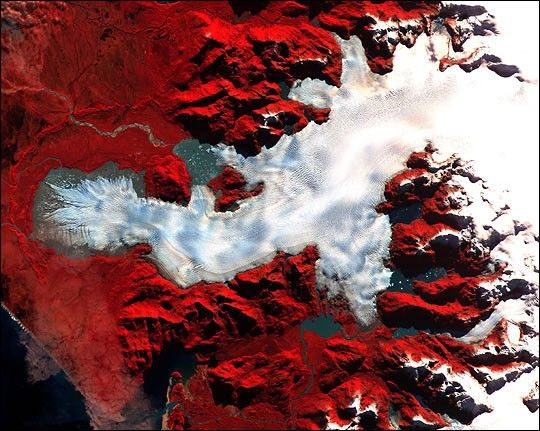
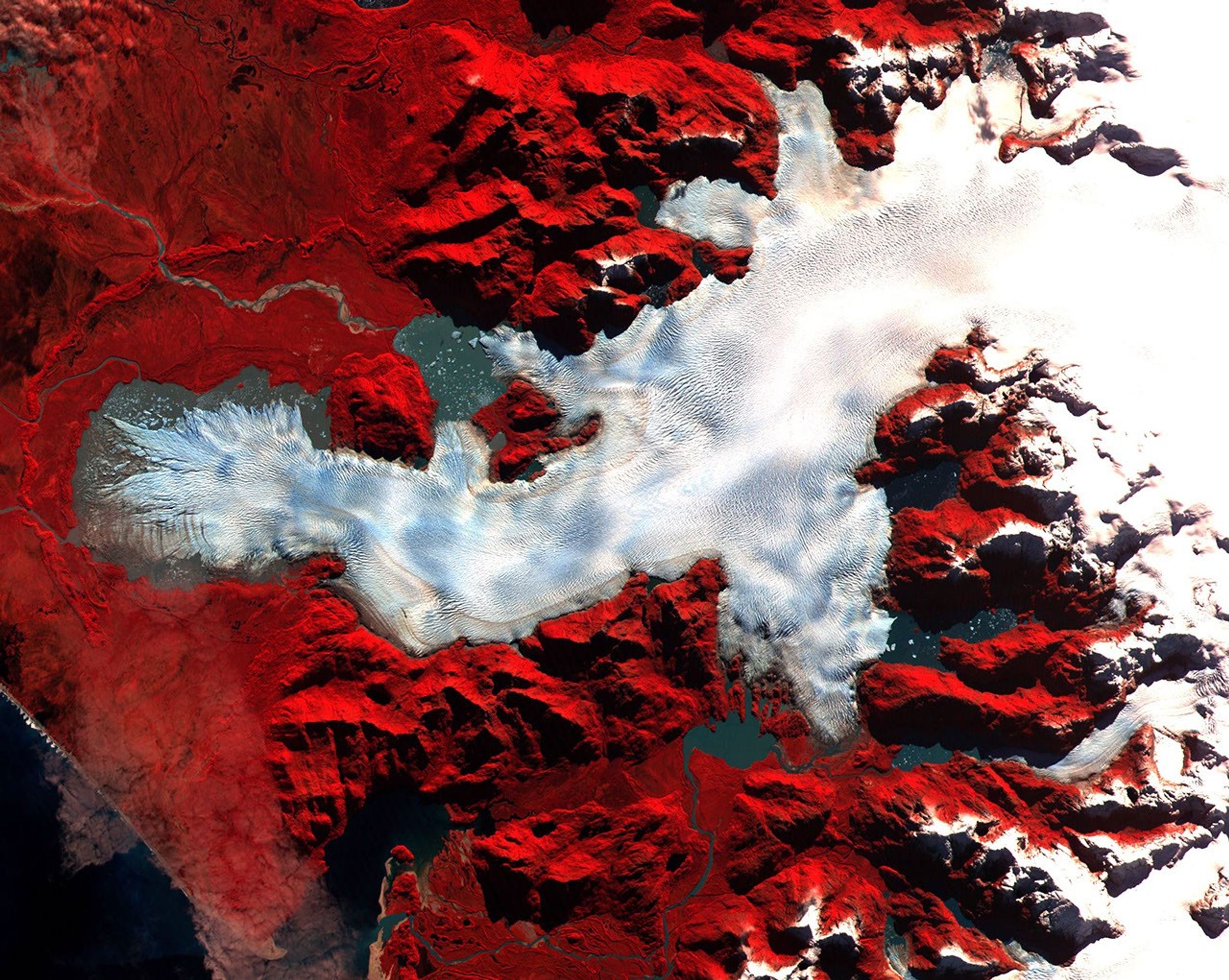
This image of a Patagonian glacier was aqcuired by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emissionand Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on May 2, 2000. Patagonia is a mountainous region spanningthe border between Chile and Argentina near the southern tip of South America. The image covers anarea of 36 x 30 km—the full-size image has a resolution of 15 meters per pixel. Vegetation appears red in the image, which is a false-color composite of near-infrared, red, and green light displayed as red, green, and blue, respectively.
This large glacier is riddled with crevasses—deep cracks in the ice. The semi-circularridge at the far left of the image is composed of rock and soil carried there by the glacierwhich was even larger in the past. This type of feature is called a “terminal moraine”. The pools of water atthe foot of the glacier are light-colored due to the fine silt suspended in them. A braided streamwinds through more silt deposited by the glacier and cuts through the terminal moraine about one thirdof the way down from its top. Along the right side of the image are a series of parallel valleysthat were likely cut by arms of the glacier which have since receded.
References & Resources
Image courtesy NASA/GSFC/MITI/ERSDAC/JAROS,and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team