What to look for:
A planetary rendezvous, meteors, and a "star forge"!
Two planets meet for a super close conjunction, the Perseid meteor shower peaks, and look for the Lagoon Nebula – a stellar nursery in Sagittarius.
Highlights
- August 4 – New moon
- August 11 – The Perseid meteor shower peaks overnight tonight! Provided you have clear skies, viewing conditions will be favorable this year, as the Moon sets by around 11:30 pm local time. Meteor activity picks up from then until dawn.
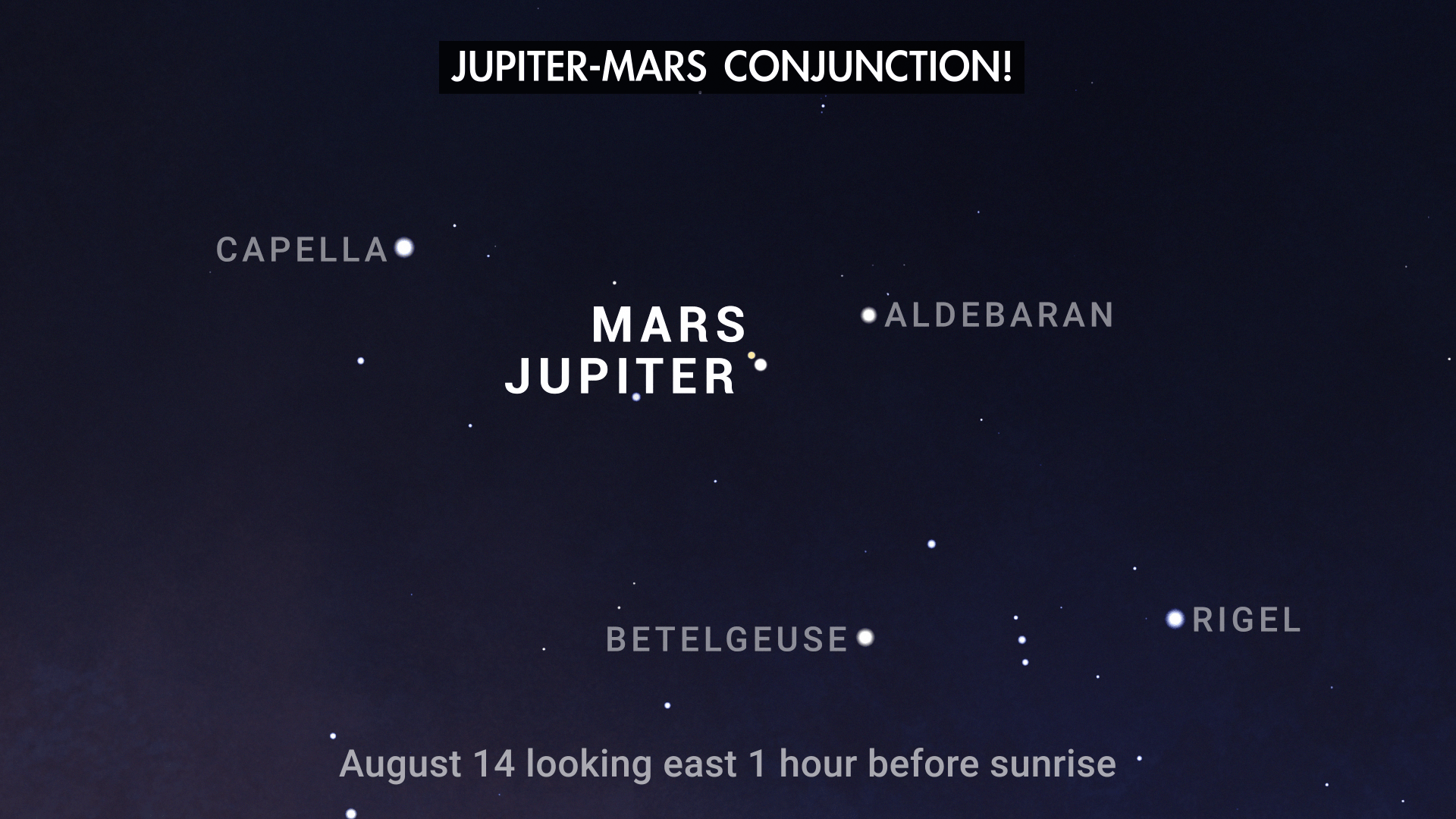
- August 14 – Jupiter and Mars have an extremely close pair-up called a conjunction this morning. They'll appear just a third of a degree apart, which is less than the width of the full Moon. Find them in the eastern sky in the couple of hours before sunrise.
- August 19 – Full moon
- August 20 – The Moon chases Saturn across the sky tonight. The pair rise in the east shortly after dark, and trek toward the west together until dawn.
- August 27 – This morning the crescent moon joins Mars and Jupiter to form a captivating trio. Look for them in the east in the hour or so before sunrise.
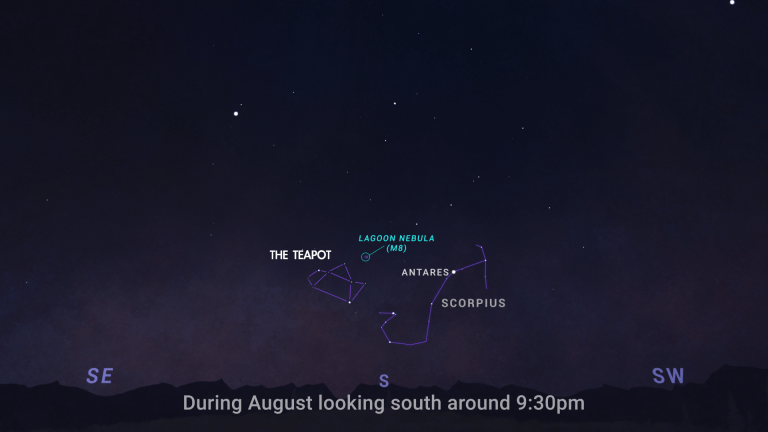
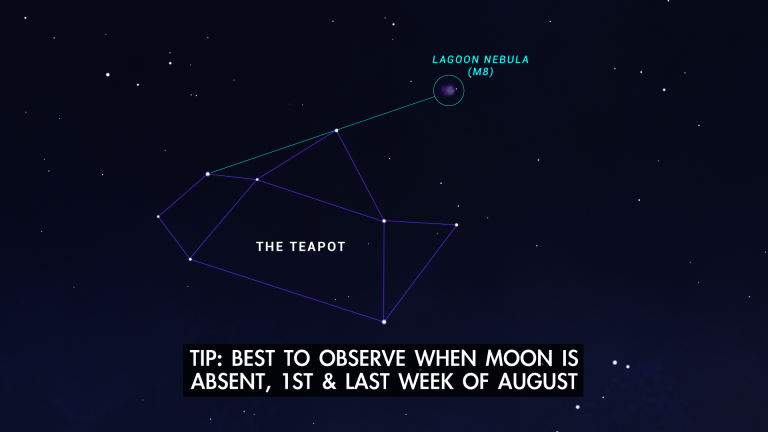
- All month – You can use binoculars or a telescope to observe the Lagoon Nebula all month in the first few hours after dark. It's located in the constellation Sagittarius near the star pattern known as "The Teapot." Similar in size and brightness to the Orion Nebula, it's a cauldron of star formation located about 4,000 light years away.
Transcript
What's Up for August? A super close meetup of Jupiter and Mars, the outlook for the Perseid meteors, and see a stellar nursery in the Lagoon Nebula.
During the month of August, the Red Planet, Mars, speeds past our solar system's largest planet, Jupiter, in the a.m. sky. They have an extremely close pair-up, called a conjunction, on August 14th, when they'll appear just a third of a degree apart, which is less than the width of the full Moon.
The view from NASA's Eyes on the Solar System reveals the two planets arranged along the same line of sight, which is why they appear so close together in the sky at this time.
Mars quickly pulls away from Jupiter over the following mornings, but on the 27th, the crescent moon joins the two planets to form a captivating trio in the morning sky.
Saturn flies solo most of the month on the opposite side of the sky, though the Moon chases close behind the Ringed Planet on August 20th. The pair rise shortly after dark, and trek toward the west together until dawn.
The warm summer nights of August in the Northern Hemisphere make the Perseid meteor shower an annual favorite. This year's peak night for Perseids comes on August 11th, and into morning twilight on the 12th. Provided you have clear skies, viewing conditions will be favorable this year, as the Moon sets by around 11:30 pm local time.
Meteor activity picks up from then until dawn. From darker viewing locations, meteor counts of 50 to 75 per hour are pretty normal at the peak.
The Perseids appear to originate from a place in the sky that rises in the northeast, so lie back and face roughly in that direction, but try to take in as much of the sky as you can in your view, as meteors can appear all over.
All the stars in the sky share a common origin in giant clouds of gas and dust called nebulas. And one such stellar nursery, the Lagoon Nebula, is well placed to observe in the August sky.