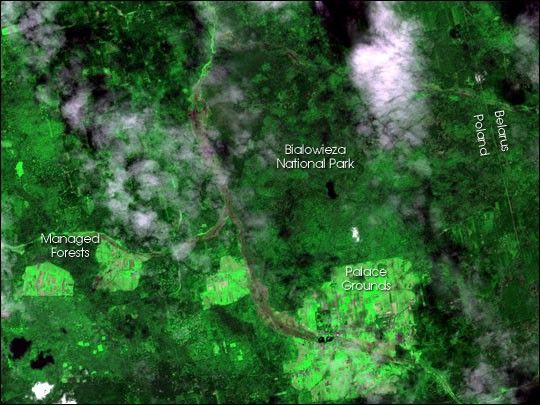
Biolowieza National Park lies on the border between Poland and Belarus. It was first established asa park in 1932, and restored in 1947 in the wake of the Second World War. The park was also declareda biosphere reserve in 1977. It is also a transboundary World Heritage site in conjunction withthe Belovezhskaya Pushcha Biosphere Reserve adajacent to it on the Belarus side of the border.It is a section carved out of the much larger Bialowieza Forest: the park is slightly less than onefifth of the forest area. The Biolowieza Forest is a unique ecosystem: not only does it contain arare European lowland old growth forest, but it also lies in aborder zone between the boreal and temperate climate zones. Within its borders are some of thesouthernmost stands of boreal species such as the norway spruce. It also contains temperate species attheir northernmost limits, such as sessile oak. The forest also contains a complex mosaic of plants and animals, including forest ungulates, birds of prey, and a wide assortment ofvascular plants, mosses, lichens, and fungi. It is also the site of successful reintroduction ofspecies including the European bison and beaver.
The preservation of this area owes a great deal to its protection over several centuries fromleading figures in central Europe, from Polish kings, Lithuanian princes and dukes,and the Russian Tsars. Their interest in maintaining the land focused on its leisure use as hunting grounds, butthis also provided protection from most agricultural use and land clearing. Its national parkstatus in the 20th century has further protected it from development, though areas around ithave been subjected to conversion to commercial lumber industry. In the summer of 2003, a newmanagement plan for the Bialowieza Forest called forremoving trees in an effort to contain infestations ofbark beetles. These new policies have been the subject of heated debate in the forestry andecology communities, with conservationists accusing the government ofclearing the most valuable timber under a dubious guise of forest protection, while governmentofficials cite the plan as an example of sustainable forestry practices. Forest clearing and poorland practices in the adjacent land in Belarus, such as felling trees that are hosts for the barkbeetle and failing to remove the logs promptly, continue to be a source of growing concern toecologists as these last stands of primeval European forest are turned to commercial land useand pressures.
In this scene, acquired on April 29, 2002, by the Terra satellite’s ASTER instrument, many of thesefeatures can be discerned. Theold palace grounds are quite evident, as are the clear cut areas in the Biolowieza Forest outsidethe park, whose boundaries are partially defined by the Lesna River and the international border withBelarus. The international boundary appears as the linear feature to the top right of this image whereforest has been cleared along the border. This image was created by combining red, near-infraredand green wavelengths (ASTER VNIR bands 2, 3, and 1).
References & Resources
Image created from data collected by NASA/GSFC/MITI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team Data processed by the American Museum of Natural History's Science Bulletins