Diversity of “Séítah” Minerals
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/CRISM/CTX/HRSC/MSSS/USGS |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
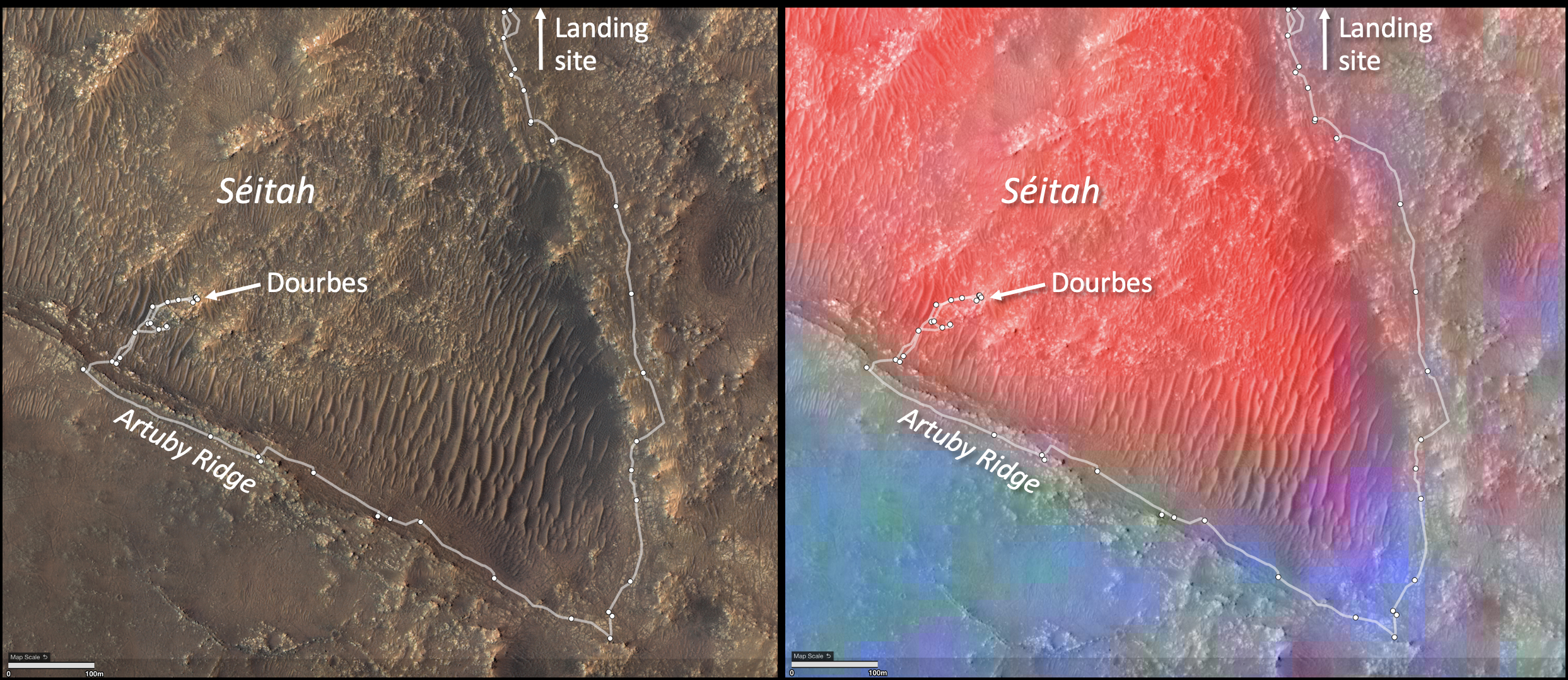
These annotated images show two views of the "Séítah" geologic unit of Mars’ Jezero Crater. The map on the left shows terrain features of the crater with annotations depicting the rover’s route during its first science campaign. "Artuby" is a ridgeline running along a portion of the southern boundary of Séítah. "Dourbes" is the name of an abrading target on a rock in South Séítah.
The multi-hued map on the right shows the diversity of igneous (solidified from lava or magma) minerals in the same region. Olivine is shown in red. Calcium-poor pyroxene in green. Calcium-rich pyroxene is in blue.
A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust).
Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California, built and manages operations of the Perseverance rover.
For more about Perseverance: