4 min read
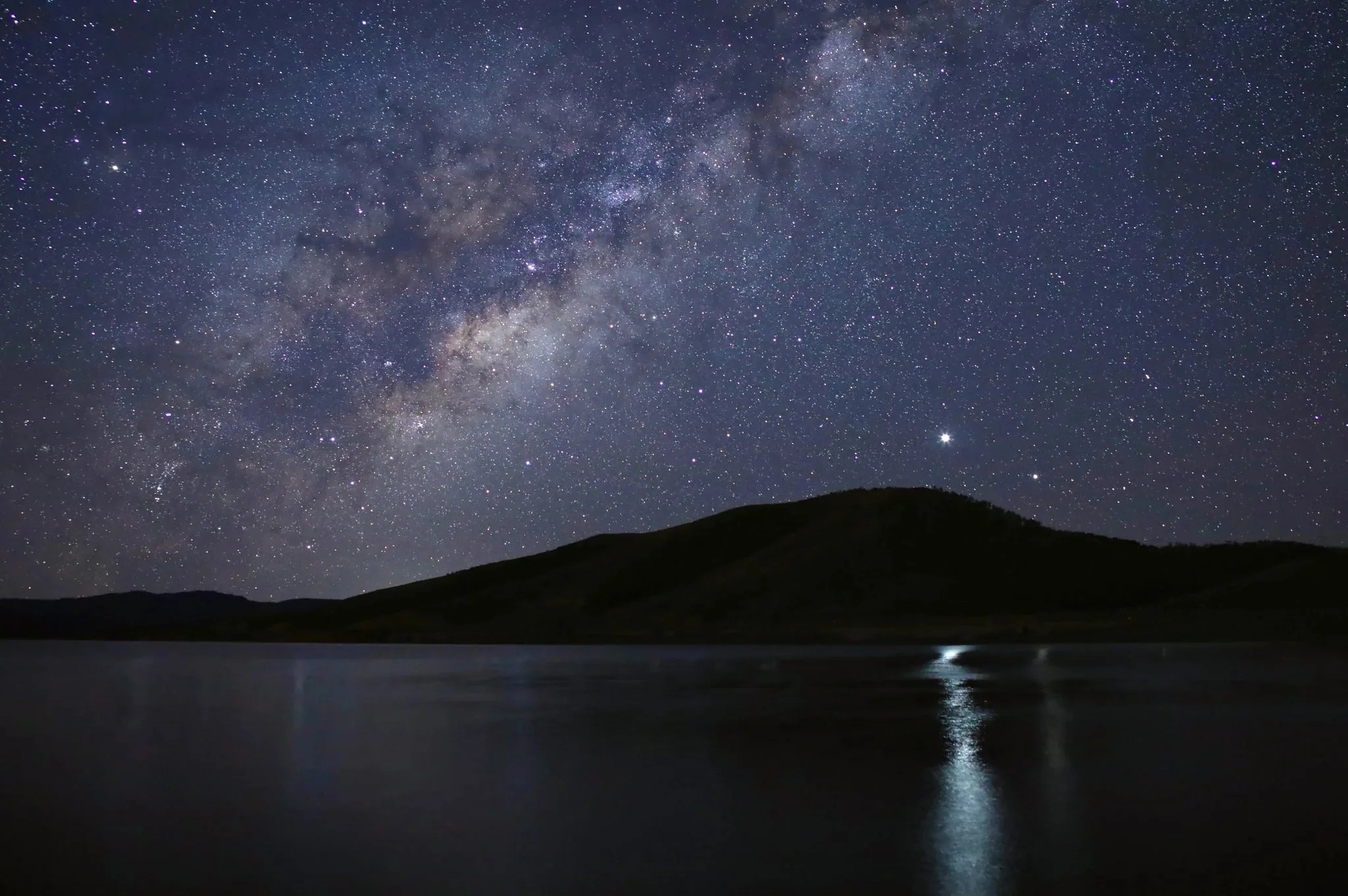

Saturn (left) and Jupiter (right) cast their reflections on the waters of Strawberry Reservoir, Utah in June 2020. During December 2020, the two gas giant planets will appear closer and closer together in the sky each evening until the 21st, when they will be just a tenth of a degree apart.
NASA/Bill Dunford
- Jupiter and Saturn will appear brighter than nearly every star. They can be seen easily from large cities, and dark sites.
- Dark skies will allow you to see fainter stars, but Jupiter and Saturn are bright enough that you don’t necessarily need to go to a dark site to take compelling photos of them. If you have a clear view toward the southwest, you have the chance to take some great photos.
- Think about composition. Jupiter and Saturn will just appear as points of light. To make your photo more interesting, try to frame the planets with something – the silhouette of a tree, an outdoor landscape, the arch of a building, or even a neon sign.
- Experiment with both wide-angle and telephoto shots. In early December, the two planets will be about 2 degrees apart, and will get progressively close toward December 21. In order to show them clearly in your photos, you might use a wide-angle composition early in December, and zoom in later in the month as they get closer.
- Be sure to go outside on a few different nights, and see how their separation changes.
- Using a tripod will help you hold your camera steady while taking longer exposures. If you don’t have a tripod, brace your camera against something – a tree, a fence, or a car can all serve as a tripod for a several-second exposure.
- These planets are visible in early evening, and you'll have about 1-2 hours from when they are visible, to when they set. The color and intensity of the sky changes during that time. Stay out for an hour or more, and try to capture shots with both the bright colors of sunset, and the darkness of the oncoming night. A photo from the same location can look completely different just an hour later!
- The crescent moon will pass near Jupiter and Saturn a few days before the conjunction. Take advantage of it in your composition!
- Jupiter and Saturn will be bright enough to detect in many cell phone cameras. You won’t see additional detail by zooming in, but you can frame Jupiter and Saturn creatively.
- Some recent cell phones have a ‘night mode,’ which will automatically stabilize a long-exposure, even without using a tripod. This can be great for capturing the dark foreground of your photo. Some phones will let you use ‘night mode’ on exposures up to 30 seconds, if you also use a tripod.
- Many cell phones have a wide-angle lens. Try using this to place a subject in the foreground, with Jupiter and Saturn above them.
- At the time of conjunction on December 21, Jupiter and Saturn may be too close to separate clearly in your photos. Images taken a few days before or after the conjunction may show them more clearly.
- Set your focus to Infinity (Manual Focus mode), so the planets will be sharp. Set your aperture wide open, to let in the maximum amount of light.
- If you have a tripod, it will help you take long exposures. If not, you can still take some great pictures with a short shutter speed (< 1/4 second). If your camera or lens has an image stabilizer, be sure it is turned on.
- If your photos show that the camera is not steady, shorten your shutter speed. You can also use a photographers’ trick to get a sharp photo when hand-holding: set up your camera to take multiple exposures, then hold the shutter button to take a series of photos. While some will be blurry due to camera shake, you may find a few that are sharp.
- If you use a 200 mm telephoto lens, you should be able to see Jupiter's four bright moons in a short exposure. Saturn’s rings will usually need a longer lens or a telescope in order to resolve clearly.
- To capture Jupiter and Saturn as sharp ‘points’ while using a tripod, use a shutter speed of up to a few seconds. More than this and the Earth's rotation will smear out the planets and stars. If you are using a wide-angle lens, you can use a longer exposure.
Related:
Share
Details
Last Updated
Jan 24, 2024
Editor
NASA Science Editorial Team
Related Terms
Keep Exploring