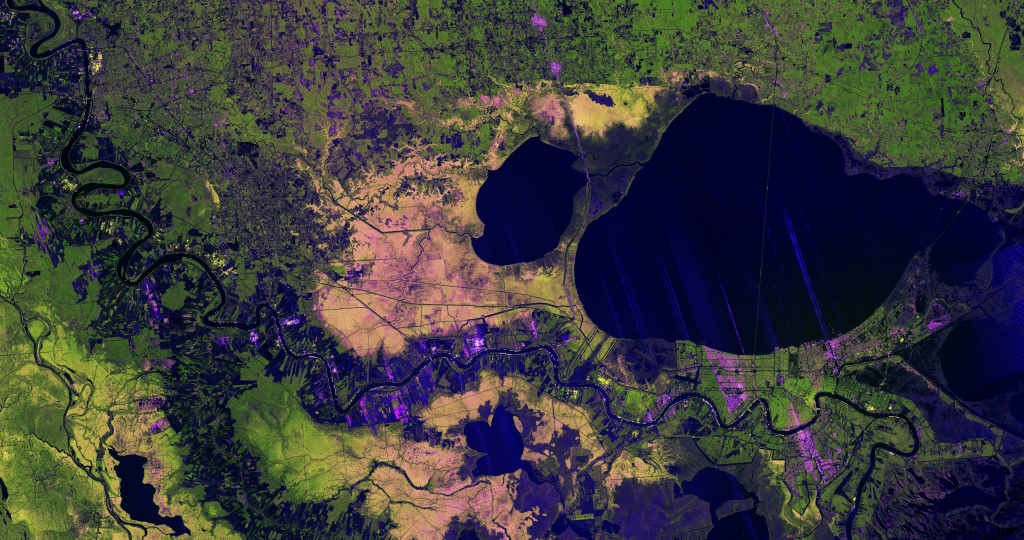
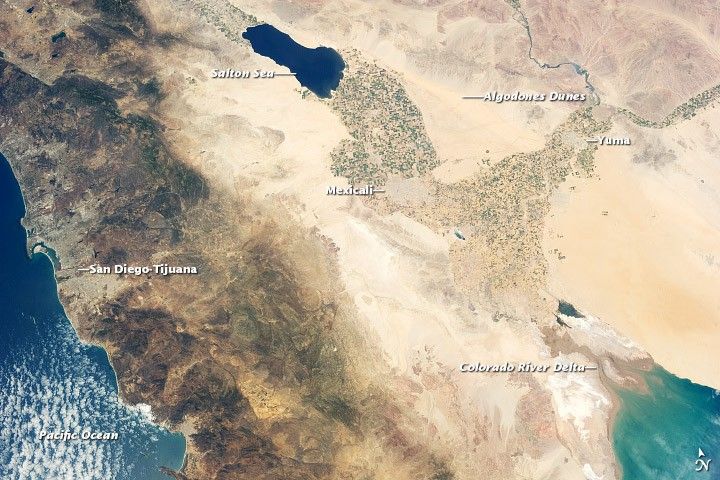
The Imperial and Coachella Valleys of southern California, and the corresponding Mexicali Valley and Colorado River Delta in Mexico, are part of the Salton Trough. This large geologic structure, known to geologists as a graben or rift valley, extends into the Gulf of California. The trough is a geologically complex zone formed by the interaction of the San Andreas transform fault system—which is, broadly speaking, moving southern California towards Alaska—and the northward motion of the Gulf of California segment of the East Pacific Rise, which continues to widen the Gulf of California by seafloor spreading.
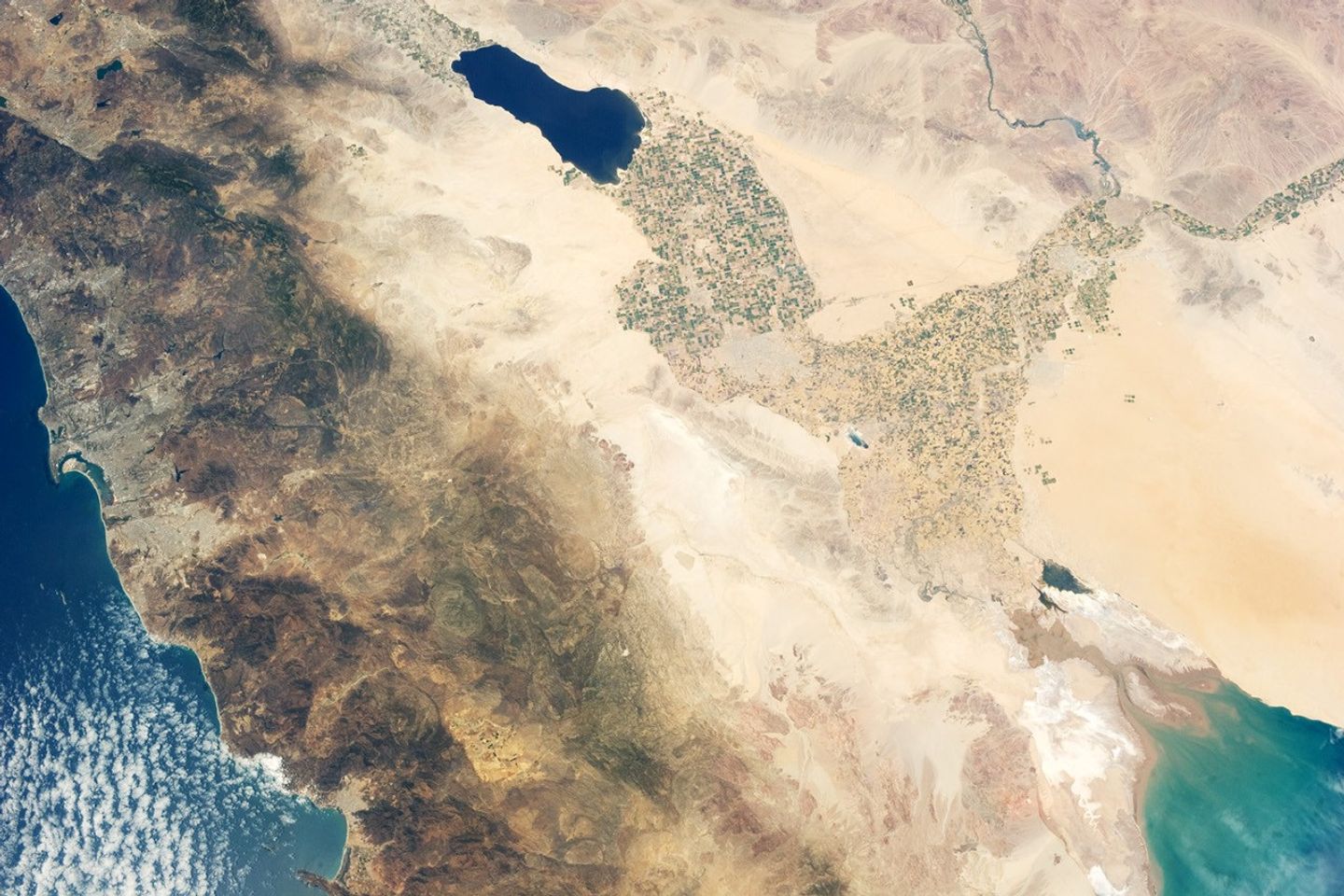
Sediments deposited by the Colorado River have been filling the northern rift valley (the Salton Trough) for several million years, excluding the waters of the Gulf of California, and providing a fertile environment for the development of extensive, irrigation-aided agriculture in the region (visible as green and yellow-brown fields at image center). The Salton Sea, a favorite landmark of astronauts in low-earth orbit, was formed by the rupture of an irrigation canal in 1905 and today is sustained by agricultural runoff water.
A wide array of landforms and land uses in the Salton Trough are visible from space. In addition to the agricultural fields and Salton Sea, several metropolitan areas are visible, including Yuma, Arizona; Mexicali, Mexico; and the San Diego-Tijuana conurbation on the Pacific Coast (image left). The 72-kilometer-long Algodones Dunefield also is visible at image top right.
References & Resources
Astronaut photograph ISS036-E-11034 was acquired on June 21, 2013, with a Nikon D3S digital camera using a 50 millimeter lens, and is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations experiment and Image Science & Analysis Laboratory, Johnson Space Center. The image was taken by the Expedition 36 crew. It has been cropped and enhanced to improve contrast, and lens artifacts have been removed. The International Space Station Program supports the laboratory as part of the ISS National Lab to help astronauts take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth. Caption by William L. Stefanov, Jacobs/JETS at NASA-JSC.