountered challenges that required its engineers to be resourceful. For instance, the rover's right-front wheel sometimes drew more current than the other wheels, so engineers often drove the rover backward to extend the right front wheel's life.
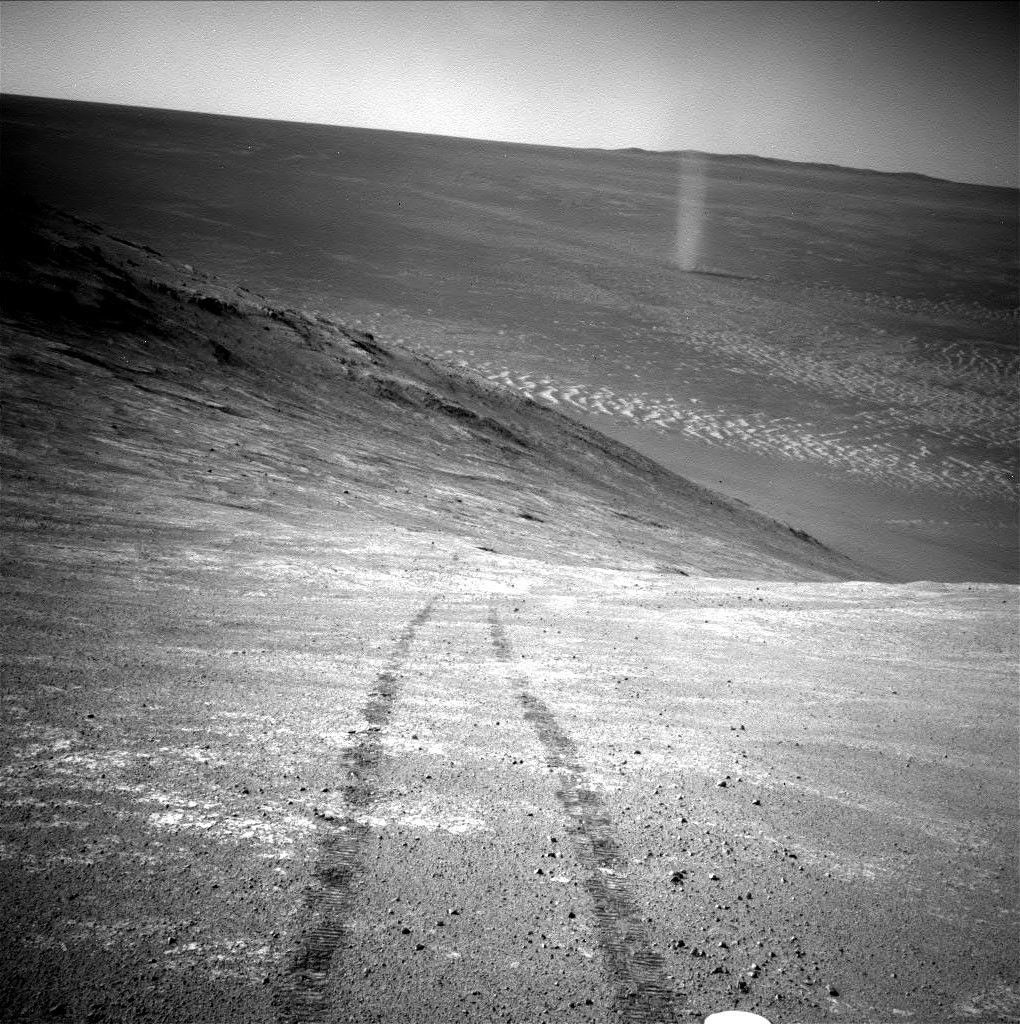
The terrain was treacherous. After the rover landed at Eagle Crater, its wheels slipped on the loose slopes when it first attempted to drive out of the crater. Rover planners had to come up with creative driving strategies to get out — something they did again at Endurance Crater, where slopes were as steep as 31 degrees. On April 26, 2005, Opportunity's wheels dug into a soft, wind-sculpted sand ripple and got stuck for several nail-biting weeks at "Purgatory Dune." But after extensive testing in a Mars-like sandbox at JPL, the team was able to carefully shimmy out of the Martian sand trap.
Opportunity encountered two mission-threatening dust storms that blocked sunlight from reaching its solar panels. It survived a dust storm in 2007 by minimizing activities and maintaining enough power in its batteries to recover when the skies cleared. Unfortunately, the 2018 dust storm blotted out even more sunlight and kept the skies above Opportunity dark about a month longer.
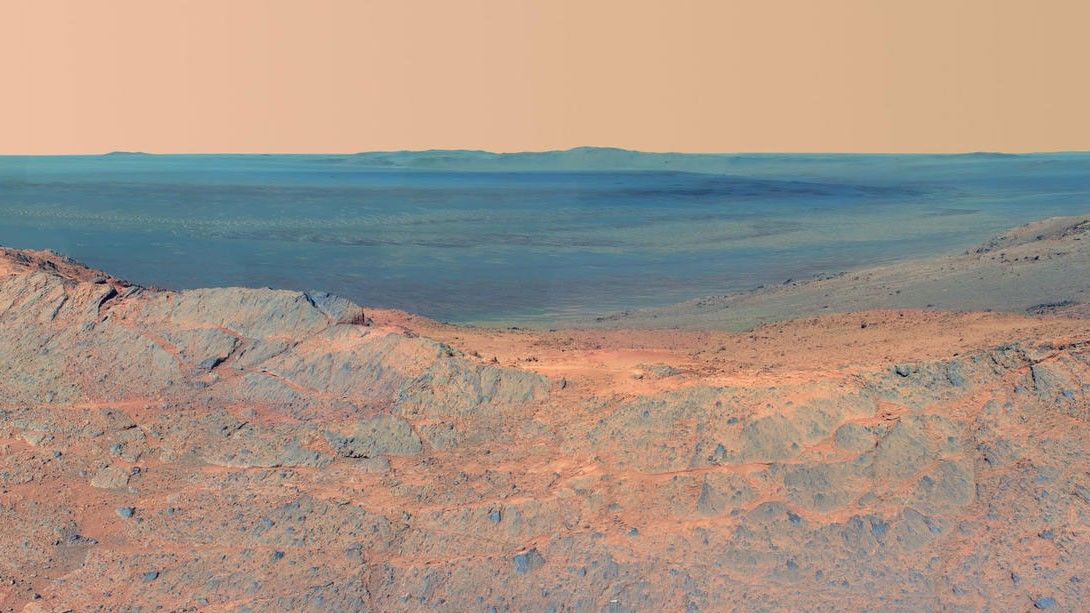

5. Opportunity and Spirit showed us the beauty of Mars.
Opportunity and Spirit were avid documentarians, giving us a human-scale view of what it was like to be on Mars. They returned over 342,000 raw images, which were promptly posted online for everyone's enjoyment. These two rovers also produced 31 stunning 360-degree color panoramas.
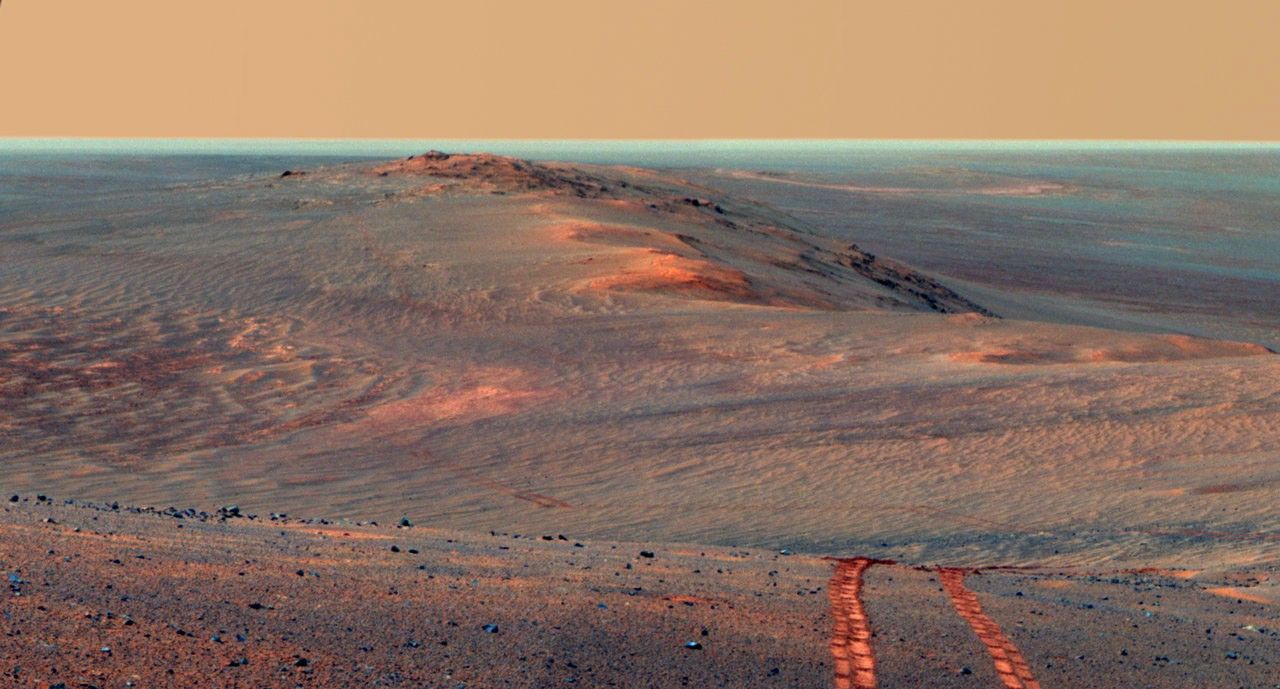
The most memorable images Opportunity took — including ripples of sand that resembled waves on water, patches of jumbled rock on a crater rim, whirling dust devils and its own tracks along a ridge — revealed the otherworldly beauty of Mars and the drama of exploration.
6. The story of Opportunity and Spirit is not over. Their lessons live on in current and future Mars missions.
The success of the Mars Exploration Rovers helped drive the growth of NASA's Mars program, building support for orbiters and new kinds of rovers. Spirit and Opportunity showed how mobile robots on Mars could communicate reliably with Earth (either directly or by employing orbiters around Mars as relays back to our home planet), use 3-D vision to navigate the Martian terrain and make autonomous science observations.
Curiosity and the upcoming Mars 2020 rovers build upon the lessons of Spirit and Opportunity. And scientists will continue to make new discoveries from the Mars Exploration Rovers data for years to come.
Spirit and Opportunity have been a fertile training ground for the many hundreds of engineers and planetary scientists who have learned at their robotic knees. A number have gone on to lead other space missions. Many of those currently operating Opportunity are sharing their expertise part-time with other missions exploring our solar system. For most, working on Spirit and Opportunity has been transformative. You can read many of their stories here.
For more highlights of the Mars Exploration Rover mission, visit:
https://mars.nasa.gov/mer/highlights/
News Media Contact
Jia-Rui Cook
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-354-5011
jccook@jpl.nasa.gov