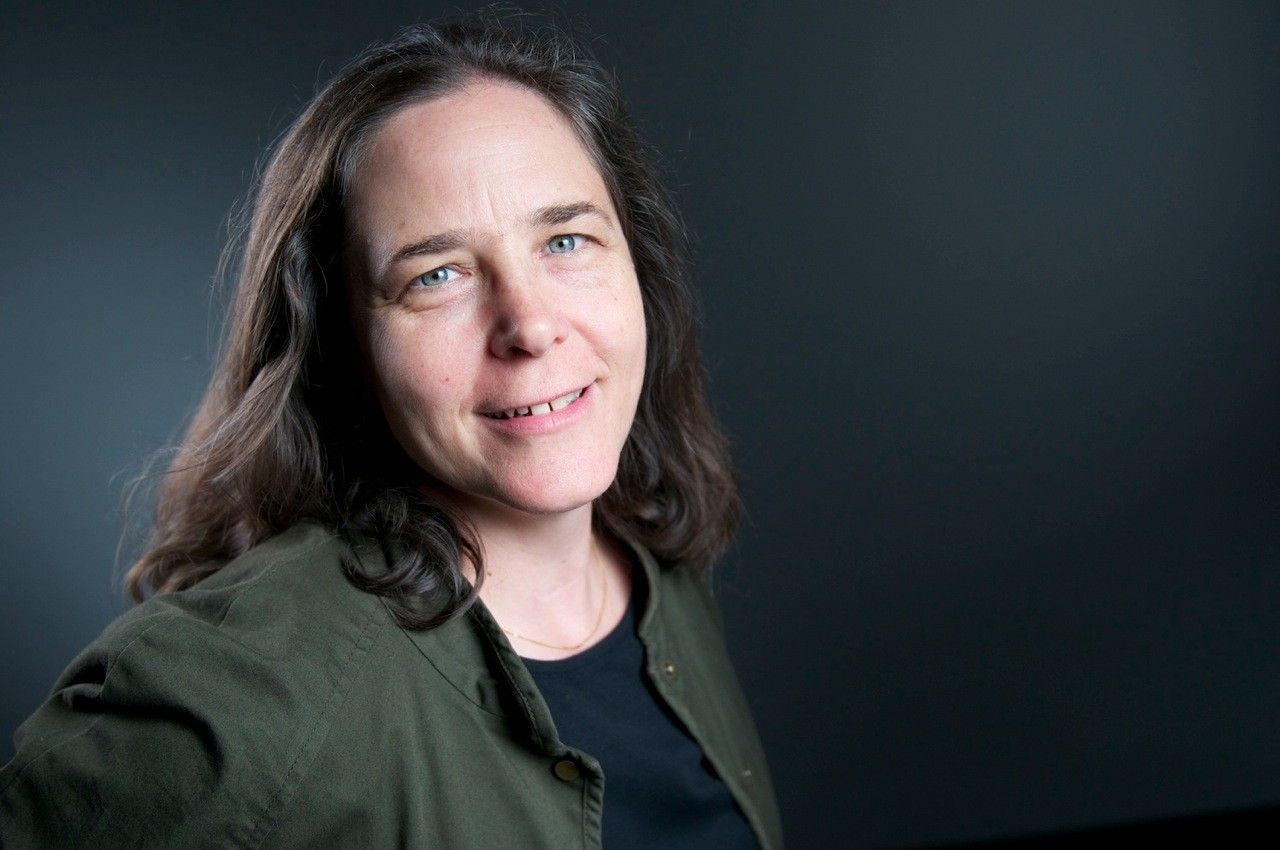
Dr. Annmarie Eldering has been with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) mission since 2010, and has been collaborating with NASA Jet Propulsion Lab since she was a gradate student at neighboring Caltech in 1990.
As OCO-2’s Deputy Project Scientist, she coordinates various teams working to make the mission happen. She helps oversee the algorithm (the calculations used to obtain accurate measurements from the instrument), data validation (the process of checking that the measurements taken from the satellite match those taken from the ground), data calibration (converting raw data numbers to meaningful physical measurements) and data processing.
Eldering started out at NASA working on a satellite instrument called the Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer (TES) that involves studying air-pollution gases, and in particular the effect of clouds, pollution and volcanic aerosols on the measurements taken. Her job is to ensure the data from OCO-2 are of a high-enough quality to enable good science.
What excites you about the job?
My job is totally fun because I work with a group of really smart, motivated people. We have made real progress getting ready for the OCO-2 launch by working with data from a Japanese satellite. We are at a really exciting time – about 30 days from launch! We think we are ready for the real data from space, but are a little nervous – the first look at data often contains surprises!
In addition, the science that drives the OCO-2 mission is really important – we will be able to make an important contribution to the science of climate change with the measurements from OCO-2. To me, that is really motivating.
OCO-2 will soon be in orbit above the Earth. What are you most looking forward to about the mission?
I’m looking forward to the excitement of the first year – getting the first data down from the satellite, making sure the algorithm works properly, delivering those data to the science community and seeing what they learn from it. In short, I’m looking forward to the challenge and the anticipated sense of success when we deliver the science data.
Complete this sentence: At heart, I'm just a frustrated …
bike racer. I love cycling for fun, exercise, to get around, explore and compete. A dream of mine is to ride (and complete) a Tour de France route!
What do you think the mission’s legacy will be?
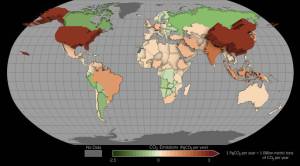
I think OCO-2 will clearly show that we can make very precise, global measurements of carbon dioxide from space. It will reduce uncertainty about how the atmosphere, plants and oceans cycle carbon dioxide from one to the other. I expect that our data will be more precise than any that have come before, and they will form the basis for the next generation of satellite-based carbon dioxide measurements. Measuring carbon dioxide is critical to completely understanding our climate.
After OCO-2, what's next for you?
OCO-3! I'm also working on the OCO-3 [Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3] project, which involves taking the spare OCO-2 instrument, repackaging it and installing it on the International Space Station. Getting the funding needed to do this is challenging at the moment, but I’m confident we will overcome that hurdle. OCO-3 would be a great complement to OCO-2 because of the differences in orbit and time-of-day information, and the fact that OCO-3 would be able to map out carbon dioxide over local regions.
How would you like to be remembered?
As an excellent leader that helped the team get the job done. As someone who delivered high-quality science data on time and communicated clearly to the outside science community what the data contains.