A new NASA study reveals a surprising way planetary cores may have formed—one that could reshape how scientists understand the early evolution of rocky planets like Mars.
Conducted by a team of early-career scientists and long-time researchers across the Astromaterials Research and Exploration Science (ARES) Division at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, the study offers the first direct experimental and geochemical evidence that molten sulfide, rather than metal, could percolate through solid rock and form a core—even before a planet’s silicate mantle begins to melt.
For decades, scientists believed that forming a core required large-scale melting of a planetary body, followed by heavy metallic elements sinking to the center. This study introduces a new scenario—especially relevant for planets forming farther from the Sun, where sulfur and oxygen are more abundant than iron. In these volatile-rich environments, sulfur behaves like road salt on an icy street—it lowers the melting point by reacting with metallic iron to form iron-sulfide so that it may migrate and combine into a core. Until now, scientists didn’t know if sulfide could travel through solid rock under realistic planet formation conditions.
Working on this project pushed us to be creative. It was exciting to see both data streams converge on the same story.

Dr. Jake Setera
ARES Scientist with Amentum
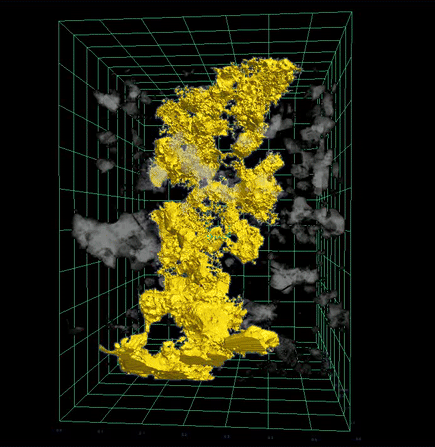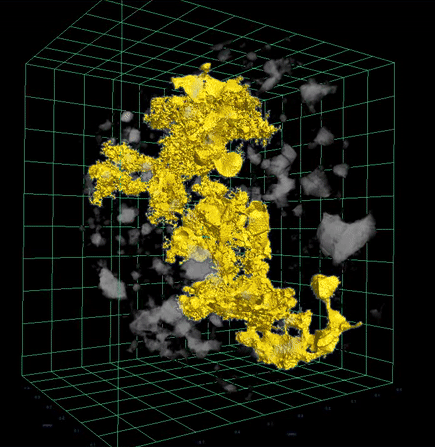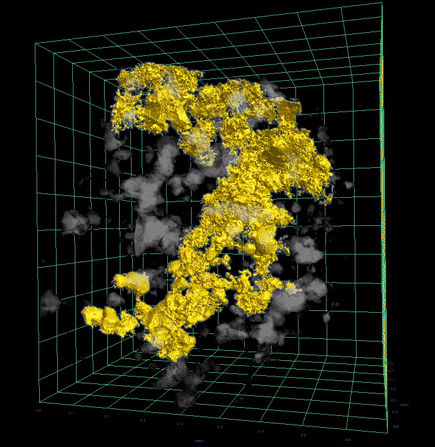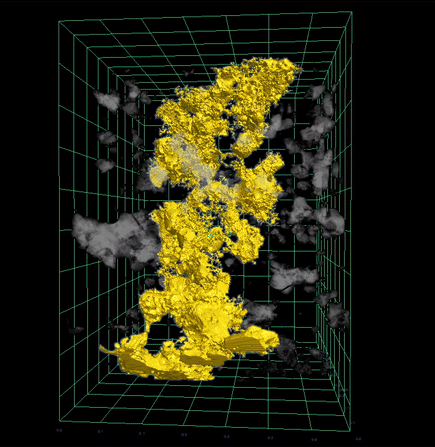
The study results gave researchers a way to directly observe this process using high-resolution 3D imagery—confirming long-standing models about how core formation can occur through percolation, in which dense liquid sulfide travels through microscopic cracks in solid rock.
“We could actually see in full 3D renderings how the sulfide melts were moving through the experimental sample, percolating in cracks between other minerals,” said Dr. Sam Crossley of the University of Arizona in Tucson, who led the project while a postdoctoral fellow with NASA Johnson’s ARES Division. “It confirmed our hypothesis—that in a planetary setting, these dense melts would migrate to the center of a body and form a core, even before the surrounding rock began to melt.”
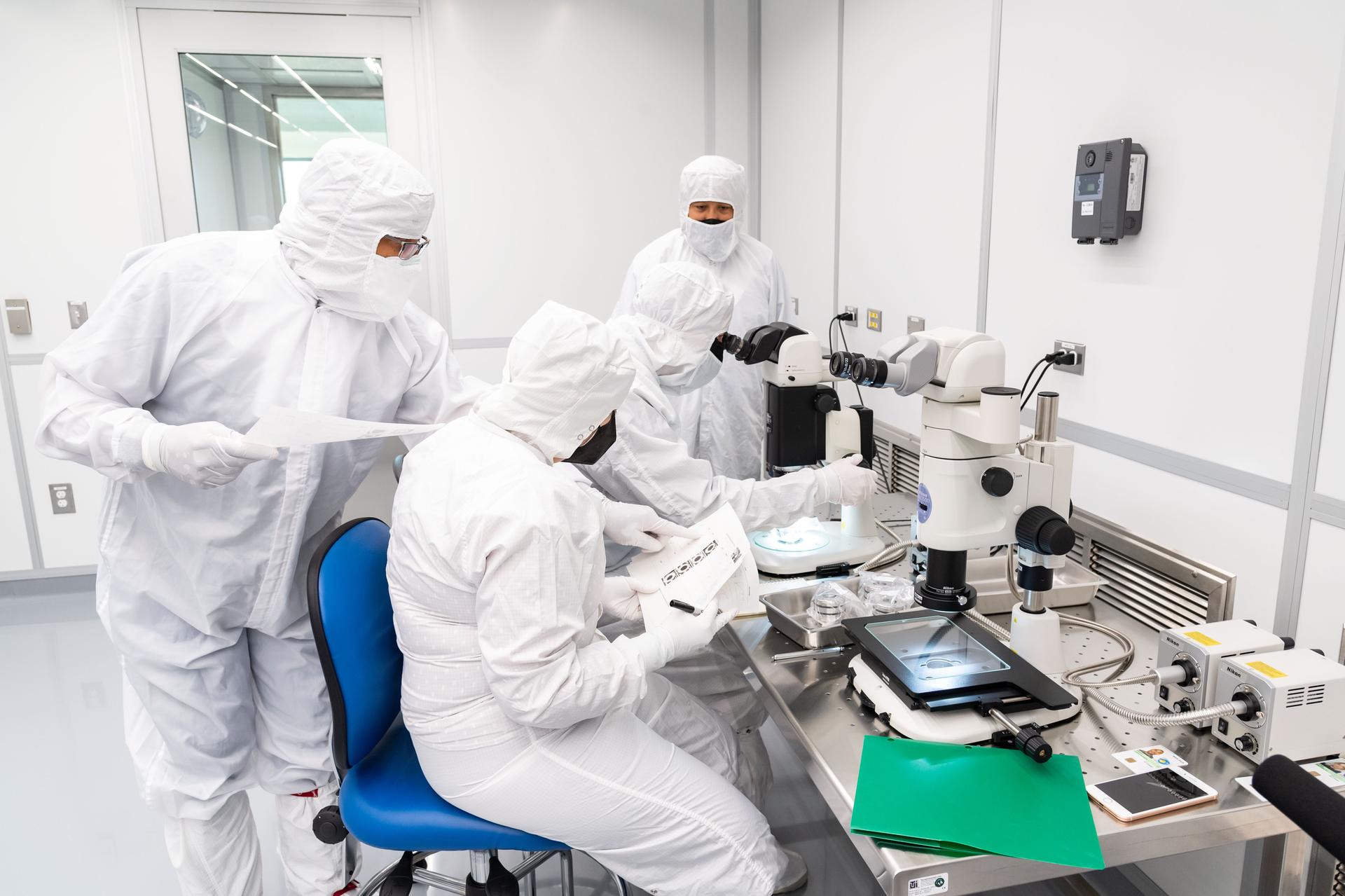
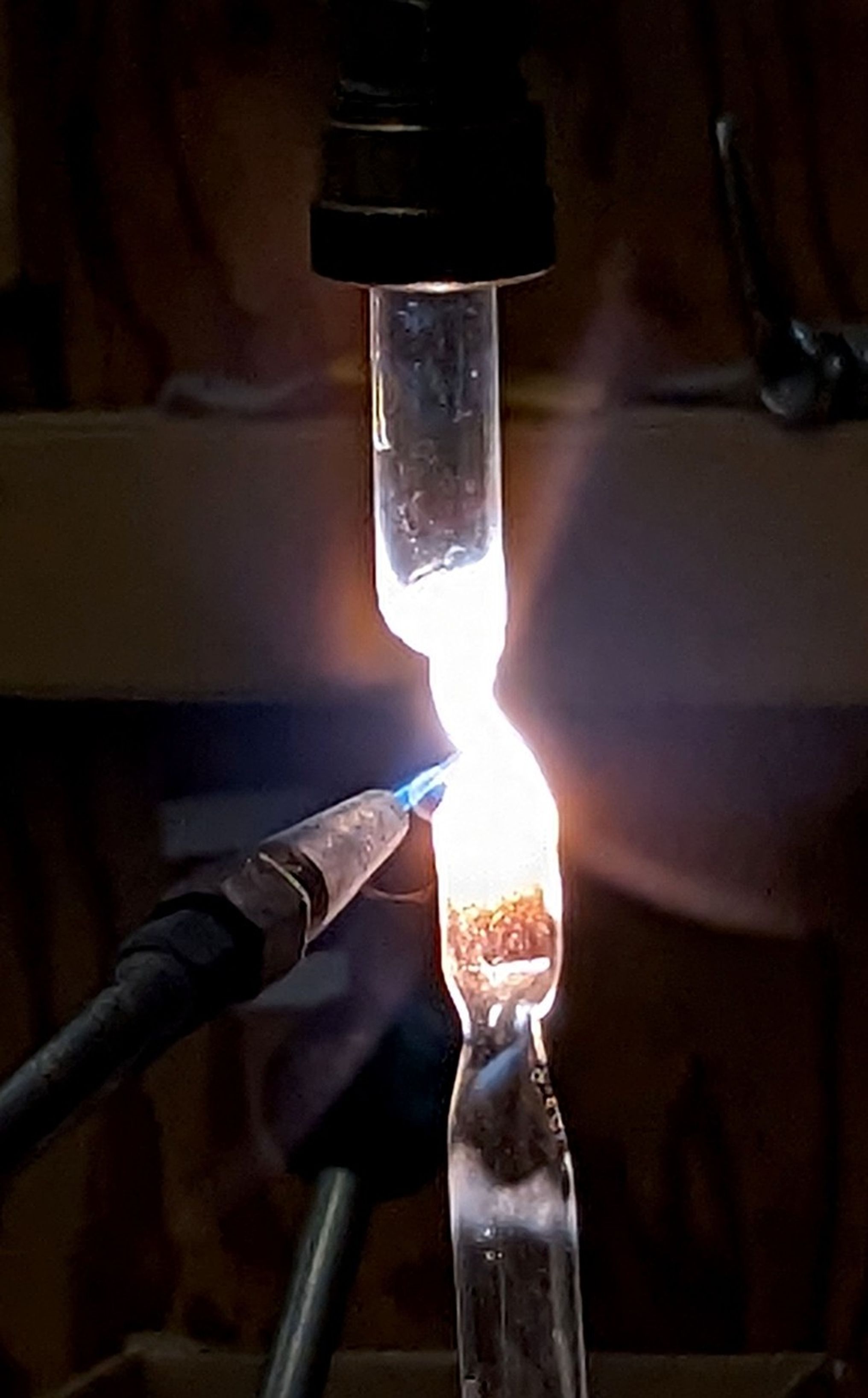
Recreating planetary formation conditions in the lab required not only experimental precision but also close collaboration among early-career scientists across ARES to develop new ways of observing and analyzing the results. The high-temperature experiments were first conducted in the experimental petrology lab, after which the resulting samples—or “run products”—were brought to NASA Johnson’s X-ray computed tomography (XCT) lab for imaging.
X-ray scientist and study co-author Dr. Scott Eckley of Amentum at NASA Johnson used XCT to produce high-resolution 3D renderings—revealing melt pockets and flow pathways within the samples in microscopic detail. These visualizations offered insight into the physical behavior of materials during early core formation without destroying the sample.
The 3D XCT visualizations initially confirmed that sulfide melts could percolate through solid rock under experimental conditions, but that alone could not confirm whether percolative core formation occurred over 4.5 billion years ago. For that, researchers turned to meteorites.
“We took the next step and searched for forensic chemical evidence of sulfide percolation in meteorites,” Crossley said. “By partially melting synthetic sulfides infused with trace platinum-group metals, we were able to reproduce the same unusual chemical patterns found in oxygen-rich meteorites—providing strong evidence that sulfide percolation occurred under those conditions in the early solar system.”
To understand the distribution of trace elements, study co-author Dr. Jake Setera, also of Amentum, developed a novel laser ablation technique to accurately measure platinum-group metals, which concentrate in sulfides and metals.
“Working on this project pushed us to be creative,” Setera said. “To confirm what the 3D visualizations were showing us, we needed to develop an appropriate laser ablation method that could trace the platinum group-elements in these complex experimental samples. It was exciting to see both data streams converge on the same story.”
When paired with Setera’s geochemical analysis, the data provided powerful, independent lines of evidence that molten sulfide had migrated and coalesced within a solid planetary interior. This dual confirmation marked the first direct demonstration of the process in a laboratory setting.
The study offers a new lens through which to interpret planetary geochemistry. Mars in particular shows signs of early core formation—but the timeline has puzzled scientists for years. The new results suggest that Mars’ core may have formed at an earlier stage, thanks to its sulfur-rich composition—potentially without requiring the full-scale melting that Earth experienced. This could help explain longstanding puzzles in Mars’ geochemical timeline and early differentiation.
The results also raise new questions about how scientists date core formation events using radiogenic isotopes, such as hafnium and tungsten. If sulfur and oxygen are more abundant during a planet’s formation, certain elements may behave differently than expected—remaining in the mantle instead of the core and affecting the geochemical “clocks” used to estimate planetary timelines.
This research advances our understanding of how planetary interiors can form under different chemical conditions—offering new possibilities for interpreting the evolution of rocky bodies like Mars. By combining experimental petrology, geochemical analysis, and 3D imaging, the team demonstrated how collaborative, multi-method approaches can uncover processes that were once only theoretical.
Crossley led the research during his time as a McKay Postdoctoral Fellow—a program that recognizes outstanding early-career scientists within five years of earning their doctorate. Jointly offered by NASA’s ARES Division and the Lunar and Planetary Institute in Houston, the fellowship supports innovative research in astromaterials science, including the origin and evolution of planetary bodies across the solar system.
As NASA prepares for future missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, understanding how planetary interiors form is more important than ever. Studies like this one help scientists interpret remote data from spacecraft, analyze returned samples, and build better models of how our solar system came to be.
For more information on NASA’s ARES division, visit: https://ares.jsc.nasa.gov/
Victoria Segovia
NASA’s Johnson Space Center
281-483-5111
victoria.segovia@nasa.gov