Season after season, year after year, century after century, snow has fallen over Greenland and Antarctica. Compressed and preserved for hundreds of thousands of years, the snow has “fossilized” into ice sheets several miles thick. Each season’s snow is different in chemistry and texture from the snow that came before. As new layers accumulate on the ice sheets, they seal off the old snow, trapping dust, volcanic particles, and even tiny air bubbles. The layers of snow in ice sheets are a vertical timeline of past climates. Scientists have drilled cores of ice more than 2 miles long out of polar ice sheets, creating a climate timeline that stretches back as far as 750,000 years in some locations.
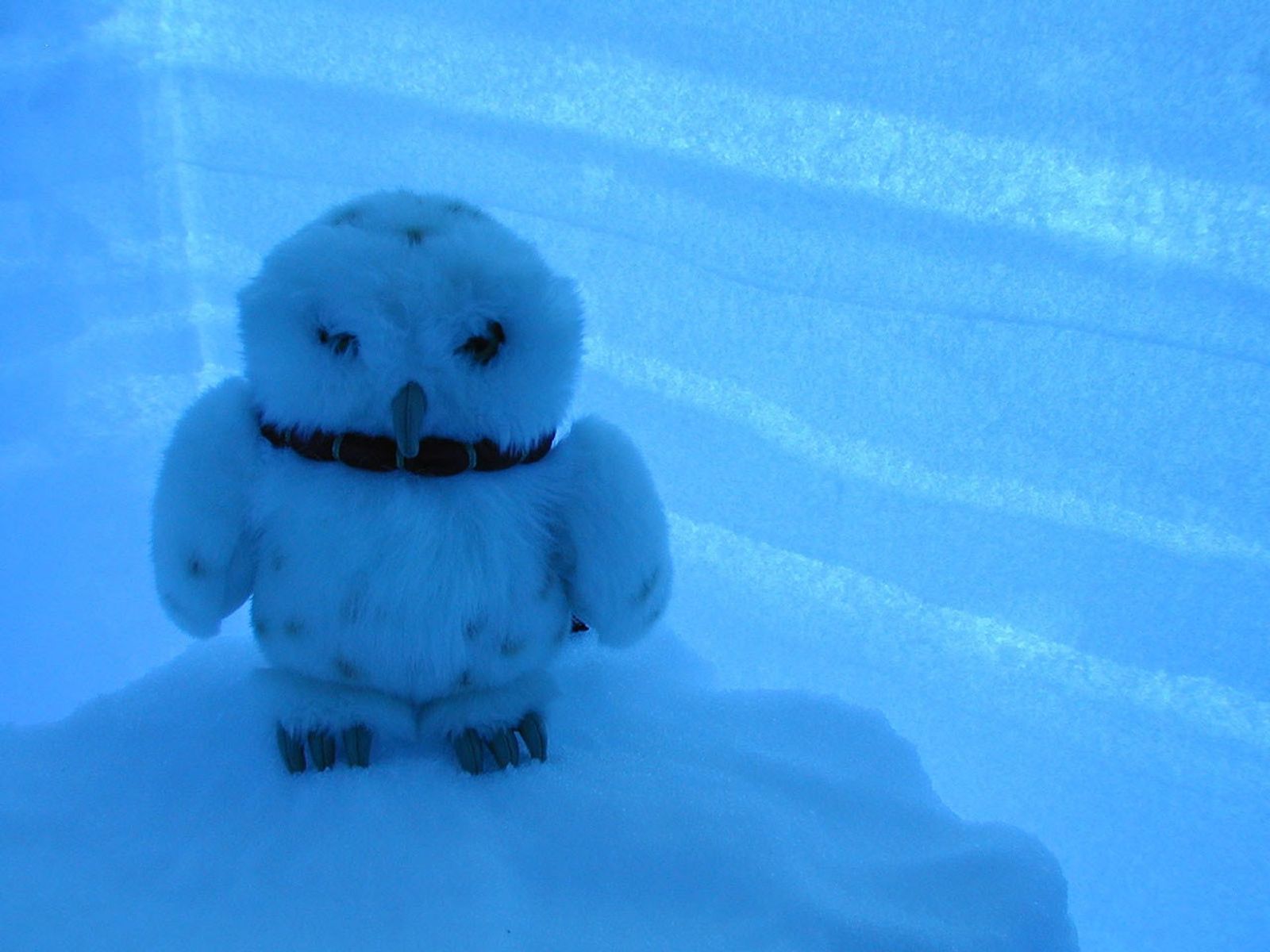
Seasonal snow layers are easy to see in snow pits. Scientists dig two pits separated by a thin wall of snow. One pit is covered, and the other is left open to sunlight. By standing in the covered pit, scientists can study the annual snow layers in the snow wall as the sunlight filters through the other side. In this image, blue light filtered through the wall of a snow pit in Antarctica illuminates “Tuck,” the mascot for Tuckahoe Elementary School in Henrico County, Virginia. The furry white owl accompanied scientists to Antarctica as part of an educational program.
In the wall of the pit, dark and light bands can help distinguish summer snow from winter snow. Summer snow tends to be coarser, creating layers that are less tightly packed and more transmissive to light (brighter). Winter snow tends to be more fine-grained, and so it is more easily compacted by overlying snow or wind. Because of the compaction, winter snow layers tend to be darker than summer layers.
To read more about how scientists use ice cores from polar ice sheets and mountain glaciers to study ancient climates, read the Ice Core installment of the Earth Observatory’s series of articles on Paleoclimatology.
References & Resources
Photograph courtesy Christopher Shuman, NASA GSFC